Blood Purification Activated Carbon
.webp)
Buy Blood Purification Activated Carbon
Activated charcoal is mainly used in blood purification using hemoperfusion. Hemoperfusion is the method where blood is taken extracorporeally (outside body) from the patient, and introduced to a cartridge or column of tiny granules of activated charcoal. The structure of activated charcoal consists of multiple pores, and amounts to a large surface area, which allows activated charcoal to adsorb a variety of toxins and metabolic waste products directly from the blood through physical adsorption and hydrophobic interactions. Activated charcoal is effective at removing small to medium-sized, unbound, and hydrophobic molecules as well as some protein-bound substances. Examples of agents that can be removed with activated charcoal are certain drugs (for example, barbiturates, theophylline), as well as toxins (for example, paraquat, Amanita phallotoxin) and uremic toxins (i.e. toxins related to liver failure or extreme poisoning.)
Industry Challenges
Biocompatibility Concerns
- The presence of uncoated charcoal particles stimulates platelets and leukocytes, which can increase the chances of thrombosis, thus once a length of time goes by microparticles can be released during perfusion which can lead to microemboli creation but also necessitates complex polymer coatings (like cellulose acetate) which can also slow the rate of adsorption.
Limited Solute Removal Capacity
- Activated charcoal can remove small-to-medium size (<~10 kDa) hydrophobic toxins (toxins such as neurotoxic drugs and poisons), but charcoal is completely ineffectual against electrolytes, urea, or larger (~20+ kDa) protein bound uremic toxins, while also requiring hybrid systems - necessitating hemodialysis/hemofiltration - ultimately complicating the treatment protocol.
Selective Capability (adsorption)
- Non-specific adsorption studies will also remove relevant medications (likely antibiotics and anticoagulants) and nutrients alongside the target toxins, making it unmanageable to monitor therapy.
- Additionally, plasma proteins will also non-specifically absorb and compete for binding capacity for the target toxins, further recommending reducing binding capacity.
Material Standardization Issues
- Performance reproducibility is complicated by differences in pore structure and surface area for each source of charcoal.
- Biocompatible coatings on the charcoal can also have differences in durability, leading to leaking charcoal particles, or impaired adsorption capacity during sustained application.
Clinical Protocol Constraints
- Therapeutic protocols are limited due to decreased adsorption capacity and adverse effects to biocompatibility - they are not restricted to a single application.
- Any re-bound toxin release that may come from the charcoal during application may require multi-sessions.
related types of activated carbon
-r8fslg51nt6wgjtvh6yldxb1gtkgm3lpe0oq1akgog.webp)
- Iodine Value: 600-1200
- Mesh Size: 1×4/4×8/8×16/8×30/12×40/20×40/20×50/30×60/40×70 (More size on request)
- Apparent Density: 400-700
-r8fsli0q1h9h3rr567ruiwtynlb71ht629zozuhoc0.webp)
- Iodine Value: 500-1300
- Mesh Size:0.9-1mm/1.5-2mm/3-4mm/6mm/8mm(More size on request)
- Apparent Density: 450-600
-r8fslbfupn0gui0p8mxgjghqhw7mjm31pdfamwrfjk.webp)
- Iodine Value: 500-1300
- Mesh Size: 150/200/300/350 (More size on request)
- Apparent Density: 450 – 550
-r8fsle9da54btbwls65c8xs4a1tq6pe8prdr2qn90w.webp)
- Iodine Value: 400-800
- Mesh Size: 100×100×100mm/100×100×50mm (Custom cell density on request)
- Apparent Density: 350-450
- Bore Diameter:1.5-8mm

- Iodine Value: 700-1200 mg/g
- Surface Area: 700-1200 m²/g
- Apparent Density: 320-550 kg/m³

- Iodine Value: 700-1200 mg/g
- Surface Area: 700-1200 m²/g
- Apparent Density: 320-550 kg/m³

- Iodine Value: 700-1200 mg/g
- Surface Area: 700-1200 m²/g
- Apparent Density: 300-650 kg/m³

- Iodine Value: 700-1200 mg/g
- Surface Area: 700-1200 m²/g
- Apparent Density: 320-550 kg/m³

- Activation Method: Steam/gas activation at high temperatures
- Pore Structure: Microporous-dominated, uniform pore distribution
- Environmental Profile: Chemical-free, low ash content
- Primary Applications: Gas-phase adsorption, drinking water purification
- Activation Method: Chemical activation (e.g., H₃PO₄/ZnCl₂) at moderate temperatures
- Pore Structure: Mesoporous-rich, higher surface area
- Process Efficiency: Shorter activation time, 30-50% higher yield
- Post-Treatment: Acid-washing required to remove residues

- Functionalization: Loaded with active agents (e.g., I₂/Ag/KOH)
- Targeted Adsorption: Enhanced capture of specific pollutants (e.g., Hg⁰/H₂S/acid gases)
- Customization: Chemically optimized for target contaminants
- Core Applications: Industrial gas treatment, CBRN protection
Why Use Our Activated Carbon
Optimized Pore Structure:
Maximizes adsorption capacity for diverse toxins while preserving essential biomolecules.

Enhanced Biocompatibility Coating:
Minimizes platelet activation and microemboli risks during hemoperfusion.

Strictly Standardized Manufacturing
Ensures batch-to-batch consistency in adsorption performance and safety.
Surface chemistry customization:
Allows targeted removal of protein-bound uremic toxins or specific poisons.

Validated clinical performance:
Demonstrates reliable toxin clearance rates across critical care scenarios.
Process and Technolog
1. Hemoperfusion For Acute Poisoning
Solution Overview
Direct blood circulation through charcoal-coated cartridges to rapidly adsorb ingested toxins/drugs before systemic absorption.
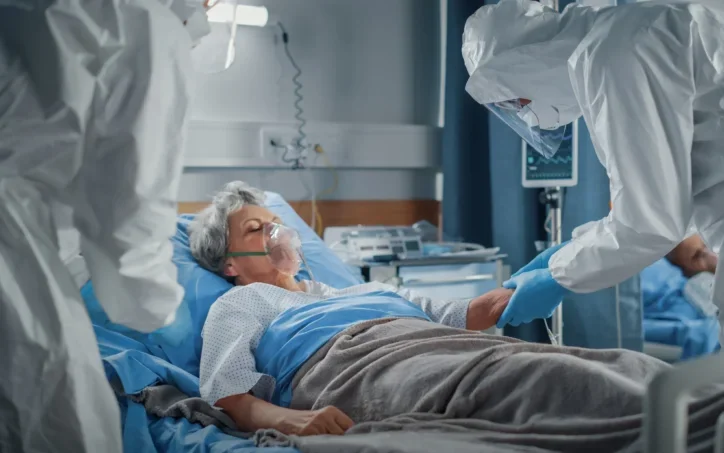

Key Advantages
- Broad-spectrum adsorption: Neutralizes diverse toxins including barbiturates, pesticides, and mushroom toxins
- Hemodynamic stability: Maintains blood pressure better than whole-blood purification methods
- Rapid intervention: Shortens toxin half-life faster than conventional hemodialysis
- Portability: Enables bedside emergency deployment
2.ombined Hemodialysis-Hemoperfusion (HD-HP) for Uremia
Solution Overview
Hybrid system pairing charcoal adsorption with conventional dialysis to address protein-bound uremic toxins.
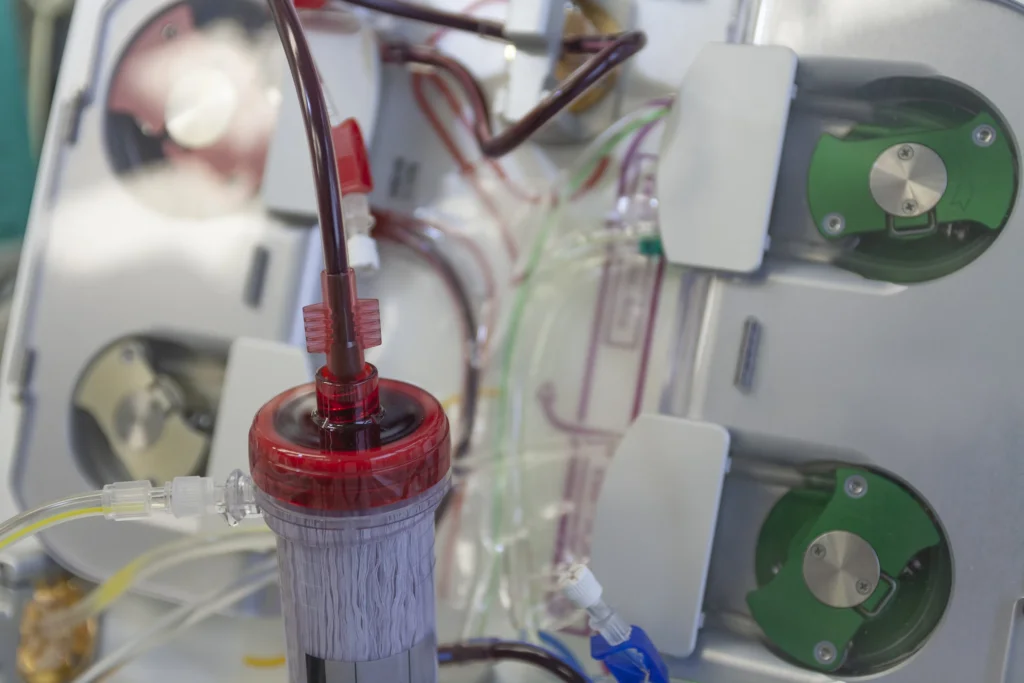

Key Advantages
- Enhanced toxin clearance: Removes both water-soluble (e.g., creatinine) and protein-bound (e.g., indoxyl sulfate) toxins
- Extended filter lifespan: Charcoal component protects dialyzer membranes from fouling
- Reduced inflammation: Lowers pro-inflammatory cytokines better than dialysis alone
- Symptom management: Better controls pruritus and neurological symptoms in renal failure
3. Hepatic Failure Support Systems
Solution Overview
Charcoal columns integrated with albumin dialysis to adsorb liver failure-associated toxins like bilirubin and bile acids.
Key Advantages
- Albumin regeneration: Clears albumin-bound toxins without albumin loss
- Bridge to transplantation: Stabilizes patients awaiting donor organs
- Multi-organ support: Simultaneously addresses renal and hepatic toxin accumulation
- Bilirubin reduction: Specifically targets jaundice-causing compounds