
Have you ever thought about why some cooking oils look clear and light, but others look dark and not as nice? Most people want their oil to look clean and pure. Many people think lighter oil means it is better and fresher. Darker oil often does not look as good to them.
Reason for Preference | Description |
|---|---|
Perception of Quality | People think lighter colors mean better quality. |
Association with Freshness | Light colors make oil seem fresher and more attractive. |
Link to Poor Quality | Darker oils are seen as lower quality and less wanted. |
You need to get rid of unwanted colors and bad stuff to meet these hopes and keep food safe. Food Decolorization Activated Carbon helps by catching pigments and harmful things. Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon also makes sure your oil is safe by removing dangerous things like PAHs and PCBs.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Role of Activated Carbon | Changes colors and takes out harmful things in edible oils. |
Contaminants Removed | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Dioxins, Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) |
Compliance | Makes sure edible oils follow strict safety rules. |
Key Takeaways
Activated carbon makes cooking oil look clear and nice by taking out unwanted colors. Decolorization makes oil look better and also makes it safer by removing harmful things. Crude oils have impurities that can spoil oil and change its taste. Activated carbon removes these impurities well. Picking the right kind of activated carbon, like powdered or granular, is important for cleaning oil. Mixing the oil well and giving it enough time with activated carbon helps remove toxins and pigments. Using activated carbon can make oil taste better and improve its quality. It also helps make sure the oil is safe to eat. We should think about the environment too. Choosing activated carbon from renewable sources can help nature. It is important to balance the cleaning process. Using too much activated carbon can take away good nutrients from the oil.
Decolorization in Edible Oil
Purpose
People want their cooking oil to look clear and nice. Decolorization helps by taking away colors that are not wanted. This makes the oil look better and meet rules for quality. Decolorization does more than just make oil look good. It also gets the oil ready for deodorization. When you take out pigments and color bodies, the oil will not turn dark again later. This step also helps the oil last longer and stay fresh.
Tip: Decolorization helps oil look good and keeps it safe and fresh for a longer time.
Common Impurities
Before refining, oil has many things in it that are not wanted. These things can lower the oil’s quality. Here are some common impurities found in crude edible oils:
Free Fatty Acids
Sterols
Pigments
Hydrocarbons
Wax and Fat Alcohol
Special Impurities
Other Fat-soluble Impurities
These impurities can make oil look cloudy or dark. They can also cause trouble when you store or cook with the oil.
Quality Impact
Impurities do more than just change the oil’s color. They can make the oil go bad by causing oxidation. Oxidation can make the oil taste and smell bad. It can also make harmful compounds. When oil goes rancid, it loses good nutrients. Rancid oil is not healthy and does not taste good. Using oil with too many impurities can make your food taste bad and may not be safe.
The fatty acids in oil can make it spoil faster.
Rancidity happens when oxidation causes bad flavors and less nutrition.
You can stop these problems by using Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon. This helps take out harmful things and keeps your oil fresh, tasty, and safe.
Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon
If you want cooking oil to be clear and safe, you need the right materials. Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon is very important in the bleaching step. It helps take out pigments, phospholipids, heavy metals, toxins, and chemicals like PAHs. This makes your oil look nicer and taste fresher.
Adsorption Properties
Activated carbon is special because it can trap many bad things. You can trust it to clean oil well. It has a huge surface area, sometimes over 1000 m² for each gram. This big surface helps it grab lots of stuff from oil. It can pull out things you do not want, like pigments. Its special shape lets it catch even tiny molecules.
Pore Structure
Activated carbon has many tiny holes called pores. These pores work like traps for color and harmful things. The pores let the carbon hold lots of bad stuff at once. Your oil gets cleaner because the pores act like small filters.
Surface Area
Surface area is important for removing more bad things. Activated carbon gives you a lot of space for adsorption. The bigger the surface, the more color and toxins you can take out. You get faster cleaning because the oil touches more carbon.
Types
You can pick powdered activated carbon or granular activated carbon. Each type works in its own way.
Powdered Activated Carbon
Powdered activated carbon (PAC) has very tiny pieces. You use PAC when you want fast results. The small size gives more surface area, so it works quickly. PAC is good for taking out pigments and other bad things fast. People often use PAC in big oil factories because it works well.
Granular Activated Carbon
Granular activated carbon (GAC) has bigger pieces. You use GAC when you want to clean oil for a long time. It works slower at first, but keeps cleaning as time goes on. GAC is good if you need steady cleaning and have lots of oil.
Characteristic | Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) | Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) |
|---|---|---|
Particle Size | Finer particles (< 0.18 mm) | Larger particles (0.2 to 5 mm) |
Surface Area | Larger surface area | Lower surface area |
Adsorption Rate | Faster due to larger surface area | Slower initially |
Overall Adsorption Capacity | Lower over time | Higher over time |
Ideal Use | Quick results | Long-term contaminant removal |
Tip: Pick PAC for fast decolorization. Choose GAC for steady cleaning over time.
Comparison
You might wonder how Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon compares to other adsorbents like activated clay.
Activated Clay
Activated clay, like bentonite, is often used for oil decolorization. It is easy to use and costs less than activated carbon. Clay removes color and phospholipids well. But you must bake it before using, and you need to wear safety gear. Clay works best outside or in a place with lots of air. You cannot change how fast the oil goes through the filter.
Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
B80 Bentonite Clay | – Naturally active adsorbent | – Requires PPE |
| – Affordable | – Adds time to the extraction process |
| – Easy to use | – Requires baking |
| – Neutral pH level | – Filtration flow rates cannot be adjusted |
| – GRAS-approved | – May cause respiratory irritation if not using proper PPE |
| – Good filtration properties | – Requires use outdoors or in a well-ventilated area |
| – Effective at removing impurities | – Not as effective as other proprietary filter media |
| – Excellent for color bodies and chlorophyll removal |
|
| – Removes phospholipids |
|
– Creates a more flavorful and aromatic oil | – Generally more expensive than B80 bentonite clay | |
| – Does not require baking |
|
| – Adjustable flow rates |
|
| – Affordable for commercial use |
|
| – Large surface area |
|
| – Effective at removing impurities |
|
| – Can be used to remove impurities from other substances |
|
Cost | B80 bentonite clay is generally more affordable than activated carbon. |
|
| B80 bentonite clay costs around $80 for 14 kilograms, while activated carbon can cost around $75 per 1 kilogram or $3,600 for 100 kilograms. |
|
Ease of Use | Both materials are relatively easy to use. B80 is added in powder form, while activated carbon is granular. | B80 tends to add unnecessary steps to the filtration process due to baking. |
Note: Activated carbon gives you more control and better taste, but it costs more than clay.
Other Adsorbents
There are other adsorbents for oil decolorization, but activated carbon is special. It can hold more and removes pigments and bad things better than most others. You get cleaner oil and better taste with Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon.
The price of activated carbon can change. Coconut shell-based carbon can cost more if weather is bad. Sometimes, other adsorbents seem better when activated carbon prices go up. You need to think about cost, how well it works, and safety when you pick your adsorbent.
Using Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon helps you get safe, tasty, and high-quality oil. You can change your process to get the best results.
Decolorization Process

Steps
There are a few main steps to decolorize edible oil. You must do each step the right way to get oil that is clear and safe.
Mixing
First, you mix the oil with Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon. You pour the carbon into the oil and stir it a lot. The carbon has many tiny holes, so it can grab lots of bad stuff. Sometimes, people add activated clay to help even more. Mixing well helps the carbon touch all the oil.
Tip: Stir the oil and carbon really well so the carbon can grab more bad things.
Contact Time
Next, you let the oil and carbon sit together for a certain time. This time is very important. The longer they sit, the more color and toxins the carbon can take out. You must watch the time closely. If you do not wait long enough, some bad things stay in the oil. If you wait too long, you might lose some good things in the oil.
Filtration
After the waiting time, you filter the oil to take out the carbon and the bad stuff it caught. You use special filters to do this. The oil comes out looking clear and clean. You should check the filter to make sure no carbon is left in the oil.
Note: Good filtering gives you oil that is safe and ready to use for cooking.
Here is an easy list of steps for decolorizing oil:
Neutralization: You use sodium hydroxide to take out free fatty acids and other bad things.
Decolorization: You mix in activated carbon and clay to make the oil lighter and cleaner.
Deodorization: You clean the oil more to get rid of any smells.
Removal Targets
Edible Oil Decolorization Activated Carbon helps you take out many things you do not want in oil.
Pigments
Pigments like chlorophyll and carotene make oil look dark. Activated carbon soaks up these pigments. This makes the oil look lighter and nicer. The oil has a lower red value, which means it is better decolorized.
Toxins
Activated carbon also helps you get rid of dangerous toxins. It catches PAH, dioxins, pesticides, and aflatoxins. These toxins are bad for your health. Using activated carbon makes your oil safer to eat.
Toxin Removed | Why Remove It? |
|---|---|
PAH | Can cause health problems |
Dioxins | Harmful to humans |
Pesticides | Unsafe for consumption |
Aflatoxins | Toxic and dangerous |
Free Fatty Acids
Free fatty acids can make oil spoil and taste bad. Activated carbon lowers these acids. This helps your oil stay fresh and taste good for longer.
Oxidation Products
Oxidation products form when oil touches air. These can make oil go bad and be unhealthy. Activated carbon takes out these things, so your oil stays safe and tasty.
Callout: Things like how hot the oil is and how much you stir can change how well you remove pigments and toxins. Always check these things during the process.
Selection Factors
Type
You have to pick the right kind of activated carbon. This helps you get the best results when cleaning oil. The type you choose can change how well it works. Activated carbon comes from things like coal or wood. Each one has its own special features. Powdered activated carbon has lots of tiny holes. These holes help it catch more color and bad stuff in oil. Coal-based and wood-based carbon work in different ways. Some types are better at removing certain colors. If you want to take out a lot of color fast, use powdered activated carbon. If you need to remove certain bad things, pick a type based on where it comes from. Always choose the type that fits what your oil needs.
Tip: Picking the right activated carbon makes your oil look better and taste better.
Dosage
You also need to think about how much activated carbon to use. The right amount helps you get clean oil without wasting anything. If you use too little, some bad stuff stays in the oil. If you use too much, you might lose good things and spend more money. Many things can change how much you should use.
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Choice of Activated Carbon | Different materials (wood, coal, coconut shells) have unique adsorption characteristics affecting efficacy. |
Particle Size | Powdered activated carbon (PAC) offers rapid adsorption, while granular activated carbon (GAC) is easier to separate. |
Operational Parameters | Factors like contact time, temperature, pH, and impurity concentration significantly influence adsorption efficiency. |
You should try different amounts to see what works best. Start with a small amount and check if the oil is clean. Change the amount until your oil looks clear and safe.
Note: Always think about both cost and quality when you decide how much to use.
Oil Type
The kind of oil you use changes how you pick your activated carbon. Each oil has its own amount of bad stuff. Some oils need more cleaning than others. You have to look at the oil’s color and what you want to take out.
Different edible oils have different amounts of impurities, so you need to pick the right activated carbon for each one.
Bleaching oil is not just about making it lighter; it also removes bad things to make the oil better.
How well bleaching works depends on the adsorbent and the way you do it for each oil.
For example, palm oil may need a different activated carbon than sunflower oil. You should always test your process with your own oil. This helps you get the best results every time.
Callout: Matching your process to your oil type gives you better and safer oil.
Process Conditions
When you use activated carbon to clean edible oil, the process conditions matter a lot. These conditions decide how well the carbon removes colors and harmful things from your oil. If you want the best results, you need to pay attention to several key factors.
Temperature plays a big role. Higher temperatures help the carbon work faster. The oil becomes thinner, so the carbon can grab more impurities. But if the oil gets too hot, you might lose some good nutrients. You should keep the temperature just right—warm enough for good adsorption, but not so hot that it damages the oil.
Contact time is another important factor. This means how long you let the oil and activated carbon mix together. If you do not wait long enough, the carbon cannot catch all the bad stuff. If you wait too long, you might start to lose some of the oil’s good qualities. Most people find that 20 to 30 minutes works well for many oils.
Mixing speed also affects how well the carbon works. If you stir the oil and carbon together well, the carbon can touch more of the oil. This helps it grab more color and toxins. You do not want to mix too fast, though, because that can break up the carbon and make it hard to filter out later.
Dosage is the amount of activated carbon you use. Using more carbon usually removes more impurities, but it also costs more. You need to find the right balance. The table below shows how different dosages of activated carbon and clay affect the removal of harmful compounds like harman and norharman in sesame seed oil.
Adsorbent Type | Dosage (%) | Harman Content (μg/kg) | Norharman Content (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
Activated Carbon (PW) | 1 | 4.43 | 0.55 |
Activated Carbon (PW) | 3 | 1.10 | 0.72 |
Activated Carbon (PW) | 5 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
Clay | 1 | 7.16 | 0.55 |
Clay | 3 | 1.24 | 0.52 |
Clay | 5 | 1.24 | 0.52 |
You can see that increasing the dosage of activated carbon lowers the levels of harman and norharman much more than clay does. The chart below shows this difference clearly.
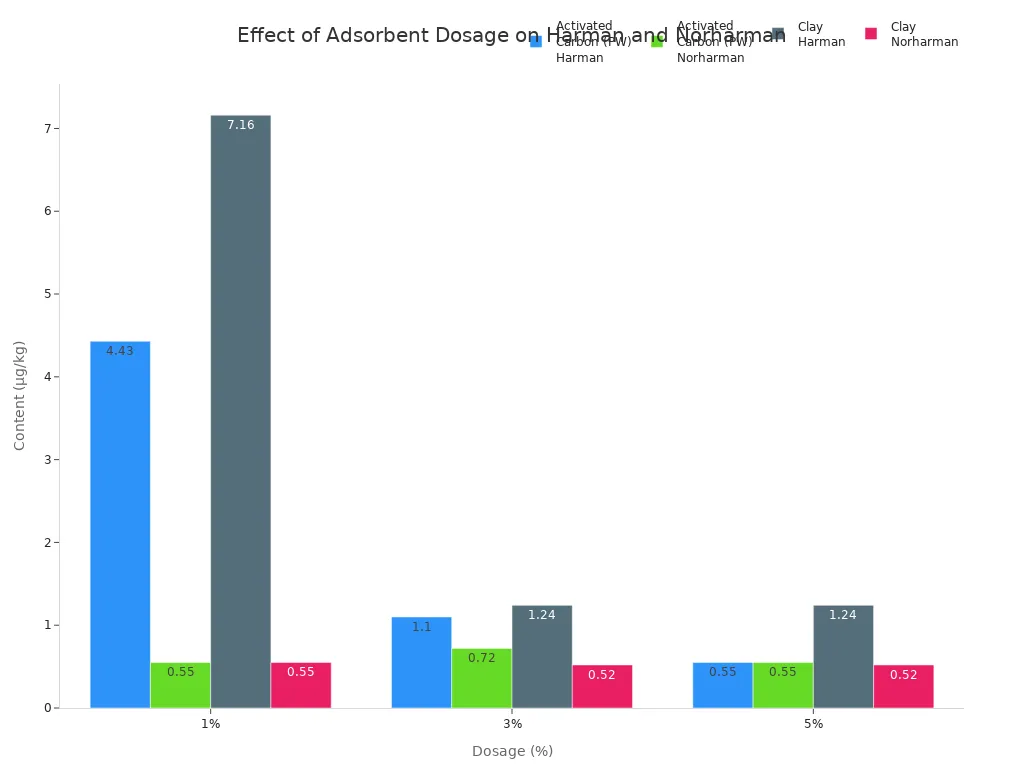
Different types of activated carbon, like wood powder and coconut shell, also work differently. Wood powder activated carbon (PW) has a special pore structure and a large surface area. This helps it remove more harmful compounds from oil than other types.
Tip: Always test your process conditions with your own oil. Small changes in temperature, mixing, or dosage can make a big difference in how clean and safe your oil becomes.
By paying close attention to these process conditions, you can make sure your edible oil is clear, safe, and high quality every time.
Benefits
Quality
You want your cooking oil to look clear and taste good. Activated carbon helps you reach this goal. It takes out color pigments and makes the oil lighter. This also removes bad smells and flavors. Your oil stays fresh longer and does not spoil fast. The oil looks better and lasts longer on the shelf.
Nutshell activated carbon is good for this job. It makes your oil clearer and improves its color. You can trust your oil will look and taste great. Activated carbon also takes out natural toxins and other bad things. This means your oil is not just pretty but also pure.
Tip: Oil that is clear and light often tastes better and is higher quality.
Safety
You want your food to be safe. Activated carbon helps make edible oils safer. It grabs and holds onto harmful things. This includes pesticides, organic pollutants, and natural toxins. Your oil is safer for you and your family.
Here are some ways activated carbon keeps oil safe:
Takes out color pigments, odors, and small impurities.
Grabs and holds onto unwanted things.
Helps remove pesticides and organic pollutants.
You can see how activated carbon makes oil safer in the table below:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Non-toxic and Harmless | Makes sure it is safe for food and medicine. |
Low Ash Content | Stops foods and medicines from losing quality during decolorization. |
High Iodine Value | Shows it can grab more bad things, making decolorization work better. |
Nutshell activated carbon is important when you clean oil. It makes oil look better and takes out toxins and bad things. This makes sure your oil is safe for everyone.
Efficiency
You want a process that works fast and does not waste much. Activated carbon helps you decolorize oil quickly. It has a big surface area and many tiny holes. This lets it grab more bad things in less time. You do not need to use a lot to get good results.
With activated carbon, you can clean lots of oil fast. You save time and energy. The process is simple and easy to control. You can change how much carbon you use to fit your needs. This helps you get the best oil without spending extra money.
Note: When decolorization is efficient, you get better oil faster and with less waste.
Environmental Impact
You may wonder what happens to nature when you use activated carbon to clean oil. The process helps your oil, but it also affects the environment. It is important to know what happens from start to finish.
Activated carbon comes from things like coconut shells, wood, or olive-waste cakes. Making activated carbon takes several steps. These steps use chemicals, heat, and drying. Each step needs energy and can put stuff into the air and water.
When you look at activated carbon made from olive-waste cakes, you find some key facts. Treating the material with phosphoric acid causes most of the problems. This step makes water and soil more acidic. It also puts too many nutrients in rivers and lakes. This can hurt fish and plants. The process also adds carbon dioxide to the air. For every kilogram of activated carbon, about 11 kilograms of CO2 go into the air. Making one kilogram uses 167.63 megajoules of energy. Most energy is used for treating, heating, and drying.
Tip: Think about how activated carbon is made before you choose it. Some types use less energy and make less pollution.
You can help nature by picking activated carbon made from waste. Using olive-waste cakes turns trash into something useful. This cuts down on waste and gives value to things that might be thrown away.
Here is a table that shows the main ways making activated carbon affects the environment:
Impact Type | Description | Main Cause |
|---|---|---|
Acidification | Makes water and soil more acidic | Chemical impregnation |
Eutrophication | Adds nutrients to water, harms aquatic life | Chemical processes |
Global Warming | Releases CO2, adds to climate change | Energy use, chemical steps |
Energy Demand | Uses a lot of energy for production | Heating, drying, impregnation |
You can lower harm to the environment by recycling activated carbon. Some companies clean and use it again. Others burn it for fuel or use it in building things. Always look for ways to use less energy and make less waste.
Callout: Picking activated carbon from renewable sources and recycling it helps protect nature.
You can help make oil processing better for the planet. When you learn about these impacts, you can make smart choices. You help keep Earth healthy while making your oil safe and clean.
Challenges
Disposal
When you use activated carbon to clean oil, you have to think about what happens after. Used activated carbon can cause problems. You cannot just throw it away because it might have harmful things in it. Getting rid of this material is not easy and brings many problems.
Challenge Category | |
|---|---|
Performance & Efficiency | Non-selective adsorption, material inconsistency, form limitations |
Regulatory & Safety Compliance | Classification conflicts, contamination risks, dust hazards |
Sustainability & Waste Management | Single-use waste, regeneration barriers, supply chain impacts |
Operational & Ethical Concerns | Detox mislabeling, process disruptions, reverse discoloration |
There are rules about how to label and store used carbon. Sometimes, the carbon makes dust that is not safe to breathe. If you want to reuse or recycle it, you might have trouble. Some companies cannot clean the carbon for reuse. This means more waste and higher costs. You also need to make sure the carbon does not cause new problems. Always follow safety steps when you handle used activated carbon.
Tip: Always check your local rules before you throw away used activated carbon. Safe disposal keeps people and nature safe.
Nutrient Loss
When you clean oil with activated carbon, you do not just take out bad things. You also lose some good nutrients. The process can lower the amount of healthy stuff in your oil.
Decolorization can lower nutrients like tocopherols and sterols.
In corn oil, tocopherol dropped by almost 30% during cleaning.
Losing these nutrients can make your oil less healthy.
You want your oil to look clear, but you also want it to keep its health benefits. If you take out too many nutrients, the oil is not as good for you. You need to find a balance between cleaning and keeping the good stuff.
Note: Use only as much activated carbon as you need. This helps keep more nutrients in your oil.
Optimization
You can make the cleaning process better by finding the right settings. If you do this, you get cleaner oil and save money. You need to look at a few things to get the best results.
Parameter | Optimum Value | |
|---|---|---|
Catalyst Concentration | 0.97 g/L | High pH helps the carbon grab more color and impurities. |
Initial Dye Concentration | 5 mg/L | Lower dye levels make it easier to clean the oil. |
Flow Rate | 1324 L/h | Faster flow can help process more oil quickly. |
Initial pH | 8.68 | Higher pH improves adsorption and cleaning. |
You can also try other ways to make the process better:
Change how much activated carbon you use and how long you let it work.
Use ultrasound or heat to help the carbon work faster.
Test different pH levels to see what works best for your oil.
Try using math and tests to find the best settings for your process.
When you use the right settings, you can take out almost all unwanted colors and bad things. You also spend less money and keep more nutrients in your oil. Always test and change your process to get the best results.
Callout: Small changes in your process can make a big difference in oil quality and cost. Keep testing and improving for the best outcome.
Activated carbon is a strong tool for making edible oils better. It helps make oil clear, safe, and high quality. You can count on it to take out pigments like carotenoids and harmful things. Studies show cotton and neem husk activated carbon works 30-80% better than old bleaching earth.
Activated carbon from plants is better for the environment.
New ways, like using heat and microwaves, help it work faster.
In the future, people will find better ways to make it and use new materials.
Oils will get even safer and cleaner as these good ideas spread.
