
Activated carbon helps control bio odor by grabbing smelly molecules. It does this through adsorption. Its special structure gives it a huge surface area. This helps trap bad smells.
Activated carbon for bio odor control has a surface area of 2276 m²/g.
The large surface area lets activated carbon hold more smelly compounds.
When you use activated carbon, it removes odors well. The material traps sulfur compounds and other organics. Bio Odor Control Carbón Activado works for many odor problems. You can count on activated carbon to remove odors reliably.
Principales conclusiones
Activated carbon gets rid of bad smells by trapping smelly molecules. This happens through a process called adsorption. Activated carbon has a big surface area. This helps it hold more odor compounds. That makes it a good choice for stopping smells. Bio odor often comes from wastewater plants, compost piles, and food factories. Activated carbon works best on sulfur compounds. These compounds usually cause strong smells in many places. You need to take care of activated carbon often. Change it when you notice smells coming back. This helps keep odor control working well. There are different kinds of activated carbon for different odor problems. Pick the right type for what you need. You can use activated carbon in air purifiers, water treatment, and factories. Keep activated carbon dry and clean. This helps it work better and stops bad bacteria from growing.
Bio Odor Overview
What Is Bio Odor
Bio odor happens when organic things break down. This process releases smelly gases into the air. These smells come from natural things like decay or fermentation. Sometimes, chemical reactions also make these odors. Bio odor usually smells very strong and bad. You often notice it where waste or food is breaking down. The main chemicals that cause bio odor are mercaptans, skatoles, indoles, inorganic acids, aldehydes, ketones, and organic compounds with nitrogen or sulfur atoms.
Consejo: You can tell bio odor by its sharp, rotten, or sour smell. These smells show that something organic is decaying nearby.
Common Sources
Bio odor comes from many different places. You find it at wastewater treatment plants, compost piles, and food processing sites. Each place makes its own mix of odor compounds.
Wastewater
Wastewater treatment plants smell when organic matter breaks down without oxygen. You might smell dimethyl disulfide, methyl mercaptan, and hydrogen sulfide. These chemicals form when there is no oxygen. The smell is often strong and unpleasant.
Compost
Compost piles smell as microbes break down organic waste. You might notice terpenes like limonene, menthol, and alpha-pinene. Acetaldehyde and volatile fatty acids also add to the smell. Composting with air smells better than composting without air. Different materials in the pile change how it smells.
Food Processing
Food processing sites make odors when food breaks down. You might smell acetaldehyde, lactic acid, and acetic acid. If the food breaks down without air, the smell gets worse. Frying and roasting food releases aldehydes, fatty acids, and ketones. Making biogas adds hydrogen sulfide and other bad-smelling gases.
Odor Compounds | Características | |
|---|---|---|
Wastewater | Dimethyl disulfide, methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide | No oxygen makes strong sulfur smells. |
Compost | Terpenes, acetaldehyde, volatile fatty acids | Different materials change smells; air helps compost smell better. |
Food Processing | Acetaldehyde, lactic acid, acetic acid | No air and easy-to-break-down food make smells worse. |
Odor Problems
Bio odor causes problems for people and their communities. Strong smells make it hard to live or work near these places. Odors from waste and farms can cause health problems like asthma, skin rashes, and nerve damage. Breathing these smells for a long time is risky, especially for workers and people living close by. Some dangerous chemicals have no smell, and some smelly ones are not dangerous. It is hard to control bio odor in big places. Leaking trash bags, rotting food, and waste can quickly become too much if not handled. Smells build up in drains, corners, and uneven floors, so these spots need special care. Too much liquid and no air in compost piles make smells worse. Organic acids are a big reason for these odors.
Nota: You can stop odor problems by fixing sources early and using good odor control methods.
Activated Carbon Mechanism
Proceso de adsorción
When you use activated carbon, it grabs odor molecules. This is called adsorption. In adsorption, molecules stick to the surface. They do not soak inside like in absorption. Activated carbon pulls small odor molecules from air or water. These molecules fill tiny spaces called pores.
Several forces help this process. These include electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. Hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions also play a part. These forces help activated carbon hold many odor molecules. Sometimes, natural organic matter blocks the pores. It can also compete for space. This lowers how much odor activated carbon can hold. Keeping the pores open and clean helps it work best.
Many things affect how well activated carbon removes bio odor:
Surface area: More surface area means more places for odor molecules to stick. This increases how much odor it can hold.
Pore size: The size and spread of pores decide which molecules fit and get trapped.
Surface chemistry: Special groups on the surface attract certain odor molecules.
Contact time: Longer contact means more odor can be adsorbed. There is a best time for top results.
Adsorbate characteristics: The size and polarity of odor molecules affect how well they stick.
To control bio odor, pick activated carbon with the right features. This helps it hold more odor and keeps air or water fresh.
Estructura de los poros
Activated carbon works well because of its pore structure. There are three main pore types: micropores, mesopores, and macropores. Each type traps different odor molecules. Micropores are tiny and catch small molecules. Mesopores and macropores trap bigger volatile organic compounds.
Here is a table that shows how pore structure affects performance:
Aspecto | Explicación |
|---|---|
Estructura de los poros | The mix of micropores, mesopores, and macropores changes how much odor it can hold. |
This depends on the surface area and pore volume of activated carbon. | |
Diffusion Rate | Pore size affects how fast molecules reach the pores. |
Surface Chemistry | Heteroatoms and special groups help trap certain odor molecules. |
The network of pores gives a huge surface area. Some activated carbon has over 3,000 square meters in one gram. This large area helps it hold more odor. Carbonization and activation steps make this complex pore network. The size and shape of pores decide which molecules get trapped. Small pores catch tiny molecules. Bigger pores grab larger ones.
Adsorption means molecules stick to the surface of activated carbon.
The big surface area lets many gas or vapor molecules bind.
The pore network is key for catching different pollutants.
Different pore sizes trap different odor molecules.
You need to match the pore structure to the odors you want to remove. This gives the best results and keeps your space odor-free.
Molecular Trapping
Activated carbon traps odor molecules at the molecular level. Odor molecules enter the pores and stick to the surface. Weak forces like van der Waals and hydrogen bonds help. Sometimes, chemical bonds form too. The structure of activated carbon lets it trap many kinds of molecules.
Some odor compounds are easier to trap. For example, 2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) sticks better because it matches basic sites on activated carbon. Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) does not stick as well, but still gets trapped by the graphene structure.
Odor Compound | Capacidad de adsorción | Surface Property Influence |
|---|---|---|
2-MIB | Más alto | Linked to basic sites |
DMDS | Baja | Linked to basic sites and graphene structure |
Activated carbon is great at trapping sulfur compounds. These often cause the worst bio odors. The table below shows how long it takes to trap different sulfur compounds:
Compound | Maximum Adsorption Time | Characteristic Peaks (cm–1) |
|---|---|---|
Na2SO3 | 20 min | 2920, 1630, 1390, 1110 |
Na2S2O8 | 60 min | 3850, 3740, 2920, 1390, 1110, 600 |
Na2SO4 | 60 min | 3430, 2920, 1630, 1390, 1110, 600 |
Fe2(SO4)3 | 20 min | 1390, 1110, 600 |
Sulfur (S) | 120 min | 1630, 1390, 600 |
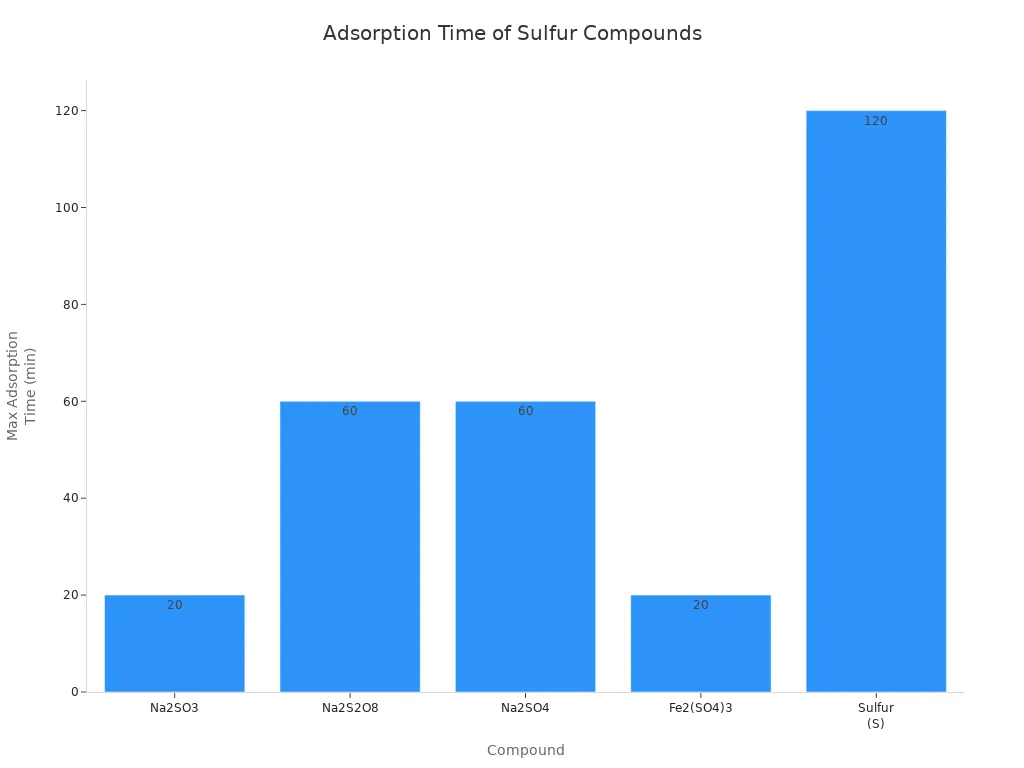
You can see activated carbon traps some sulfur compounds faster than others. How much it can hold depends on the compound and the carbon’s structure. To remove strong odors, pick activated carbon with the right pore structure and surface chemistry. This gives you the best results for your needs.
Consejo: Keep your activated carbon clean and dry. This helps it work well and keeps your odor control system strong.
Eficacia
You might wonder if carbón activado really helps with bio odor. The answer is yes, it does. Carbón activado is good at removing many kinds of smells from air and water. You can count on it for both strong and weak odors.
Carbón activado works best on sulfur compounds. These are the main cause of bad bio odors. Hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan, and dimethyl disulfide are common sulfur smells. You often smell these at wastewater plants, compost piles, and food factories. Carbón activado grabs these molecules fast. Its big surface area and special pores help catch even tiny odor molecules.
It also works well on other organic odors. These are things like aldehydes, ketones, and volatile fatty acids. Carbón activado holds onto these molecules tightly. You will notice a big drop in bad smells after using it.
Here is a table that shows how well carbón activado removes different odors:
Odor Type | Eficacia de eliminación | Typical Source |
|---|---|---|
Sulfur Compounds | Muy alta | Wastewater, compost, food |
Compuestos orgánicos volátiles (COV) | Alta | Food waste, fermentation |
Fatty Acids | Alta | Compost, food processing |
Aldehydes and Ketones | Alta | Food, industrial processes |
Puede utilizar carbón activado in many places. It works in filters, air cleaners, and water systems. You will see it in big factories and small homes. Carbón activado keeps working if you keep it clean and dry.
Consejo: Change your carbón activado when smells come back. This helps your system stay strong.
Carbón activado does not just hide odors. It takes them out of the air or water. This makes your space safer and nicer. You can trust carbón activado for long-lasting odor control.
Carbón activado also works fast. You do not have to wait long to smell a difference. Most of the time, you will notice fresher air in just a few hours. This quick action makes carbón activado a great choice for odor control.
Puede confiar carbón activado for many reasons: – It removes both sulfur and organic odors. – It works in many places. – It acts fast. – It keeps working if you take care of it.
If you want a way to control bio odor that works, carbón activado is a smart choice.
Bio Odor Control Carbón Activado
Specialized Products
Hay muchos tipos de bio odor control activated carbon for different jobs. Each one has lots of tiny holes to catch smelly molecules from the air. This makes it a good choice for small rooms and big buildings. You might pick granular activated carbon for most smells. For harder jobs, like cleaning wastewater or medical waste, you can use catalytic activated carbon.
Here is a table that lists some common types and what makes them special:
Tipo de carbón activado | Unique Features |
|---|---|
Virgin Activated Carbon | Broad-spectrum odour removal, cost-effective, reliable for moderate H₂S concentrations. |
Chemically Impregnated Activated Carbon | Targeted removal of specific compounds: Caustic for H₂S, Acid for ammonia, KI for mercaptans. |
Carbón activado catalítico | Converts H₂S to sulfuric acid, water-regenerable, extends operational life, reduces waste. |
Some products are very good, easy to use, and safe for the environment. Many are made from things that can grow back and can be used again after use. When you need to control smells from medical waste, these special products help you follow safety and environmental rules.
Consejo: Pick the right kind of bio odor control activated carbon for your smell problem. This helps you get the best results and keeps your system working well.
Removal of Organic Odors
Bio odor control activated carbon is great at removing smells from organic compounds. You find these smells at compost sites, food plants, and when treating medical waste. Activated carbon and helpful microbes work together to clean water and air. Biologically activated carbon (BAC) is popular because you can use it many times and not make extra waste.
BAC works better at removing dissolved organic carbon (DOC) when the water is warm and more good microbes grow on it. If you use ozone before BAC, you can break down tough organic compounds and remove more smells. This makes BAC a smart pick for medical waste treatment, where strong smells are common.
Here is a table showing how well different types of activated carbon remove organic odors:
Tipo de carbón activado | Effectiveness in Removing Compounds |
|---|---|
Coconut shell based granular activated carbon | Effective for VOC removal and low levels of H2S |
Bituminous coal based catalytic carbon | High capacity for H2S, used in wastewater treatment |
Caustic impregnated carbon | High capacity for H2S, rarely used due to hazards |
You can use bio odor control activated carbon in many places. It helps keep the air clean and safe, especially when treating medical waste with strong, bad smells.
Sulfur Compound Removal
Sulfur compounds like hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) make some of the worst smells. Bio odor control activated carbon can remove these odors fast and well. Activated carbon also protects your machines from damage and helps you follow air quality rules. This is very important when treating medical waste, where sulfur smells are a big problem.
Activated carbon, especially coconut activated carbon, works better when you change its surface or add bi-metal compounds. These changes help it catch more sulfur compounds, even if the air is wet or there is a lot of H₂S. Sometimes, you can remove more than 98% of sulfur smells, like when using woodchips-derived biochar at the right pH and moisture.
Here is a table showing how well different materials remove sulfur compounds:
Descripción de las pruebas | Eficacia de eliminación | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
Woodchips derived biochar for H2S removal | Initial concentrations of 105, 510, and 1020 ppmv, pH 8.0, moisture content 80-85% |
Activated carbon removes sulfur compounds better than nitrogen compounds. If you use ozone with activated carbon in a biofilter with air, you can remove over 80% of sulfur smells.
Nota: Keep your bio odor control activated carbon dry and change it when smells come back. This helps you keep high removal rates, especially when treating medical waste.
Activated Carbon for Odour Control
Eficacia
You might wonder how well activated carbon works. Efficiency means how much bad smell gets removed. To check this, you test the air before and after it goes through activated carbon. The change tells you how much odor is gone. You can also compare different systems using elimination capacity. This helps you choose the best one for your needs.
Here is a table that shows how people measure efficiency:
Measurement Method | Descripción |
|---|---|
Removal Efficiency (RE) | You figure this out by checking the amount of contaminants before and after the system. |
Elimination Capacity (EC) | This lets you compare different odor control systems. |
Activated carbon works quickly for odour control. You notice results in just a few hours. Its big surface area helps trap lots of odor molecules. This makes activated carbon a great choice for homes and factories. It removes many odors, especially sulfur and organic compounds.
Tip: Check your system often. Change the activated carbon when smells come back. This keeps your odour control working well.
Seguridad
You need to be careful when using activated carbon for odour control. Activated carbon can get too hot and catch fire if used wrong. Wet activated carbon can grow biofilms. These biofilms make new smells and lower how well it works. You should keep the carbon dry and watch for overheating.
Here is a table with safety risks:
Safety Risks | Descripción |
|---|---|
Overheating | Activated carbon can get too hot and burn. |
Biofilm Growth | Wet carbon can grow biofilms and cause new smells. |
Follow safety rules to stay safe. Store activated carbon away from heat. Keep it dry. Watch for biofilm growth. If you see slime or smell new odors, change the carbon. This keeps your odour control safe and working well.
Versatilidad
Activated carbon helps control odors in many places. You use it in factories, homes, kitchens, and cars. It also helps with waste and even in your fridge. Activated carbon traps odor molecules in its pores. This makes it useful for many things.
Here are some ways people use activated carbon:
Industrial settings: You use it in vents to stop bad smells.
Residential applications: You put it in air purifiers and fridge filters.
Commercial kitchens: You use it to fight strong cooking smells.
Waste management facilities: You use it to control trash odors.
Automotive cabin air filters: You use it to keep your car smelling nice.
You can also use activated carbon bags in shoes, drawers, and cupboards. These bags soak up odors and keep spaces fresh. Activated carbon works because it traps the molecules that make bad smells. You get cleaner air and a nicer place to live.
Nota: Activated carbon fits many odour control units. You can use it almost anywhere you want to remove odors.
Coste
When you pick carbón activado for odor control, you should think about cost. Many things can change how much you pay. The price of coal, wood, or coconut shells can go up if they are hard to get. Making carbón activado needs a lot of heat, which uses energy and adds to the price. If you work in food, drink, chemical, or medicine factories, you might pay more. These places have strict rules about smells and pollution, so costs can rise.
You also have to think about costs that keep coming back. Carbón activado does not last forever. You need to change it often to keep your system working well. Most people swap out the carbon every two to six months. This means you spend money on new carbon and on workers to change it. If you use a lot of carbon, these costs can get big over time.
Here is a table that shows the main things that affect cost:
Factor de coste | Descripción |
|---|---|
Raw Material Price | Cost of coal, wood, or coconut shells |
Production Energy | High heat needed to make activated carbon |
Replacement Frequency | Carbon needs changing every 2-6 months |
Labor and Maintenance | Time and effort to replace and manage carbon |
Cumplimiento medioambiental | Meeting strict odor and emission standards |
You may wonder how carbón activado stacks up against other ways to control odor. Carbón activado filters are used in about 65% of places. People like them because they work well and do not cost too much at first. But you have to change the carbon more often than with some other systems. For example, ultrafiltration costs more at the start, but you do not have to change it for three to five years. These systems also make less waste, which can save money and help the planet.
Here are some things to think about when looking at costs:
Carbón activado is cheaper at first but needs to be replaced often.
Ultrafiltration costs more at the start but lasts longer and makes less waste.
Carbón activado is popular because it is easy to use and works quickly.
You should also think about the earth. Making carbón activado can let out greenhouse gases. If you use new carbon from nature, you might worry about using up resources. Some companies now sell recycled or renewable carbon to help with these problems.
Consejo: If you want to save money, check how often you need to change your carbon. Try recycled or renewable carbon to help the environment.
When you plan your odor control, balance the starting cost, how often you need to change the carbon, and how it affects the earth. This helps you pick the best choice for your needs and your wallet.
Aplicaciones

Tratamiento de aguas residuales
You find activated carbon in wastewater plants to stop bio odor. These plants smell bad because things break down and make gases. Activated carbon filters catch smelly molecules like hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan. When these filters work, the air smells much better. Workers and people nearby breathe cleaner air and complain less.
Activated carbon filters also help at waste transfer sites. These places move trash and sewage, which can smell really strong. You use carbon filters to trap and stop these smells. This makes things safer for workers and the community.
Application Context | Descripción |
|---|---|
Wastewater Treatment Plants | Activated carbon filters stop bad smells by grabbing odor molecules, making things cleaner. |
Waste Transfer Facilities | Used to trap and stop strong odors, helping workers and people nearby have a better place. |
Consejo: Change your activated carbon filters often. This keeps odor control strong and stops smells from coming back.
Purificación del aire
Utiliza activated carbon in air cleaners at home and in public places. Air purifiers with carbon filters take away smells from kitchens, pets, and bathrooms. You get fresh air right away and the machines are quiet. These filters are safe to use inside and do not let out bad chemicals.
In offices, hotels, and bathrooms, ceiling carbon panels and special scrubbers work quietly. You notice cleaner air and fewer people complain about smells. These systems do not need much care and fit in the room without standing out.
Application Setting | Descripción | Principales ventajas |
|---|---|---|
Residential/Household | Used in air purifiers, kitchen fans, and pet spots to grab odors. | Fast odor removal, quiet, safe for inside use. |
Commercial/Public Spaces | Ceiling carbon panels and special scrubbers for offices, hotels, and bathrooms. | Hold lots of odors, easy to care for, blend in with the room. |
Nota: You can put activated carbon bags in shoes, closets, and cars. These bags soak up smells and keep things fresh.
Composting
You see activated carbon used at compost sites. Compost piles smell strong as microbes break down waste. Activated carbon grabs smelly gases and other bad compounds. You use carbon filters in vents to trap these smells before they get out.
Some compost places use big carbon towers with many layers. These towers clean lots of smelly air and keep the area nice. You also find mobile units with activated carbon for short-term odor control when turning compost or moving waste.
Application Setting | Descripción | Principales ventajas |
|---|---|---|
Waste Recycling & Processing | Big carbon towers and mobile units for landfill gas and sewage. | Catch water-hating smells, safe from fire, easy to use in many places. |
Consejo: Keep your compost pile with air and dry. This helps activated carbon work better and lowers odor problems.
Activated carbon gives you lasting removal of organic smells from air, water, and soil. You find it in filters, vents, and mobile units. You can trust activated carbon to keep your space clean and free of bad smells.
Uso industrial
You find carbón activado in many industries to control bio odor. Factories, chemical plants, and food factories use it to keep air clean. You see carbón activado in filters, scrubbers, and exhaust systems. These tools catch and remove bad smells before they leave the building.
Factories often make strong smells from chemicals, solvents, and waste. You might smell these near paint shops, refineries, or paper mills. Carbón activado works well here because it traps organic and sulfur smells. You use it to meet air quality rules and keep workers safe.
How Activated Carbon Works in Industry:
Carbon Filters: You put these in vents. They trap odor molecules as air moves through.
Exhaust Systems: You add carbón activado to exhaust stacks. This stops bad smells from getting outside.
Air Scrubbers: These machines clean lots of air. They often use carbón activado with other filters for better results.
Consejo: Check your filters often. Change the carbón activado when you smell odors again. This keeps your system working well.
Here is a table that shows where you use carbón activado in industry:
Industry Type | Common Odor Sources | Aplicación del carbón activado |
|---|---|---|
Food Processing | Cooking, fermentation | Air filters, exhaust scrubbers |
Chemical Plants | Solvents, byproducts | Ventilation filters, scrubbers |
Gestión de residuos | Decomposition, landfill gas | Odor control units, carbon beds |
Pulp and Paper | Sulfur compounds | Stack filters, air cleaning units |
You can also use carbón activado to treat water in factories. Many plants use it to take out organic smells from wastewater before letting it go. This helps you follow environmental rules and keeps water clean.
Some industries use carbón activado to clean soil. If there is a spill, you can mix carbón activado into the dirt. It traps smelly chemicals and helps fix the land.
Benefits of Activated Carbon in Industry:
Removes strong and stubborn odors
Works for air, water, and soil
Helps you follow safety and environmental rules
Easy to add to systems you already have
Puede confiar carbón activado for lasting odor removal. It keeps your workplace safe and nice. You also help the environment by stopping bad smells from spreading.
Consejos de uso
Choosing Activated Carbon
You need to choose the right activated carbon for your odor problem. First, figure out what kind of smell you want to remove. Some activated carbon works best for sulfur odors. Others are better for organic smells. Check the pore size and surface area. A bigger surface area means it can trap more odor molecules. Think about what the carbon is made from. Coconut shell activated carbon is good for cleaning air. Bituminous coal activated carbon is better for cleaning water.
Consejo: Ask your supplier for test results. These results show how well the activated carbon removes certain odors.
Here is a table to help you compare options:
Tipo | Mejor uso | Superficie (m²/g) |
|---|---|---|
Coconut Shell | Purificación del aire | 1200 – 1600 |
Bituminous Coal | Tratamiento del agua | 800 – 1200 |
Wood-Based | Composting | 600 – 900 |
Application Methods
You can use activated carbon in a few different ways. The most common ways are filters and pellets.
Filters
Filters use activated carbon to clean air or water. You put these filters in vents, air cleaners, or water systems. When air moves through the filter, odor molecules stick to the carbon. This gives you fast results and is easy to set up. Many homes and factories use these filters because they work well and do not need much care.
Put filters where smells are strong.
Change filters if you start to smell odors again.
Use fans with filters to move air better.
Pellets
Pellets are small pieces of activated carbon. You can use them loose or in special cartridges. Pellets go into trays or containers. They are good for big rooms or factory systems. Pellets last longer than powder and can handle lots of air.
Pour pellets into trays or cartridges.
Spread pellets out so they work best.
Change pellets every few months.
Nota: Always follow the instructions from the maker. This helps your activated carbon work its best.
Mantenimiento
You need to take care of your activated carbon to keep it working. Check your filters or pellets often. If you smell bad odors again, the activated carbon is full. Change it right away. Clean around your odor control system. Dust and water can block the pores and make it work less well.
Check your system every month.
Change activated carbon when you need to.
Keep the system dry and clean.
🛠️ Regular care helps stop odor problems and keeps your space fresh.
If you use activated carbon in a big system, make a schedule for checks and changes. This keeps your odor control strong and working well.
Solución de problemas
Lifespan
You need to know how long activated carbon lasts in your odor control system. The lifespan depends on how much odor the carbon has to remove and the type of smells in your space. Most activated carbon works well for two to six months. If you use it in a place with strong odors, you may need to change it more often. When the carbon gets full, it cannot trap any more odor molecules. You will notice smells coming back when this happens.
You can make your activated carbon last longer by keeping it dry and away from dust. If you use it in a filter, check the airflow. Good airflow helps the carbon work better and last longer. If you see dust or water on the carbon, clean or replace it right away.
Consejo: Write down the date when you install new activated carbon. This helps you remember when to check or change it.
Necesidades de mantenimiento
You must take care of your activated carbon to keep it working well. Regular checks help you spot problems early. Look at your filters or pellets every month. If you see dust, dirt, or water, clean the area. Wet carbon does not work as well and can even grow mold or bacteria.
Make a simple checklist for your maintenance:
Check for bad smells every week.
Look for dust or water on the carbon.
Replace the carbon if you notice odors coming back.
Clean the area around your odor control system.
If you use activated carbon in a big system, set a schedule for checks and changes. This keeps your system strong and stops odor problems before they start.
🛠️ Regular care helps your activated carbon last longer and keeps your air or water fresh.
Limitaciones
Activated carbon works well for many odors, but it does have limits. You need to know these limits so you can plan for the best results. Some smells, like high levels of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), can fill up the carbon quickly. When this happens, you must replace the carbon more often, which can cost more money.
The table below shows some main limitations and what they mean for you:
Limitation | Explicación |
|---|---|
Activated carbon cannot hold much H₂S at once. In places with lots of H₂S, the carbon fills up very fast. | |
Equilibrium Driven | The carbon stops working when it cannot hold any more odor. At this point, it releases as much as it traps. |
Risk of Spontaneous Combustion | If you use activated carbon with high H₂S, it can get hot and even catch fire. This is a safety risk. |
You can handle these limits by checking your system often and using the right type of carbon for your needs. In places with lots of H₂S, you may need special carbon or extra safety steps. Always follow the maker’s instructions to stay safe and get the best results.
Nota: Knowing the limits of activated carbon helps you avoid problems and keeps your odor control system working well.
Saturation Signs
You need to know when your activated carbon has reached saturation. Saturation means the carbon cannot trap any more odor molecules. If you miss these signs, your odor control system will stop working well. You might notice smells coming back or even getting worse.
Common Signs of Saturation:
Return of Odors: The most obvious sign is the return of bad smells. If you start to notice odors again, your activated carbon is likely full.
Weaker Airflow: Sometimes, the carbon gets clogged with particles. You may feel less air coming through your filter or system.
Change in Color: Some activated carbon changes color as it fills up. If your carbon looks darker or gray, it may be time to replace it.
Moisture Buildup: Wet or damp carbon can fill up faster. If you see water or feel dampness, check for saturation.
Visible Dust or Debris: Dust on the surface can block pores. If you see a layer of dust, your carbon may not work as well.
Consejo: Trust your nose. If you smell odors where you did not before, check your activated carbon right away.
Quick Checklist for Saturation:
Symptom | What You Notice | Qué hacer |
|---|---|---|
Odors return | Smells come back or get worse | Replace the carbon |
Airflow drops | Less air from vents or filters | Check for clogs or replace |
Cambios de color | Carbon looks darker or gray | Inspect and change if needed |
Moisture present | Carbon feels wet or sticky | Dry or replace the carbon |
Dust buildup | Dust covers the carbon | Clean or swap out carbon |
You can also set a schedule to check your carbon. Many people mark their calendars for monthly checks. This helps you catch problems before they get big.
Other Ways to Check Saturation:
Use a simple odor test. Hold the carbon near your nose (if safe) and see if it smells bad.
Some systems have sensors or indicators. Watch for warning lights or alerts.
If you use carbon in water, test the water for taste or smell changes.
🛑 Nota: Never ignore the signs of saturation. Old or full carbon can release trapped odors back into your space.
You keep your air or water fresh by watching for these signs. Replace your activated carbon as soon as you notice saturation. This keeps your odor control system strong and reliable.
You can trust activated carbon to help with bio odor in many places. It grabs odor molecules using adsorption. You will notice it works quickly and keeps air or water fresh. Activated carbon takes away sulfur and organic smells from homes, factories, and compost piles. You can find it in filters, pellets, and air systems. It helps with lots of different odor problems. Activated carbon is safe and simple to use. It works well in both small and big spaces. You get a cleaner and healthier place when you use it. Try activated carbon and look for more ways to make your odor control better.
