
Yes, you can use reusable activated carbon again, but you should know some key things first. Many factors determine if reusable activated carbon still works after you use it:
The kind of substance matters. Things that stick physically come off the activated surface more easily than things that bond with chemicals.
How much is used up shows how much activated surface is left. If the carbon is only partly full, it may still work. If it is totally full, it usually cannot be used again.
How you clean reusable activated carbon is very important. Bad cleaning can damage the activated structure and make it less useful later.
When you learn about using reusable activated carbon again, you can make safer and smarter choices.
Key Takeaways
Activated carbon can be used again. How well it works depends on how much you use it. It also depends on how you clean it.
Pick coconut shell activated carbon for better results. It lasts longer in refillable filters.
Magnetically harvestable activated carbon makes cleaning easier. It also makes reusing faster. This helps cut down on waste and saves time.
Using activated carbon again is good for the environment. It lowers waste and cuts down greenhouse gas emissions.
You can clean activated carbon with heat or chemicals. Both ways work well, but each has good and bad sides.
Always look for signs that your carbon filter is full. Watch for color changes or bad smells. These signs mean you should replace your filter.
Safety is very important when using old activated carbon. Wear safety gear and work where air moves well.
You can try other options like biochar. Biochar is better for the planet if you cannot reuse activated carbon.
What Is Activated Carbon?

How It Works
Activated carbon is used in many purifier systems. It has lots of tiny pores. These pores give it a big surface area. This helps trap things we do not want. The activation process makes these pores. It helps the carbon clean better.
Activated carbon has a network of carbon atoms. This network gives it more surface area. It helps with adsorption.
The surface is rough and has small holes. Oxygen groups help attract and hold chemicals.
Activated carbon traps substances in three main ways. These are π–π dispersion, hydrogen bonding, and electron donor–acceptor interactions.
Physical adsorption happens when molecules stick to the surface. They use weak forces to stay on the carbon.
People use activated carbon in filtration. It grabs and holds many contaminants. This is why it is popular for water and air filters. Its chemical structure helps remove chlorine, odors, and volatile organic compounds.
Tip: Activated carbon works best for things that stick to surfaces. It does not work as well for things that react with chemicals.
Common Uses
Activated carbon is found at home and in factories. Its special pores make it useful for cleaning. You see it in products that remove chemicals or bad smells.
Type of Activated Carbon | Common Applications |
|---|---|
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) | |
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) | Household water filters, industrial gas purification |
Extruded Activated Carbon (EAC) | Air purification, chemical recovery |
Impregnated Activated Carbon | Removing mercury from industrial emissions |
Bead Activated Carbon (BAC) | Medical applications, gas purification |
Activated carbon cleans water, air, and soil. It helps in medicine, food, gold recovery, and cars. You also see it in metal finishing and other industries.
Clean water and air are important. Activated carbon helps with this. You use it in your home water filter. It removes chlorine and other harmful things. You also find it in air purifiers. These keep indoor air fresh.
Note: Activated carbon comes from organic sources. Its pores trap many contaminants. This makes it important for cleaning at home and in factories.
Reusable Activated Carbon
Coconut Shell vs. Bamboo Charcoal
You might ask which material is best for reusable activated carbon. Coconut shell activated carbon has a much bigger surface area. It ranges from 800 to 3000 m²/g. This means it has more places to trap things. It can catch more organic compounds, odors, and toxic gases. Coconut shell carbon lasts longer than bamboo charcoal. It works better for many uses in refillable carbon filters. Bamboo charcoal is strong and dense. But it does not trap as much as coconut shell carbon. If you want your filter to work well after cleaning, pick coconut shell activated carbon.
Tip: For the best results and reuse, choose coconut shell carbon for your refillable carbon filters.
Magnetically Harvestable Carbon
There is new technology called magnetically harvestable reusable activated carbon. This type is easier to clean and use again. You can see what makes it special in the table below:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Lets you take out and collect carbon fast with magnets. | |
Inductive Regeneration | Lets you make carbon active again using magnetic fields. |
High Adsorption Efficiency | Removes tiny organic pollutants for many uses. |
You can use this carbon in refillable carbon filters for water and air. You pull out the carbon with magnets, clean it, and put it back. This saves time and helps your filter last longer. It also helps the environment by making less waste.
Sustainability Benefits
Reusing activated carbon is good for the planet. It makes your reusable activated carbon last longer. You do not need to use as many new resources. Reactivating carbon can double or even triple the life of your filters. You throw away less, so there is less trash in landfills. Making new carbon creates more CO2 than reusing old carbon. By reusing, you lower greenhouse gases and help keep the earth clean.
Reusable activated carbon helps your filters last longer.
You make less waste and save money by reusing.
You help stop climate change by lowering your carbon footprint.
Note: Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) and Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) are made to be reused. You can reactivate them and use them in refillable carbon filters many times. Single-use types cannot do this.
Choosing reusable activated carbon for your refillable carbon filters is smart. You get cleaner water and air, save money, and help the earth.
Reuse Methods
Thermal Regeneration
Thermal regeneration is a strong way to make your carbon filter work again. You use very high heat to get rid of the trapped pollutants. The carbon filter goes into a special furnace. The heat breaks down or makes the pollutants disappear. This leaves the carbon ready to work again.
Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Regeneration | Removes adsorbates with high heat, making the carbon work again. | Works well, cleans deeply, and does not make waste water. |
You need heat between 800°C and 1000°C for the best results. At these high temperatures, most of the carbon filter’s power comes back. Some studies say you can get back 60–80% of the original power. Sometimes, the filter works even better than before for some pollutants. Lower heat, like 350°C, can also work for some uses. It may help your carbon filter last longer.
Note: Using high heat too much can make your carbon filter wear out faster. Try to use the lowest heat that still works well.
Thermal regeneration is good for many carbon air filters. It works for both water and air cleaning. You get a clean filter and do not make dirty water.
Chemical Methods
Chemical methods use special liquids to clean your carbon filter. You soak the carbon in acids or bases to take out the trapped stuff. This way is popular because you do not need high heat. You can do it with simple tools.
Method | Benefits | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Regeneration | 1. Needs a lot of energy, so it costs more. | |
2. Works for many different pollutants. | 2. Needs special furnaces or kilns. | |
3. Makes sure the filter works well after cleaning. | 3. Can make harmful gases. | |
Chemical Regeneration | 1. Uses less energy because it needs lower heat. | 1. Chemicals can cost a lot. |
2. Can be chosen for certain pollutants. | 2. You must handle and throw away chemicals safely. | |
3. Makes less harmful gas. | 3. Does not work for every pollutant. |
You might use chemical methods if your filter has lots of organic pollutants. This way is easy and does not use much energy. But not every chemical works for all pollutants. You need to pick the right one for your filter. Chemical cleaning is softer on the filter than high heat. Still, it may not clean every kind of pollutant.
Tip: Always be careful with chemicals. Wear gloves and work where there is fresh air when you clean your carbon filter.
Washing and Rinsing
Washing and rinsing is the simplest way to clean your carbon filter at home. You use water to wash away some trapped things. This works best for things that dissolve in water or for heavy metals. It is cheap and safe for the earth.
But washing does not clean every kind of pollutant. If your filter has things like VOCs, water may not remove them. Also, if you wash your filter, it can soak up water and dry slowly. If it stays wet, mold can grow inside. This can make your air worse.
Washing does not remove every pollutant from your filter.
Wet filters can grow mold if they are not dried fast.
Rinsing with cold water will not make your filter work like new.
Note: Washing your carbon filter is not a good idea for most uses. If you must wash it, dry it all the way before using it again.
Washing and rinsing can help your filter last longer, but it is not enough. You may need to use thermal or chemical regeneration for the best results.
Inductive Regeneration
Inductive regeneration is a new way to make activated carbon work again. It uses a process called electrothermal temperature swing adsorption, or ETSA. This method heats the carbon with electricity. The heat spreads quickly and evenly. You do not need fire or hot air. Induction heats the carbon from inside.
Here is how it works:
Adsorption: First, activated carbon traps pollutants like VOCs from air or water.
Induction Heating: Next, induction heats the carbon. The heat makes pollutants leave the carbon. This is called desorption.
Cooling: After heating, the carbon cools down. Pollutants turn into vapor. You can collect them by condensation at medium temperatures.
Inductive regeneration has many benefits:
You heat the carbon directly. This saves energy and time.
The system does not touch the carbon with anything hot. This keeps things clean and simple.
You can control the heating easily. This stops overheating or damage.
The process heats the carbon fast and evenly.
You can use the same carbon many times. ETSA lets you repeat adsorption and regeneration. The carbon may lose some power after many cycles. But it still works well for several uses.
You can collect valuable VOCs by condensing them after they leave the carbon.
Tip: Inductive regeneration works best for magnetically harvestable carbon. You can remove, clean, and reuse this carbon with less waste and more efficiency.
Inductive regeneration is a smart and green way to reuse activated carbon. You get cleaner filters, spend less money, and help the environment. If you want a modern way to clean your carbon filters, try this advanced method.
Limitations and Risks
Loss of Effectiveness
If you reuse activated carbon, there is a big problem. The carbon loses its power after some time. Pollutants fill up the tiny pores inside the carbon. When the pores are full, the carbon cannot trap new things. Your filter may not work as well as it did before.
Activated carbon gets saturated. Over time, pollutants fill up the adsorption sites. When it is full, the activated carbon cannot trap more pollutants.
Carbon filters only work for a short time. The pores slowly close, so the filter cannot catch unwanted stuff.
Carbon filters stop working well after a while. This happens because the pores close up, and the filter cannot catch particles anymore.
If you keep using a full filter, pollutants can get through. Your water or air might not be as clean as you want.
Contamination Risks
Cleaning activated carbon does not always remove every pollutant. Some contaminants, like APIs, can stay on the carbon after cleaning. These substances may break apart, but small pieces can stick again. It is hard to get rid of them all.
You might think your filter is clean, but some hidden contaminants can stay. If you use the filter again, leftover substances can get into your water or air. This can cause new pollution in your home.
If you do not replace saturated activated carbon, it can cause pollution indoors.
You should know what kinds of pollutants your filter has trapped. Some are harder to remove and may stay after cleaning.
Safety Concerns
Trying to reuse or clean activated carbon at home can be dangerous. You might touch toxic impurities. These can hurt your eyes, skin, or breathing. Always wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when you handle used carbon.
Before you clean carbon, ask local safety experts for help. They can help you avoid accidents and keep you safe.
Here are some safety tips for activated carbon:
Wear gloves and goggles.
Work where there is fresh air.
Keep kids and pets away from cleaning.
Throw away waste safely.
If you do not follow safety steps, you can get hurt. Always be careful with used carbon.
Safe Reuse Steps
When to Reuse
You may want to reuse your filter, but you should check if it still works. Activated carbon loses its power over time. You can look for signs that show it is no longer effective:
Color changes: If the carbon looks lighter or turns brown, the pores may be blocked.
Odor change: If you notice bad smells, the filter may not remove pollutants anymore.
Decreased adsorption: You can test the water or air before and after the filter. If the filter does not clean as well, it may be time to replace it.
Service life: If you have used the filter longer than the recommended time, you should get a new one.
Saturation test: Some devices can measure how full the carbon is.
Tip: If you see any of these signs, you should think about replacing your filter instead of reusing it.
Home Regeneration Guide
You can try to clean your filter at home. Follow these steps to make the process safe and effective:
Stop using the filter and release any pressure inside.
Take apart the filter using the right tools.
Remove dust and dirt with a soft brush or vacuum.
Rinse the carbon bed with water or use reverse airflow.
Soak the carbon in a cleaning solution that matches the type of pollutant.
Rinse again with clean water and repeat backwashing if needed.
Let the filter air dry completely. This helps prevent mold and keeps the filter working.
Put the filter back together and install it as the instructions say.
Note: Washing can remove some impurities, but it does not fully reactivate the carbon. The filter may not work as well after cleaning.
Safety Tips
You should always protect yourself when handling activated carbon. Here are some important safety tips:
Wear gloves, goggles, and a mask to avoid touching or breathing in dust.
Do not crush the carbon. Crushing makes more dust.
Work in a place with good airflow. This keeps you safe from dust and low oxygen.
Store carbon in a dry container, away from chemicals and heat.
Keep the carbon away from sunlight and high temperatures. This prevents fire.
Follow the instructions from the manufacturer for safe use and replacement.
Use separate tools for cleaning to avoid mixing pollutants.
Alert: Activated carbon can catch fire if stored wrong. Always keep it away from flames and heat sources.
You can keep your home safe and your filter working by following these steps.
When to Replace Activated Carbon Filters
Signs Replacement Is Needed
You need to know when your carbon filter stops working well. If you keep using an old filter, it may not clean your water or air. Here are some clear signs that tell you it is time to replace activated carbon filters:
You notice a change in the taste or smell of your water. This means the filter cannot remove bad substances anymore.
Water flow slows down a lot. A clogged carbon filter blocks water and lowers pressure.
The filter has passed its recommended lifespan. Even if it looks fine, you should change it after the suggested time.
When you check the filter, it looks dirty or clogged. Dirt and buildup show that the filter cannot trap more pollutants.
If your water smells or tastes strange, or if the pressure drops, your carbon filter may be full.
Health and Safety Reasons
Using a spent carbon filter can put your health at risk. When the filter gets saturated, it cannot trap harmful substances. Pollutants may pass through and enter your water or air. You might breathe in or drink these contaminants without knowing.
Pollutants can escape back into your home.
The filter loses its power to clean.
You may get exposed to hazardous substances if you do not replace the filter.
In labs, old filters can let dangerous fumes through, which is unsafe.
Low-quality or poorly maintained filters can also cause health problems. If you use a carbon filter past its limit, hazardous vapors may get into your home. Even small amounts can be harmful.
Always check your carbon filter and replace it when needed to keep your family safe.
Alternatives to Reuse
You have options if you want to avoid reusing your carbon filter. Some people use powdered activated carbon for cleaning, but making it uses a lot of energy and costs more. Biochar is a cheaper choice and helps store carbon in the soil. It can clean water, but its power depends on how you make it and what you want to remove.
Material | Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
PAC | Removes micropollutants | High energy use, costly |
Biochar | Varies by production | Lower impact, stores carbon |
Wood biochar often has less impact on the environment than PAC. It works well for some uses and helps reduce waste. If you want a greener option, biochar may be the right choice, especially if it has high adsorption capacity.
You can choose biochar for a more sustainable solution if you want to lower your carbon footprint.
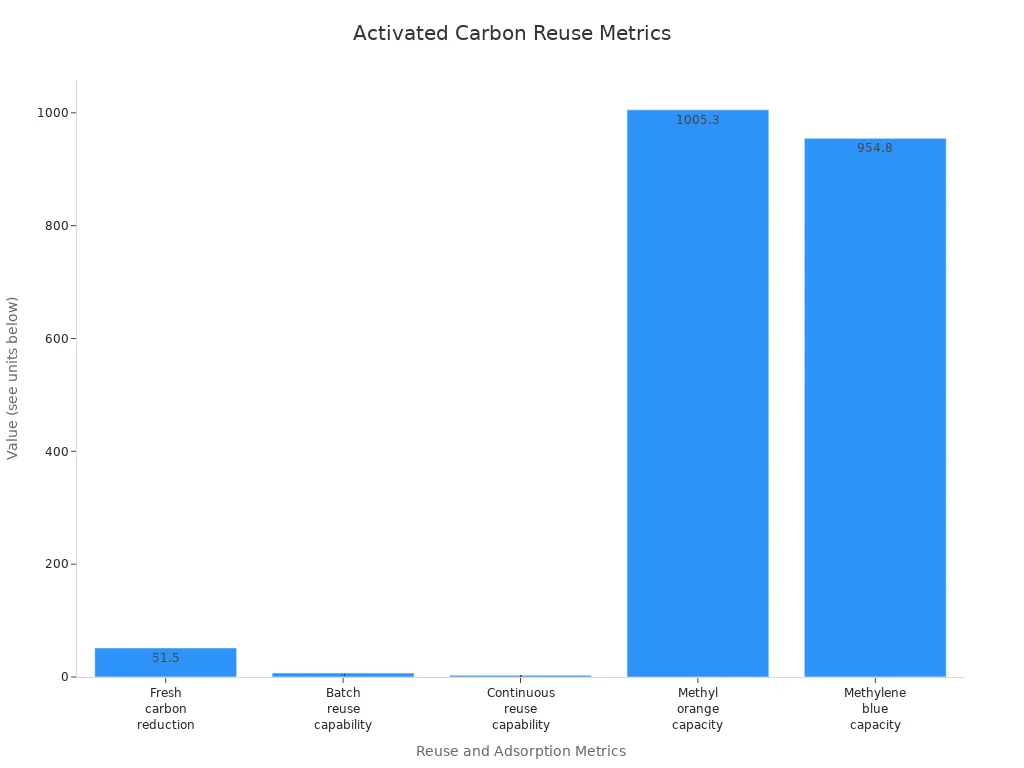
You can use activated carbon more than once. Drying methods help you reuse it and get back valuable adsorbates. This also means you make less waste.
Results | |
|---|---|
You use less new activated carbon | 51.5% or below |
You recover more valuable adsorbate | Significant |
You can use it in factories | Yes |
You can reuse it in batch mode | 7 times |
You can reuse it in continuous mode | More than 3 times |
It adsorbs methyl orange over many cycles | 1005.3 mg/g |
It adsorbs methylene blue over many cycles | 954.8 mg/g |
Look for changes in water taste or flow.
Pick eco-friendly choices and take care of your filter.
If you follow these tips, you keep things safe and clean. You also help the planet and make your filter work well.
