
Catalytic activated carbon is different from regular activated carbon. It can break down chloramine and hydrogen sulfide better. This is important in water treatment and air cleaning. It helps make drinking water safer. Regular activated carbon filters remove many contaminants. These include chlorine, VOCs, and heavy metals. Catalytic activated carbon filters work better for hydrogen sulfide and chloramine. The table below shows how each carbon filter removes certain impurities. This helps improve water filtration and purification.
Type of Carbon | Common Contaminants Removed | Removal Rates / Effectiveness Description |
|---|---|---|
Regular Activated Carbon | Chlorine (taste and odor), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), heavy metals, PFOS, THMs, pesticides, herbicides | Removes between 60 and 80 impurities; can reduce contaminants to below detection limits; effective for broad organic chemicals and heavy metals |
Catalytic Activated Carbon | Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chloramine | Converts hydrogen sulfide to sulfuric acid for easy regeneration; excels at chloramine removal |
Key Takeaways
Catalytic activated carbon breaks down hard chemicals better. It works well on things like chloramines and hydrogen sulfide. Regular activated carbon removes many bad things from water. It takes out chlorine, VOCs, and heavy metals. This makes water taste and smell better. Catalytic carbon filters work faster than regular ones. They also last longer when cleaning tough pollutants. This makes them good for city water and strong smells. Picking the right type of activated carbon helps a lot. You can choose powdered, granular, or extruded forms. This helps the filter work best for your needs. Catalytic activated carbon costs more at first. But it saves money later because you replace it less. It also needs less care. Both types of carbon filters are good for the environment. They are eco-friendly if made from things like coconut shells. You can also reuse them to make less waste. Regular activated carbon is good for most cleaning jobs. Catalytic activated carbon is better for hard-to-remove stuff. It also lasts longer. Always check how your filter is working. Replace it when needed to keep water and air clean and safe.
Activated Carbon Basics

What Is Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is special for cleaning water and air. It is made from things like wood, coal, peat, or coconut shells. These materials get heated to very high temperatures. Sometimes steam or chemicals are used in this process. This creates many tiny holes called pores. The pores give activated carbon a very large surface area. This helps it trap lots of different contaminants.
The material used to make activated carbon changes how well it works. Hard things like bone or shells make carbon with smaller surface areas. Softer things like leaves or soft plants make carbon with bigger surface areas. Chemicals like zinc chloride or potassium hydroxide help make both small and medium pores. This lets activated carbon catch many kinds of impurities. Coconut shell activated carbon has lots of small pores. It is great at trapping tiny molecules. People use coconut shell activated carbon in water filters. It works well and is good for the environment.
Tip: The material used to make activated carbon matters for how well it works and if it is good for the planet. Coconut shells can be replaced, but coal and wood cannot be replaced as easily.
Forms of Activated Carbon
Activated carbon comes in different forms for different jobs. The three main types are powdered activated carbon, granular activated carbon, and extruded activated carbon. Each type has special features for certain uses.
Form of Activated Carbon | Physical Description | Typical Filtration Applications |
|---|---|---|
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) | Very fine powder with lots of surface area | Used in small filters and faucet attachments |
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) | Bigger loose pieces | Used for whole-house water filters and chemical removal |
Extruded Activated Carbon (EAC) | Shaped into small pellets with a binder | Used for cleaning gases and in carbon block filters |
Granular activated carbon is used in water and air filters. It is good for whole-house water filters because it lasts a long time. Powdered activated carbon is very fine and works in small filters. It can also be put right into water treatment. Extruded activated carbon is shaped like pellets. It is strong and does not make much dust. This makes it good for cleaning gases. Some special types, like bead activated carbon or impregnated carbon, have unique jobs. They can stop germs from growing or remove certain contaminants.
Activated carbon filters use these forms to remove many impurities. Picking the right type helps your filter work better and last longer.
Catalytic Activated Carbon Overview
What Is Catalytic Activated Carbon
Catalytic activated carbon is a special kind of carbon filter. It does more than just trap bad stuff. It can change harmful chemicals into safer ones. This makes it different from regular activated carbon. Regular activated carbon mostly holds onto impurities. Catalytic activated carbon has a special surface. This surface helps speed up chemical reactions. You can use it to remove tough things like chloramines and hydrogen sulfide from water. Many water treatment plants and home filters use catalytic carbon. It helps remove more contaminants.
Note: Catalytic activated carbon is not the same as carbon mixed with chemicals. It keeps its natural adsorption power. It also gets new abilities to break down some pollutants.
How Catalytic Carbon Filters Work
Catalytic carbon filters use two actions: adsorption and catalysis. When water or air goes through these filters, the carbon traps many impurities. At the same time, the special surface helps start chemical reactions. These reactions break down stubborn contaminants. For example, it can turn chloramines into harmless things. It can also change hydrogen sulfide into forms that are easier to remove.
Here are some benefits of catalytic carbon filters:
They remove chloramines and hydrogen sulfide better than regular carbon filters.
They last longer when used for these contaminants.
They are used in places with high levels of chloramines, like city water supplies.
Regular activated carbon is good for general cleaning and making water taste and smell better. But it cannot break down tough chemicals like catalytic carbon can.
Production and Surface Modification
Manufacturers make catalytic activated carbon by changing the surface of regular activated carbon. They use high-temperature gas processing to treat the carbon. This process changes the electronic structure of the carbon. It also increases its catalytic activity. The treatment does not add chemicals to the carbon. So, it keeps its strong adsorption abilities. During this process, gases like CO and CO2 are released. The surface charge of the carbon changes. These changes help the carbon act as a catalyst for breaking down tough contaminants.
There are different ways to change the surface of activated carbon to make it catalytic:
Heat treatment at high temperatures changes the surface chemistry. It makes the carbon more basic.
Chemical treatments can add special groups or metals like silver or copper. This boosts catalytic activity.
Plasma treatment increases surface acidity. It does not harm the pores.
Some new methods use biological processes to change the carbon for environmental uses.
These changes help catalytic carbon filters work better in water treatment, air cleaning, and factories. You can trust catalytic activated carbon for jobs that need more than simple filtration.
Removal of Contaminants
Remove Chloramines
Many cities use chloramine to keep water safe. Chloramines are harder to get out than chlorine. Regular activated carbon can only trap some chloramines. It also works slowly. Catalytic activated carbon has a special surface. This surface helps chemical reactions happen faster. So, it removes chloramines much quicker and more completely. Using catalytic carbon gives better protection from chloramines and trihalomethanes. These can hurt your health and change the taste and smell of water.
The difference in how they work is easy to see. Catalytic activated carbon lasts much longer before it stops working. It also breaks down peroxide much faster. This means it keeps removing chloramines for a longer time. The chart below shows how much better catalytic carbon is at removing chloramines during water treatment.
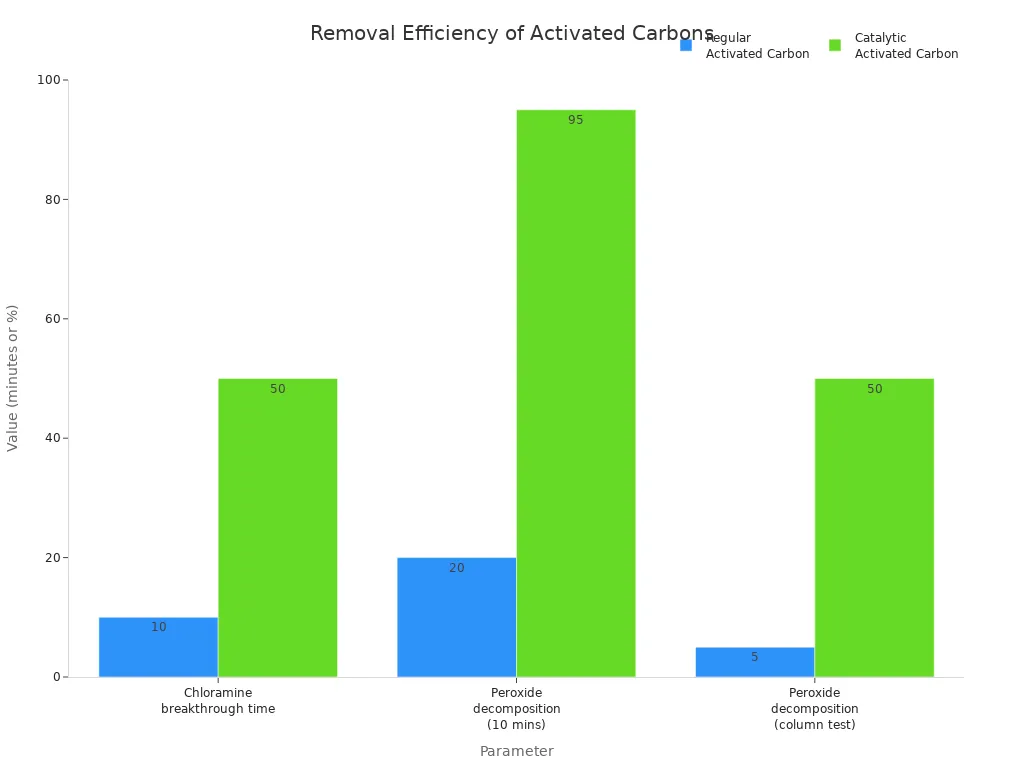
Parameter | Regular Activated Carbon (GAC) | Catalytic Activated Carbon |
|---|---|---|
Chloramine breakthrough time | ~10 minutes | |
Peroxide decomposition (10 mins) | ~20% | >95% |
Peroxide decomposition (column test) | <5% | >50% |
Surface treatment | None | High-temperature gas processing |
If you want to remove chloramines well, use catalytic activated carbon. It works faster and gives safer water.
Chlorine and VOCs
Chlorine is often in tap water to kill germs. But it can make water taste and smell bad. Regular activated carbon filters help by trapping chlorine and VOCs. They make water taste and smell better. Catalytic carbon does even more. It changes chlorine into harmless chloride. This makes it better at removing chlorine and tough VOCs.
Both types of carbon can help clean your water. But catalytic activated carbon removes more chlorine and VOCs. This gives you better-tasting water and safer drinking water.
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide smells like rotten eggs in water. It can make water taste bad and hurt pipes. Regular activated carbon can only trap a little hydrogen sulfide. Catalytic activated carbon does more. It traps hydrogen sulfide and uses oxygen to turn it into safe sulfur. This works even if there is a lot of hydrogen sulfide.
Catalytic carbon needs less care and lasts longer for this job. It works best if the water has enough oxygen. If your water smells like rotten eggs, catalytic activated carbon is the best choice. It gives you cleaner water and helps protect your pipes.
Other Impurities
You might wonder how these filters handle other impurities. Both regular and catalytic activated carbon can catch many contaminants. These include pesticides, herbicides, medicines, and heavy metals. Regular activated carbon is good for organic chemicals and pollution from factories. It traps these things in its tiny holes. This helps make your water and air cleaner.
Catalytic activated carbon can do even more. It can break down some chemicals that regular carbon only holds. For example, it helps get rid of ozone, formaldehyde, and some nitrogen compounds. This gives you better protection from hard-to-remove contaminants. Catalytic carbon also helps lower smells from sulfur gases and other bad odors. This makes it helpful in places with lots of different pollution.
Tip: If you want to remove many kinds of impurities, pick a filter with both regular and catalytic activated carbon. This helps you catch and break down more contaminants.
Here is a table that shows how each type of activated carbon works for other common impurities:
Impurity Type | Regular Activated Carbon | Catalytic Activated Carbon |
|---|---|---|
Pesticides/Herbicides | Good removal | Good removal |
Pharmaceuticals | Good removal | Good removal |
Ozone | Limited removal | Excellent removal |
Formaldehyde | Limited removal | Excellent removal |
Nitrogen compounds | Limited removal | Good removal |
Sulfur gases | Some removal | Excellent removal |
You should think about what impurities are in your water or air before picking a filter. If you have tough chemicals or strong smells, catalytic activated carbon gives you better protection.
Efficiency and Performance
Contact Time
You want clean water or air fast. Contact time means how long water or air touches the filter. If the filter works well, you do not need much contact time. Catalytic carbon filters can clean tough contaminants quickly. Their special surface helps break down chemicals faster. This means you get clean water in less time.
Regular activated carbon filters need more contact time for some impurities. You may need to slow the flow or use a bigger filter. This helps the carbon trap more contaminants. Catalytic carbon works better for chloramines and hydrogen sulfide. You do not have to wait as long for safe water.
Filtration Speed
Filtration speed is how fast a filter cleans water or air. You want a filter that works quickly and removes harmful substances. Catalytic carbon filters clean faster because they use adsorption and chemical reactions. Their special surface breaks down chemicals while trapping them. You get high filtration speed and strong contaminant removal.
Regular activated carbon filters mostly trap impurities in tiny pores. They work well for many chemicals, but some stubborn contaminants take longer to remove. If you need to clean water with chloramines or hydrogen sulfide, catalytic carbon gives better speed and results. You can use these filters where you need fast and complete cleaning.
Tip: For quick and thorough filtration, pick a filter with catalytic carbon for the best results.
Lifespan
You want your filter to last a long time. How long a filter lasts depends on pollution, how often you use it, and the environment. Regular activated carbon filters usually last three to six months. Some high-quality filters can last up to six years if used in good conditions. High pollution, humidity, and temperature can make filters wear out faster.
Catalytic carbon filters remove more stubborn contaminants. There is no clear proof they last longer than regular activated carbon filters. Both types can last months or years depending on use. Check your filter often and replace it when performance drops. Clean water and air need fresh filters.
Filter Type | Typical Lifespan (months) | Maximum Lifespan (years) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Regular Activated Carbon | 3–6 | Up to 6 | Lifespan depends on usage and environment |
Catalytic Carbon | 3–6 | Up to 6 | No proven lifespan advantage |
Note: Always follow the manufacturer’s advice for replacing filters. This keeps your water and air safe.
Cost Comparison
Price Differences
When you look for activated carbon filters, you see a big price gap. Regular activated carbon filters cost less at first. You can buy them in many stores. They fit most water and air filter systems. Catalytic activated carbon filters cost more when you buy them. Their special surface and new technology make them pricier to make.
Here is a simple table to help you compare the usual prices:
Filter Type | Average Initial Cost | Replacement Frequency | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
Regular Activated Carbon | $30–$80 | Every 3–6 months | Manual replacement |
Catalytic Activated Carbon | $150–$400 | Every 3–5 years | Automated backwash |
You might want to pick regular activated carbon because it is cheaper. But you should think about how often you must change the filter. Regular activated carbon fills up fast, so you buy more replacements. Catalytic activated carbon filters last much longer. This means you buy fewer filters and have less work.
Tip: If you want to save money over time, look at the total cost, not just the first price.
Value Over Time
You want a filter that gives you clean water or air and saves money. Regular activated carbon filters work for many contaminants, but fill up in 3 to 6 months. You need to change them often, which costs more. You also spend more time and effort on upkeep.
Catalytic activated carbon filters give better value as time goes on. Their catalytic reduction process breaks down contaminants without using up the carbon. These filters usually last about 5 years. An automated backwash system cleans the filter, so you do not need to change cartridges as much. This system stops clogging and keeps the filter working well.
When you look at the total cost, catalytic activated carbon filters stand out. You pay more at first, but you save on replacements, energy, and downtime. You also have fewer stops and less work. Life-cycle cost models show that filters with longer lives save you more money.
Benefits of catalytic activated carbon filters over time:
Fewer replacements
Lower maintenance costs
Less downtime
Better cost efficiency
If you want a filter that lasts and saves money, catalytic activated carbon is a smart pick. You get steady performance and lower costs over the years.
Applications
Water Filtration
You want your drinking water to be safe. Carbon filters help clean water at home. Catalytic carbon filters are best for tough chemicals. These chemicals include chloramines and chlorine. Chloramines can hurt reverse osmosis units. They also change how water tastes. Catalytic carbon filters break down chloramines. This makes your water safer to drink. They also lower chlorine fast. This helps protect your water system.
Catalytic carbon filters are used in city water plants. You also see them in home water systems. They help make drinking water better. They remove VOCs, pesticides, and other chemicals. Activated carbon has a large surface area. It traps these impurities. This gives you cleaner water and better taste. You find these filters in pitchers and faucet attachments. They are also in under-sink and whole-house systems. Changing the cartridge often stops bacteria from growing.
Tip: Use catalytic carbon filters for water with chloramines or strong smells. Activated carbon filters work well for most organic chemicals.
Application Type | Best Filter Choice | Main Benefit |
|---|---|---|
City water with chloramines | Catalytic carbon filters | Removes chloramines, protects RO units |
Well water with odors | Catalytic carbon filters | Removes hydrogen sulfide, improves taste |
General home filtration | Activated carbon filters | Removes VOCs, pesticides, improves taste |
Air Filtration
You want clean air at home or work. Carbon filters trap gases and bad smells. Granular activated carbon removes VOCs, smoke, and fumes. You find these filters in air purifiers and HVAC systems. They are also in vent filters. Catalytic carbon filters do even more. They break down tough gases like formaldehyde and ozone. Regular carbon filters cannot handle these as well.
Catalytic carbon filters are best for strong smells or chemical pollution. You see them in labs, hospitals, and factories. They help keep air safe to breathe. For most homes, activated carbon filters are enough. If you need extra protection, use catalytic carbon filters.
Industrial Uses
Industries need strong cleaning systems. Catalytic activated carbon is used in water plants and chemical factories. It is also used in labs. Catalytic activated carbon does more than trap contaminants. It starts chemical reactions. These reactions change harmful chemicals into safer ones. This makes cleaning more effective than just trapping impurities.
Catalytic carbon is used in vent filters. It protects water tanks from airborne chemicals. It also helps in big water and air cleaning systems. Industries pick catalytic carbon for tough chemicals. It works fast and well. Regular activated carbon is good for general pollution. Catalytic carbon is better for advanced cleaning.
Note: Pick catalytic carbon for industrial water treatment if you need to break down chloramines, hydrogen sulfide, or VOCs. For basic cleaning, activated carbon is a good choice.
Maintenance
Replacement
You want your filter to work well each day. You need to know when it is time to change it. How long your activated carbon filter lasts depends on a few things. The quality of the filter is important. Good filters last longer than cheap ones. If your water has lots of contaminants, the filter fills up faster. Using more water makes the filter wear out sooner. Manufacturers give you basic rules for changing filters. But you should also think about how much you use your filter. Watch for signs like bad taste, weird smells, or low water pressure. These signs mean you should change the filter soon.
Good filters last longer.
More contaminants fill the filter faster.
Using more water shortens filter life.
Manufacturer rules help, but check your own usage too.
Bad taste, smell, or low pressure means it is time to change.
Catalytic activated carbon filters usually need changing every 6 to 12 months. This gives you a clear plan for maintenance. Regular activated carbon filters do not have a set time for replacement. You need to watch them and change them when water quality drops. If you want clean water, check your filter often and follow the schedule.
Tip: Set a reminder to check your filter every few months. This helps you find problems early and keeps your water safe.
Regeneration
Regeneration lets you use your carbon filter again instead of throwing it away. Regular activated carbon needs high heat for regeneration. You need special machines like rotary kilns. The temperature gets very hot, up to 1000°C. This method works well but uses lots of energy and costs more money. You lose some carbon each time you do this. The process takes a long time and needs skilled workers.
Catalytic activated carbon uses a different way to regenerate. You can do it at lower temperatures. You can use liquid-phase oxidation or direct oxidation on the catalyst surface. This method is faster and uses less energy. You do not need fancy machines. Sometimes you can regenerate the filter right where it is. You lose less carbon, so the filter lasts longer. The cost is lower because you save energy and time. You need to check the catalyst’s strength, but the process is more efficient.
Aspect | Regular (Thermal) Regeneration | Catalytic Regeneration |
|---|---|---|
Temperature Range | Lower temperatures | |
Process Type | Thermal desorption and reactive treatment | Liquid-phase or direct oxidation on catalyst-modified AC |
Facilities Required | Special units (rotary kilns) | Simpler, sometimes in situ |
Carbon Loss | 5–15% per cycle | Less carbon loss |
Regeneration Time | Longer | Shorter |
Efficiency | Effective, energy-intensive | More efficient, less energy |
Cost Implications | Higher operational costs | Lower operational costs |
Note: If you want to save money and make less waste, catalytic regeneration is a smart choice. You get better efficiency and lower costs.
Environmental Impact

Sustainability
You might wonder if activated carbon is good for Earth. Both catalytic activated carbon and regular activated carbon use things like coconut shells, bamboo, and fruit peels. These come from waste, so using them helps cut down on trash and pollution. Picking these filters also helps recycling and reuse.
Both types are made by physical or chemical activation. Chemical activation uses less energy and makes more tiny holes for trapping bad stuff. Catalytic activated carbon has eco-friendly features like being non-toxic and not rusting. This makes it safe for cleaning water and air. Both types can be recovered and reused, which means less waste.
Aspect | Catalytic Activated Carbon | Regular Activated Carbon |
|---|---|---|
Raw Materials | Renewable biomass waste | Renewable biomass waste |
Production Methods | Chemical/physical/microwave activation | Chemical/physical/microwave activation |
Eco-Friendly Features | Non-toxic, reusable, corrosion stable | Environmentally benign, reusable |
Sustainability Factors | Low energy, recovery, pretreatment | Low energy, recovery, pretreatment |
You help the planet even more by using renewable energy to make activated carbon. Using power from plants or the sun can lower human toxicity by 60%. It can also cut global warming potential by 80%. Moving raw materials to places with clean energy helps even more. Coconut shell activated carbon has a smaller carbon footprint than coal-based carbon. Picking filters made from these sources is a smart way to help the environment.
Tip: Choose activated carbon filters made from coconut shells or plant waste. These are better for the planet and help you go green.
Disposal
You need to think about what happens when your activated carbon filter is used up. There are three main choices: regeneration, landfill, or burning. Regeneration means cleaning the filter so you can use it again. This uses heat or chemicals to clean the carbon. Regeneration saves money and cuts down on waste. Most granular activated carbon gets cleaned and reused. Powdered activated carbon often goes to landfills because it is cheaper.
If you put used carbon in a landfill, it can cause pollution and must follow strict rules. Some used carbon can help bacteria grow. You need to control bacteria with heat, pH changes, or special chemicals. Dangerous carbon must go to special places to keep people and nature safe.
Burning the carbon at high heat destroys bad stuff but uses lots of energy. You need to watch for smoke and follow safety rules. Regeneration is the best choice for the planet. You can restore up to 90% of the filter’s power with good thermal treatment. This lowers waste and helps protect nature.
Ways to get rid of used activated carbon:
Regeneration (best for the planet)
Landfill (can cause pollution)
Burning (uses lots of energy)
Note: Always follow local rules for getting rid of filters. Regeneration helps you make less waste and keep the planet clean. You help the environment when you pick green disposal methods.
You want to pick the best carbon filter for your house or business. Regular activated carbon is good for taking out chlorine and organic compounds. It also helps water taste and smell better. If you have hard-to-remove things like chloramine or hydrogen sulfide, catalytic activated carbon works better. It can last longer and help you save money in the long run. When picking a filter, think about these things: what you need to remove, how often you want to change the filter, how much money you want to spend now and later, and what the carbon is made from and how many pores it has.
What do you need to take out of your water or air?
How often do you want to change your filter?
How much can you spend at first and over time?
What is the carbon made from and how is it built?
Tip: Use regular activated carbon for most cleaning jobs. If you need stronger cleaning or want your filter to last longer, choose catalytic activated carbon. This gives you cleaner water or air and a filter that lasts.
