
Activated carbon plays a crucial role in wastewater treatment by effectively capturing harmful substances from water. You can utilize wastewater treatment activated carbon in various applications. In the context of wastewater treatment, activated carbon is essential as it removes chemicals, unpleasant odors, and colors that other filters may fail to eliminate. This process is vital for improving water quality. The small pores in activated carbon trap pollutants, resulting in safer water. Activated carbon is a key tool for enhancing water cleanliness. If you’re interested in helping the environment, understanding wastewater treatment activated carbon can be incredibly beneficial.
Key Takeaways
Activated carbon is very important for cleaning wastewater. It helps make water safer to use. Its big surface and tiny holes help it catch many bad things. These include chemicals, smells, and colors. Activated carbon uses a process called adsorption. This means dirty stuff sticks to its surface as water moves through. Using activated carbon in the last cleaning step makes sure water is safe. The water must be safe before it goes back to nature. People must test and take care of these systems often. This keeps them working well and removes pollution. Granular activated carbon (GAC) is good for cleaning water all the time. Powdered activated carbon (PAC) works best for fast cleanups. Activated carbon helps follow the rules for clean water. It keeps people and nature safe from dirty water. Picking the right kind of activated carbon for each problem helps clean water better. This makes the treatment work best.
What Is Activated Carbon?

Properties of Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is special because it has many tiny pores. These pores give it a very large surface area. One gram of activated carbon can have more than 500 square meters of surface area. Some types can reach up to 3,000 square meters per gram. This big surface area helps it trap lots of things from water. Activated carbon has pores in different sizes. This lets it catch many kinds of pollutants. It is also chemically stable. That means it does not react with most things in water. Because of this, it is safe for cleaning water.
Tip: Activated carbon’s large surface area and special pores help it remove contaminants very well.
How Activated Carbon Is Made
Manufacturers make activated carbon in two steps. First, they use things like coconut shells, wood, or coal. These go through carbonization. In this step, the material is heated without oxygen at less than 800°C. This removes things like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Next is activation. The carbonized material is heated again at 800–900°C. Air, carbon dioxide, or steam is passed through it. This step makes the pores that give activated carbon its large surface area.
Here is a simple table to show the process:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Carbonization | The raw material is heated in an inert environment below 800°C. Elements like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur are removed. |
Activation | The carbonized material is oxidized at 800–900°C with air, carbon dioxide, or steam to create pores. |
This is how activated carbon is made for water treatment systems.
Why Activated Carbon Works
Activated carbon works well because of its special properties. Its large surface area and many pores help it trap many pollutants. In wastewater treatment, it acts like a sponge. It grabs and holds chemicals, colors, and odors you want to remove. The process is called adsorption. This means molecules stick to the surface of activated carbon. Van der Waals forces help keep these molecules in place. Surface active carbon double bonds also make it work better.
Scientists use the Polyani adsorption theory to explain how activated carbon traps organic substances. This theory shows why activated carbon in wastewater treatment removes tough contaminants so well.
Note: Activated carbon is great for cleaning water because it has a huge surface area, special pores, and strong adsorption forces.
Role of Activated Carbon in Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater Treatment Activated Carbon
You use wastewater treatment activated carbon to help clean water. It works like a strong sponge. It grabs chemicals, colors, and smells that other filters miss. You see it in big factories and city water plants. These places need wastewater treatment activated carbon to get rid of hard-to-remove pollutants. When you add it to the process, it traps bad things before they reach rivers or lakes.
Wastewater treatment activated carbon works well because it has a huge surface area. Its tiny pores catch many kinds of contaminants. You can use it to treat water from factories, homes, and hospitals. This makes it very important for cleaning water and treating wastewater.
Did you know?
Wastewater treatment activated carbon can take out tiny pollutants called micropollutants. These include medicines, pesticides, and personal care products. The surface of activated carbon pulls these substances in and holds them tight. Sometimes, organic matter in water helps turn granular activated carbon into biologically activated carbon. This change helps break down pollutants and makes cleaning better.
Tertiary Treatment and Polishing
You often see activated carbon used at the end of the treatment process. This last step is called tertiary treatment or polishing. Here, you want the water to meet strict rules before it leaves the plant. Wastewater treatment activated carbon helps remove any leftover chemicals, colors, or smells. It also gets rid of things that earlier steps missed.
Tertiary treatment with activated carbon gives you cleaner water. You can use it to polish water so it is safe for people and nature. This step is important for safe discharge to rivers and lakes. When you use activated carbon here, you help protect water from pollution.
Here is a simple table to show how activated carbon fits into the treatment process:
Stage | Main Goal | Role of Activated Carbon |
|---|---|---|
Primary Treatment | Remove solids | Not used |
Secondary Treatment | Break down organic matter | Sometimes used |
Tertiary Treatment | Remove remaining pollutants, polish water | Key role in removing chemicals, colors, odors |
Regulatory Importance
You must follow strict rules when you treat wastewater. Governments set limits for what you can put into the environment. Wastewater treatment activated carbon helps you meet these rules. It removes pollutants that can hurt fish, plants, and people. If you run a factory water plant, you need to make sure your water is clean before it leaves. City water plants also use activated carbon to follow local and national laws.
Activated carbon is important for safe water discharge. It helps you avoid fines and keeps people healthy. You can count on this material to help you reach your goals for clean water and safety.
Tip:
Using activated carbon in wastewater treatment helps you feel sure. You know your water meets the highest standards before it leaves.
How Activated Carbon Works
Adsorption Process
What Is Adsorption
You might ask how activated carbon cleans water. The answer is adsorption. Adsorption means molecules from water stick to another surface. Here, activated carbon acts like a magnet for pollutants. When water moves through activated carbon, bad stuff leaves the water and sticks to the carbon. This does not change what the pollutants are made of. It just keeps them stuck on the carbon.
Activated carbon has many tiny pores. These give it a huge surface area. More surface area means more places for pollutants to stick. This is why activated carbon works so well in wastewater treatment.
How Contaminants Are Trapped
Think of activated carbon like a sponge. But instead of soaking up water, it soaks up contaminants. When water goes through a filter with activated carbon, chemicals, colors, and smells get pulled in. They stay on the carbon’s surface. Physical forces, like van der Waals forces, help keep them there. Sometimes, chemical reactions help trap some substances too.
Here is a simple list of what happens during activated carbon adsorption:
Water moves through activated carbon.
Pollutants leave the water and stick to the carbon.
The carbon holds these pollutants in its pores.
Clean water comes out the other side.
Tip:
Activated carbon filtration works best if you use enough carbon and let water flow at the right speed.
Factors Affecting Performance
You want activated carbon to work its best. Many things can change how well it works. The type and size of the pores matter a lot. Small pores trap tiny molecules. Big pores catch bigger ones. Using more activated carbon helps clean more water.
How fast water flows is important. If water moves too fast, there is less time for adsorption. If it moves too slow, cleaning takes longer. Water temperature also matters. Warm water can help, but very hot water can make it work worse.
The kind of contaminants in the water is important too. Some chemicals stick to activated carbon better than others. If there is a lot of organic material, the pores fill up fast. You may need to change the carbon more often.
Here is a table to help you see what affects adsorption efficiency:
Factor | Effect on Adsorption Efficiency |
|---|---|
Pore size and surface area | More pores and bigger surface area mean better trapping of pollutants |
Amount of activated carbon | More carbon can clean more water |
Water flow rate | Slower flow gives more time for adsorption |
Water temperature | Moderate warmth can help, but too hot can hurt performance |
Type of contaminants | Some stick better than others |
Note:
You can make activated carbon work better by picking the right kind and keeping your system in good shape.
Activated carbon is very important in wastewater treatment. It uses both physical and chemical forces to pull pollutants to its surface. Its big surface area and special pores help remove many types of contaminants from water.
Contaminants Removed by Activated Carbon
Organic Compounds
Activated carbon is great at taking out organic compounds from water. These compounds can come from factories, homes, or nature. It works best with big organic molecules but can catch small ones too. Using activated carbon helps keep harmful things out of the environment.
Here are some organic compounds that activated carbon can remove:
Pesticides and herbicides
Pharmaceuticals and personal care products
Industrial solvents
Synthetic chemicals
Natural organic matter
Taking out organics is important because they can hurt people and animals. Activated carbon uses its large surface area and special pores to grab and hold these contaminants. This process is a good way to remove contaminants in wastewater treatment.
Tip:
Activated carbon is very helpful for removing organic compounds that other methods cannot break down easily.
Heavy Metals
Activated carbon is also important for taking out heavy metals from water. These metals, like lead, mercury, and cadmium, are harmful even in tiny amounts. You need to keep them out of drinking water and streams. Activated carbon can remove about 99% of heavy metals. This makes it a top choice for treatment plants.
Here is how activated carbon helps with heavy metals:
Adsorption is the main way it traps toxic metals.
The pores in activated carbon hold metals tightly so they do not go back into the water.
You can use activated carbon in city and factory wastewater systems.
Taking out heavy metals keeps people and the environment safe. It helps stop pollution and meets safety rules. Activated carbon is a good way to handle these contaminants removed from water.
Color, Odor, and Taste
Sometimes water has a strange color, smell, or taste. These problems can come from dyes, rotting plants, or chemicals. Activated carbon is very good at removing dyes that make water look colored. It also traps the molecules that cause bad smells and tastes.
Here is a simple table showing how activated carbon helps:
Problem | Source | Activated Carbon Solution |
|---|---|---|
Color | Dyes, organic matter | Removal of dyes and pigments |
Odor | Decaying plants, chemicals | Adsorbs odor-causing molecules |
Taste | Industrial pollutants, chlorine | Removes taste contaminants |
You can use activated carbon to make water look, smell, and taste better. Taking out dyes, odors, and tastes makes water nicer for everyone.
Note:
Activated carbon helps you fix many water problems by removing lots of contaminants. This gives you cleaner and safer water for your community.
Other Pollutants
You might ask if activated carbon can take out more than just organic compounds, heavy metals, or color and odor. The answer is yes, it can. Activated carbon also helps remove other things that can make water dirty. These are chemicals that do not fit in the main groups we talked about before.
Some other pollutants you can take out with activated carbon are:
Chlorine and chloramine, which water plants use to clean water
Disinfection byproducts, like trihalomethanes (THMs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as benzene and toluene
Petroleum-based chemicals and fuels
Some pesticides and herbicides that were not removed earlier
Microplastics and some synthetic fibers
You can find these things in water from factories, farms, or homes. Activated carbon acts like a filter and grabs these bad materials. When you use it in your system, you help keep these pollutants out of rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Note:
Activated carbon does not take out every contaminant. Some things, like ammonia, fluoride, or some dissolved minerals, can still get through. You should always test your water to know what needs to be removed.
Activated carbon works well for many new contaminants. These are chemicals that scientists have found can cause problems. For example, you may hear about PFAS, which are sometimes called “forever chemicals.” Activated carbon can lower some PFAS in water, but it may not get them all. You might need special carbon or extra steps for the best results.
Here is a table that shows some other pollutants and how activated carbon helps:
Pollutant Type | Example Substances | Activated Carbon Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
Disinfection Byproducts | THMs, haloacetic acids | High |
VOCs | Benzene, toluene | High |
Microplastics | Synthetic fibers, beads | Moderate |
PFAS | PFOA, PFOS | Moderate to High (varies) |
You should pick the right kind of activated carbon for your needs. Some types work better for certain pollutants. You may also need to use other treatment methods with activated carbon to get the cleanest water.
Tip:
Regular testing and checking help you know when to change your activated carbon. This keeps your system working well and protects your water from many contaminants.
Types of Activated Carbon in Wastewater Treatment
When you clean wastewater, you can pick from different types of activated carbon. Each type is best for certain jobs. Knowing how they are different helps you choose the right one for your system.
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
Granular activated carbon is made of small, hard pieces. You often see GAC in big filter beds or columns. Water moves through these beds, and the activated carbon catches pollutants as water passes. GAC is good for cleaning water all the time. You can use it in city and factory plants.
Key features of GAC:
Large surface area to catch contaminants
Good for taking out organic chemicals, taste, and odor
Simple to handle and replace
You can clean GAC by washing or heating it again. This makes it a good choice for many systems. GAC also lets helpful bacteria grow, which can help break down some pollutants.
Tip:
Use GAC when you need to treat lots of water for a long time.
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC)
Powdered activated carbon is very fine and powdery. You usually add PAC right into the water or mix it in tanks. PAC works fast because it has a lot of surface area in a small size. You can use it for quick problems or when you need to remove certain contaminants fast.
When to use PAC:
Emergency spills or sudden pollution
Taking out taste and odor during some seasons
Treating water with lots of organic matter
PAC does not stay in the system. After it grabs pollutants, you take it out with other solids during settling or filtering. This makes PAC easy to use for special cases.
Type | Form | Best Use Case | Removal Method |
|---|---|---|---|
GAC | Granules | Continuous, large-scale use | Filter replacement |
PAC | Powder | Short-term, targeted removal | Settling/filtration |
Specialty Carbons
Sometimes, you need activated carbon with special features. Specialty carbons are made for tough jobs. Makers can change the pore size, surface chemistry, or add coatings. These changes help the activated carbon catch certain pollutants.
Examples of specialty carbons:
Carbons for taking out heavy metals
Carbons made for PFAS or other “forever chemicals”
Carbons with extra catalytic features
You might use specialty carbons when regular types do not work well enough. These carbons can cost more, but they fix special water problems.
Note:
Always test your water to see if you need a specialty carbon. Picking the right one gives you better results and saves money.
Choosing the right type of activated carbon helps you clean water better. You can match the carbon to your goals and keep your system working well.
Benefits of Activated Carbon in Wastewater Treatment
High Efficiency
Activated carbon works fast in water treatment. It removes many pollutants quickly. Its large surface area traps more contaminants than most filters. You can trust activated carbon to take out chemicals, colors, and odors. Other methods might miss these. Many plants use activated carbon to meet strict water standards.
Tip:
Try activated carbon as the last step. It can polish water and make it cleaner.
Versatility
Activated carbon is useful in many ways. You can use it in small home filters or big city systems. Add it as a powder for quick fixes. Use it in large beds for ongoing cleaning. Activated carbon works well with other treatment steps. You can mix it with sand filters or biological processes. This makes it a top choice for water treatment.
Here are some ways to use activated carbon:
Remove pesticides and medicines from water
Make drinking water taste and smell better
Treat factory wastewater before release
Clean up after chemical spills
Activated carbon can handle many jobs in water treatment.
Environmental Impact
Activated carbon helps protect the environment. It traps harmful chemicals and keeps them out of rivers and lakes. Some types can be reused or recycled, which cuts down on waste. Many plants pick activated carbon because it helps keep water clean and the planet healthy.
Benefit | How Activated Carbon Helps |
|---|---|
Pollution control | Stops chemicals from reaching nature |
Resource savings | Can be regenerated and reused |
Safer water | Removes toxins for people and wildlife |
Note:
Activated carbon is a simple way to make water safer and help the environment.
Practical Use and Considerations
Selection and System Design
When you pick activated carbon, think about what you want to take out of the water. Some types work better for certain things. Granular activated carbon is best for big systems that run all the time. Powdered activated carbon is good if you need a quick fix or only treat water for a short time.
Look at the pore size in the activated carbon. Small pores catch tiny molecules. Bigger pores grab larger ones. The amount of activated carbon you use is important. More carbon means it can clean more water. You can build your system with beds or columns filled with activated carbon. Water moves through these beds, and the carbon traps the bad stuff.
Tip:
Test your water before choosing a type of activated carbon. This helps you pick the right one and get the best results.
Maintenance and Replacement
Activated carbon does not last forever. Its pores fill up with pollutants over time. When this happens, it cannot trap more contaminants. You need to replace or clean the activated carbon to keep your system working well.
Check your system often. If water starts to smell or taste bad, it may be time to change the carbon. Some systems let you clean the activated carbon by heating or washing it. This is called regeneration. Not all types can be cleaned, so you might need to replace them.
Here are some signs you need to maintain or replace your activated carbon:
Water smells or tastes bad again.
The water color changes.
Tests show more pollutants in the water.
Regular maintenance keeps your system working well and protects your water.
Cost Factors
When you plan your wastewater treatment, you need to think about costs. Activated carbon can cost more than some other ways, but it works well and is reliable. The price depends on the type, how much you use, and how often you need to replace it.
Here is a table that shows the costs of different treatment methods:
Treatment Method | Cost (£ per 1000 m3) |
|---|---|
Ozonation | 112 |
Granular Activated Carbon | 205 |
Solar Photo-Fenton | 238 |
You can also see the cost comparison in this chart:
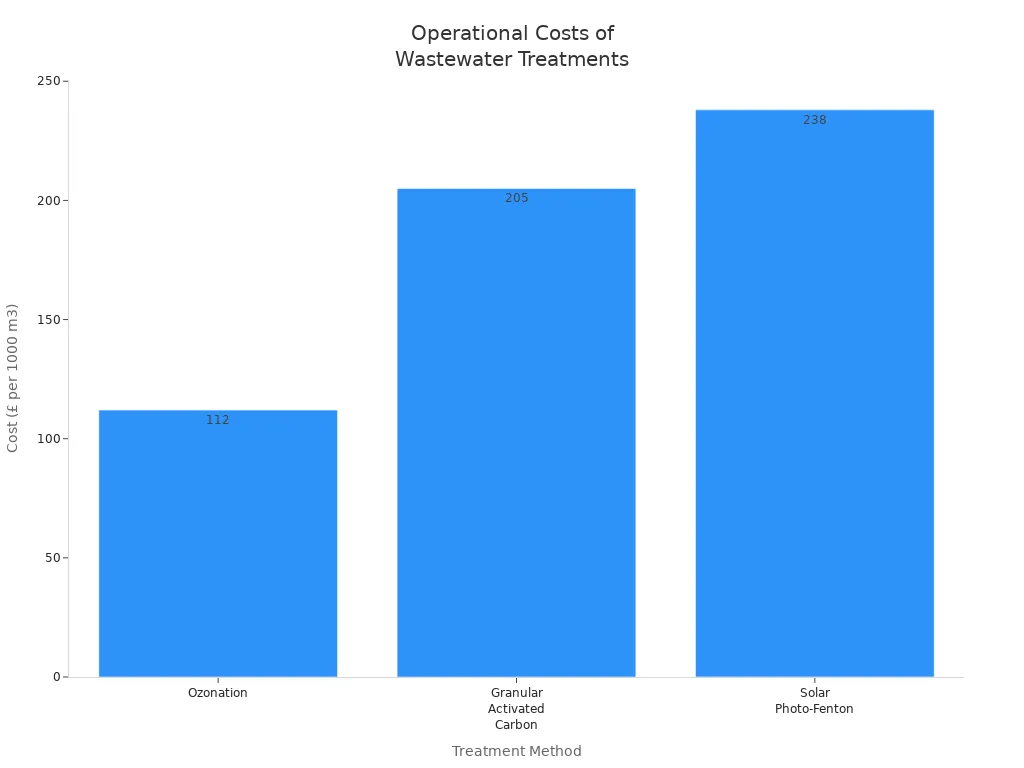
Activated carbon may cost more than ozonation, but it removes more types of pollutants. You get cleaner water and meet strict rules. You should think about both the cost and the benefits for your system.
Note:
Good design and regular maintenance help you get the most from your activated carbon.
Now you understand how activated carbon helps clean water. It catches many pollutants and makes water better. Activated carbon can take out chemicals, colors, and smells that other filters miss. This helps keep water safe for people and animals. Using activated carbon is good for the environment. Try this method if you want cleaner water where you live.
