
你可能会问什么 金属去除活性炭 这种碳能吸附有害金属,从而帮助净化水质。许多人用它处理废水,使水更安全。铅、汞、镉、砷和铬等重金属会污染水源。这些金属可能引发严重健康问题,也会损害环境。.
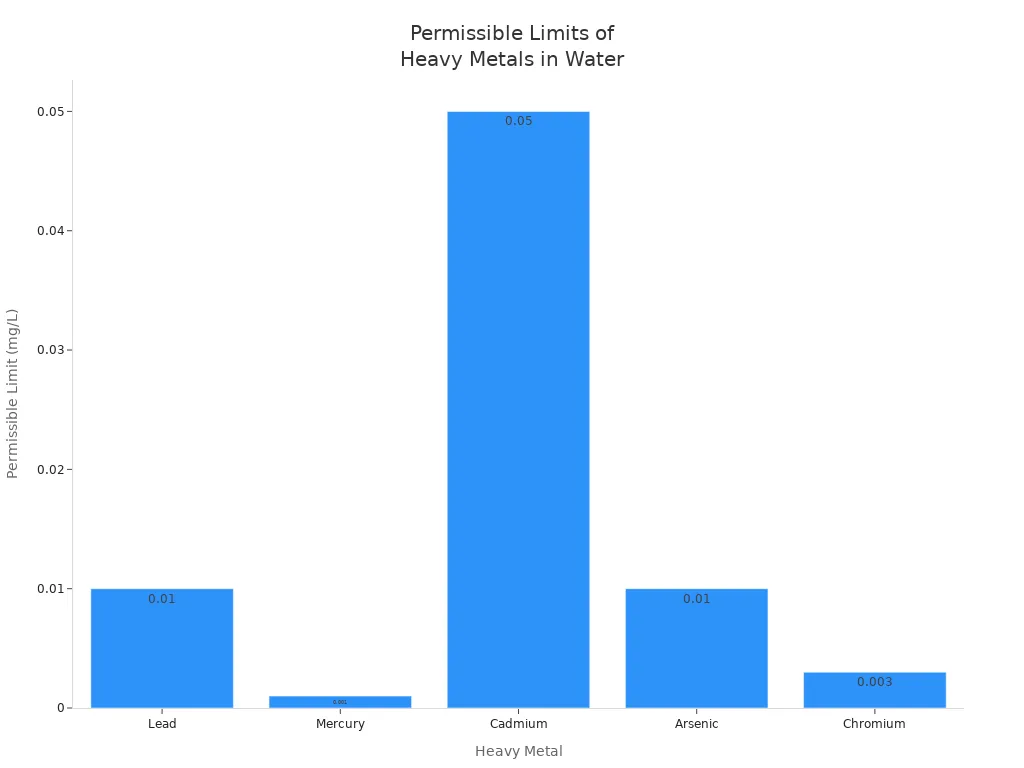
重金属 | 健康风险 | 环境影响 | |
|---|---|---|---|
领导 | 0.01 | 思维障碍、高血压、肾脏问题 | 不利于植物和鱼类的生长 |
汞 | 0.001 | 神经损伤,肾脏问题 | 动物的行为方式和生育方式令人心痛 |
镉 | 0.05 | 肾脏问题可能导致癌症 | 污染土壤和水源,危害水生动物 |
砷 | 0.01 | 皮肤问题,患癌风险更高 | 阻碍植物正常生长,降低农作物产量 |
铬 | 0.003 | 肺部肿胀,皮肤溃疡 | 可能导致健康问题,如胰岛素抵抗 |
选用合适的解决方案,既能保持健康,又能保护地球。.
主要收获
金属去除活性炭有助于净化水质. 它能吸附铅和汞等有害重金属。.
使用由生物质制成的活性炭对环境有益。它能有效去除水中的多种金属。.
活性炭有多种类型。颗粒状和粉末状的活性炭在特定用途和金属类型上效果最佳。.
应经常检查水质。同时需监测pH值,确保活性炭系统运行良好。.
根据需要去除的金属类型选择合适的活性炭,这有助于获得最佳效果。.
活性炭可以重复使用. 这使得它成为一种更经济的净水方式。.
系统设置得当并预先处理水质,有助于提升活性炭的净化效果。.
切勿重复使用旧滤芯或忘记检测pH值。这能确保水质安全。.
什么是金属去除活性炭
金属去除活性炭 通过吸附有害金属来净化水质。人们利用它使水源安全,适用于饮用、农业灌溉和工业生产。这种特殊活性炭源自椰壳、煤炭、木材或废弃物等原料。众多企业选择生物质活性炭,因其更环保且能高效去除重金属。.
主要功能
关于金属去除活性炭,有几点重要事项:
高比表面积: 碳含有大量微小孔洞。这些孔洞形成了巨大的表面积。更大的表面积使其能够吸附更多金属。.
多孔结构: 这些孔隙有助于捕获铅、镍和镉等金属。.
强吸附: 碳能牢牢吸附金属,因此适用于重金属去除。.
环保选项: 许多人使用生物质衍生活性炭。它源自椰壳、坚果壳或木质废料,因此成为治理污染的绿色选择。.
可定制: 您可以获得不同形状和尺寸的产品。某些类型更适用于特定金属或供水系统。.
这里有一个 展示不同活性炭可捕获金属量的表格:
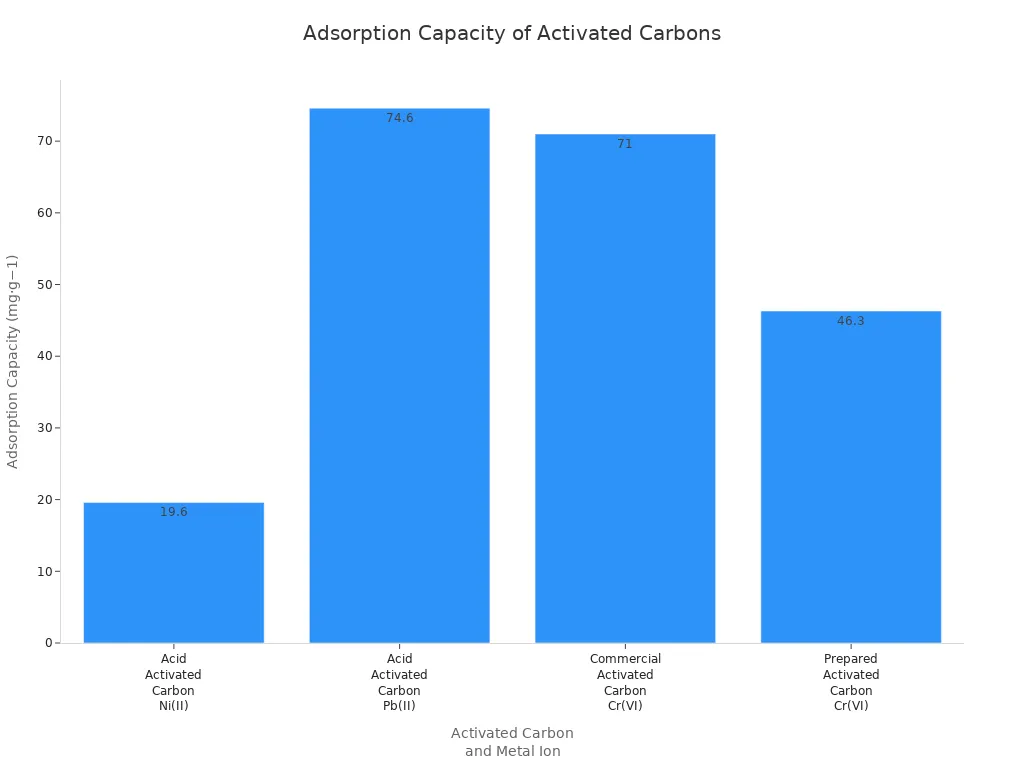
活性炭类型 | 重金属离子 | 吸附容量(mg·g⁻¹) |
|---|---|---|
酸活化活性炭 | 镍(II) | 19.6 |
酸活化活性炭 | Pb(II) | 74.6 |
商业活性炭 | 六价铬 | 71 |
预制活性炭 | 六价铬 | 46.30 |
酸活化活性炭 | 二价阳离子 | 低浓度下高亲和力 |
商业活性炭 | 二价阳离子 | 低浓度下亲和力差 |
提示:生物质衍生活性炭常能吸附多种金属。您可将其用于小型或大型水处理系统。.
类型
用于去除重金属的活性炭种类繁多,每种都有其独特优势。如今许多人选择生物质衍生活性炭,因其可再生且效果显著。.
颗粒活性炭(GAC): 这种类型常见于水过滤器中。其颗粒大小为中粒或大粒。适用于家庭和工厂。.
粉末状活性炭: 此类产品含有微小颗粒,可将其溶于水中进行快速处理。.
颗粒状活性炭: 这些是小而坚实的颗粒。它们在色谱柱中使用起来很方便。.
蜂窝状活性炭: 这种类型具有特殊形状。它能提供大表面积且便于堆叠。.
椰壳活性炭: 本产品由椰壳制成,是一种广受欢迎的生物质活性炭。其强度高且比表面积大。.
坚果壳与木质活性炭: 这些活性炭源自坚果壳或木质废料,同样属于生物质衍生活性炭。.
煤基活性炭: 此类材料源自煤炭,强度高,适用于多种金属。.
物理活性炭: 通过在蒸汽或空气中加热富含碳的物质制成。.
化学活化炭: 通过在加热前用化学物质处理材料制成。.
浸渍活性炭: 该类型含有额外化学物质,有助于捕获特定金属。.
这里有一个 比较主要类型的表格:
活性炭类型 | 碘值(毫克/克) | 网孔尺寸 | 表观密度(千克/立方米) |
|---|---|---|---|
颗粒活性炭 (GAC) | 600-1200 | 1×4 至 40×70 | 400-700 |
粒状活性炭 | 500-1300 | 0.9-8毫米 | 450-600 |
粉末活性炭 | 500-1300 | 150-350 | 450-550 |
蜂窝活性炭 | 400-800 | 100×100×100毫米 | 350-450 |
椰壳活性炭 | 700-1200 | 不适用 | 320-550 |
果壳活性炭 | 700-1200 | 不适用 | 320-550 |
煤基活性炭 | 700-1200 | 不适用 | 300-650 |
木质活性炭 | 700-1200 | 不适用 | 320-550 |
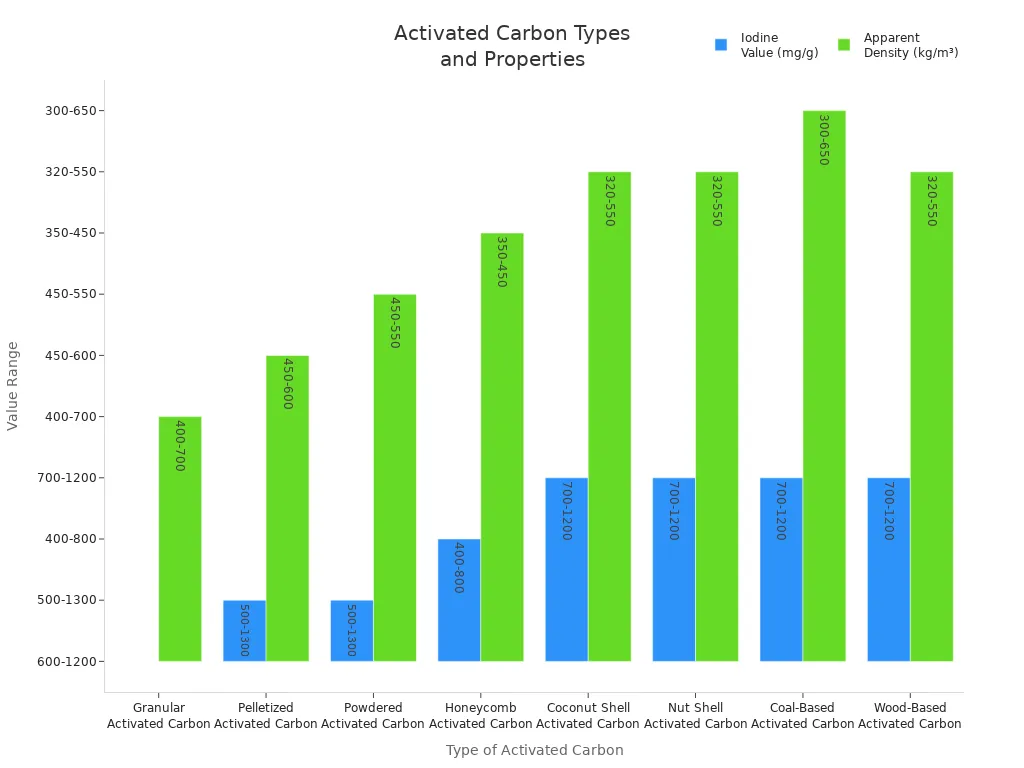
注:生物质衍生活性炭(如椰壳或木质活性炭)通常具有较高的碘值,这意味着它能吸附更多金属。.
目标金属
可使用金属去除活性炭来吸附多种有害金属,其中最常见的有:
铅 (Pb)
镉(Cd)
镍(Ni)
铜(Cu)
生物质衍生活性炭对这些金属效果显著。它还能帮助去除铬和锌等其他金属。您可以在以下内容中看到活性炭去除这些金属的效果: 下表:
重金属 | 80 °C 下的去除效率(%) | 60分钟去除效率(%) |
|---|---|---|
镉 | 93.23 ± 0.035 | 99.235 ± 0.148 |
铜 | 96.71 ± 0.097 | 96.711 ± 0.083 |
镍 | 92.01 ± 0.018 | 95.34 ± 0.015 |
领导 | 95.42 ± 0.067 | 97.750 ± 0.166 |
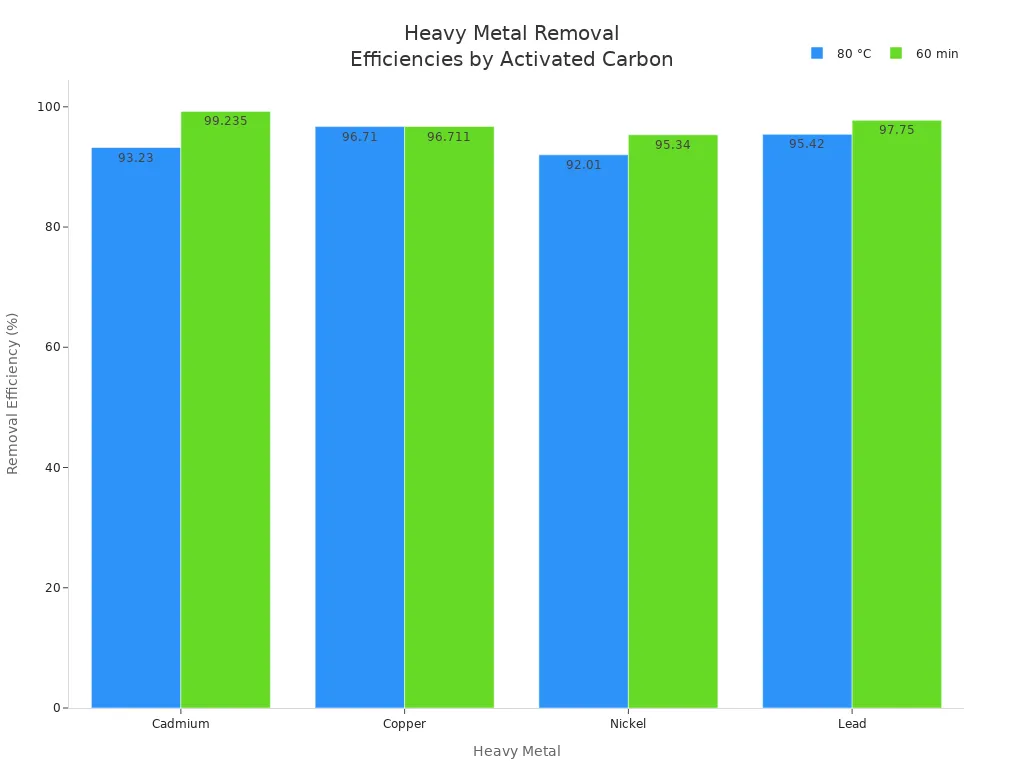
生物质衍生活性炭对多种金属具有高效去除率,适用于家庭或工业用水处理。.
活性炭对重金属的去除效果显著。如今许多人选择生物质衍生活性炭,因其性能优异且环保。使用这些解决方案,您既守护自身健康,也守护自然生态。.
重金属去除:为何至关重要

健康风险
水中的重金属会让你病得很重。即使少量也可能伤害身体。某些金属,比如 铅、汞和镉, 立即引发问题,并在日后生活中造成困扰。.
铅会使人疲倦并引发头痛,还可能导致胃部不适。长期接触铅会损害大脑和肾脏功能。摄入铅的儿童可能出现学习困难或思维障碍。.
汞会损害大脑和肾脏。你可能会健忘或手抖。它还会影响视力和听力。孕妇必须格外小心,因为汞会伤害胎儿。.
镉会干扰人体对营养物质的利用。它还会对细胞造成压力,使人感到虚弱。.
饮用含重金属的水很危险。保持水源清洁有助于保障家人安全。.
环境影响
重金属不仅危害人类,也损害自然。当这些金属进入河流、湖泊或土壤时,它们会在鱼类和植物体内不断积累,这种现象称为生物累积。食用受污染植物或动物的鱼类和动物会因此生病甚至死亡。.
水中的重金属会毒害鱼类及其他水生动物,从而破坏整个生态系统。.
脏污的土壤会阻碍植物生长. 作物可能枯死,土壤会流失优质养分。.
土壤中的微小生物也会受到伤害。它们生长变慢,无法像往常那样帮助植物。.
清除重金属有助于遏制污染。洁净的水源和土壤意味着更健康的植物、动物和人类。.
规章
许多国家对水中的重金属含量制定了严格规定。这些规定能保护您和自然免受污染危害。美国环境保护署(EPA)等机构为饮用水中的铅、汞、镉等金属设定了限量标准。.
金属 | EPA限值(毫克/升) |
|---|---|
领导 | 0.015 |
汞 | 0.002 |
镉 | 0.005 |
若您经营水厂或处理废水,必须遵守这些规定。达到这些标准有助于遏制污染,保障社区安全。去除重金属不仅是明智之举——在许多地区,这更是法律要求。.
遵守规则 采用正确的方法能确保水质安全,维护环境清洁。.
重金属吸附:原理解析
您或许会好奇生物质衍生 活性炭吸附金属 脱水。答案在于一种名为重金属吸附的过程。该过程使碳能捕获并固定金属离子,从而让水质更洁净、更安全。.
机制
重金属的吸附主要通过两种途径实现:物理吸附与化学吸附。这两种吸附方式对生物质衍生活性炭的性能表现至关重要。.
物理吸附
物理吸附利用了碳的天然形态。生物质衍生活性炭具有大量微小孔隙,这些孔隙如同金属离子的陷阱。使用该活性炭时,金属离子会附着于其表面,孔隙逐渐被离子填满。最初形成单层金属离子,随后可堆积成多层结构,从而形成抵御污染的强效屏障。.
机制 | 说明 |
|---|---|
孔隙的大小和形状决定了碳能捕获多少金属。微孔承担主要工作,而中孔则帮助金属在内部移动。. | |
吸附过程 | 该过程始于一层金属离子。随后形成更多层,最终构成厚实的屏蔽层。. |
功能组 | 碳表面上的特殊官能团(如羧基)通过离子交换和螯合作用,有助于捕获金属离子。. |
提示:更多的孔隙和更大的表面积意味着对重金属的吸附效果更好。.
化学吸附
化学吸附更进一步 与物理吸附相比,生物质衍生活性炭表面具有特殊化学基团。这些基团能与金属离子发生反应并形成强键。羧基尤为重要,它们可与金属离子进行离子交换或形成紧密的螯合键,从而增强重金属吸附强度并延长吸附时效。.
当物理吸附与化学吸附协同作用时,效果更佳。这种双重作用增强了活性炭捕获金属的能力,使其成为净化废水和防治污染的理想选择。.
影响吸附的因素
许多因素会影响生物质活性炭的性能表现。了解这些因素才能获得最佳效果。.
pH值与化学性质
水的pH值会改变金属离子与碳表面之间的相互作用。每种金属都有其最适宜的pH范围,以实现重金属的最佳吸附效果。.
重金属 | |
|---|---|
铅(Pb²⁺) | 5.5 – 6 |
镉(Cd²⁺) | 7 – 8 |
当pH值过低或过高时,吸附效果会下降。例如,铅在pH值5.5至6的条件下对生物质衍生活性炭的吸附效果最佳,而镉在pH值7至8时吸附效果更佳。为获得最佳效果,应始终监测并调节pH值。.
表面积
生物质衍生活性炭的比表面积至关重要。更大的比表面积意味着金属离子有更多附着位点。其多孔结构同样发挥着重要作用:微孔捕获金属离子,而介孔则使其能够向更深处迁移。.
大表面积 提供了更大的吸附空间。.
多孔结构有助于捕获不同金属离子。.
随着时间推移,您可能需要清洁您的碳,以保持其良好工作状态。.
注意:为获得最佳重金属去除效果,请始终选用高比表面积的生物质衍生活性炭。.
最新研究发现
科学家们测试了多种生物质衍生的活性炭及其他材料。某些新型材料,如轮胎衍生的吸附剂和生物炭,表现极为出色。您可通过下表了解这些材料的卓越性能。.
材料 | 重金属 | |
|---|---|---|
化学活化轮胎炭 | 铬(II) | 201 |
化学活化轮胎炭 | Pb(II) | 196 |
飞机轮胎橡胶灰 | 六价铬 | 92.24 |
菠萝皮基生物炭 | 六价铬 | 41.67 |
橙皮生物质 | 六价铬 | 100.4 |
半纤维素衍生的活性炭 | 六价铬 | 349.6 |
可见,半纤维素衍生的活性炭能有效吸附大量铬元素。轮胎衍生的活性炭对镉和铅的吸附效果同样显著。这些结果表明,在生物质衍生的活性炭领域,存在多种具有强吸附能力的选择方案。.
你知道吗?利用废弃物(如轮胎和果皮)制备生物质活性炭,既能减少污染,又能增强重金属吸附能力。.
若需去除铅、镉、镍、铬、锌或钴等金属,请确认所用活性炭的吸附能力。不同类型活性炭对特定金属的吸附效果各异。例如,轮胎衍生的活性炭每克可吸附高达201毫克的镉;而半纤维素衍生的活性炭每克可吸附高达349.6毫克的铬。.
使用高吸附性的生物质活性炭时,可获得更优异的重金属去除效果,同时有助于保护环境。这使得吸附技术成为处理废水或污染问题的明智之选。.
金属去除活性炭法
若您想使用生物质衍生的 活性炭 对于重金属去除,您有几种选择。每种方法都以独特的方式利用重金属的吸附特性。您应根据自身需求选择最合适的方法。主要有三种方法:批处理法、柱法和流化床法。.
批处理
批处理工艺可一次性处理固定水量。将生物质衍生活性炭投入含金属的水箱中,使炭与水充分混合。当金属离子附着于活性炭表面时,重金属吸附过程便开始发生。静置混合物一段时间后,过滤去除活性炭。该方法适用于小规模处理或新型活性炭测试。.
批处理过程的步骤:
将生物质衍生的活性炭放入水中。.
充分搅拌或摇匀混合物。.
等待重金属的吸附过程发生。.
过滤掉水中的碳。.
检查水中是否残留金属。.
提示:您可以使用批处理过程来测试不同生物质衍生活性炭样品的性能表现。.
列式反应
柱式工艺适用于持续流动的水体。将生物质衍生活性炭填充于柱体中,水流自上而下穿过柱体。当水流经过活性炭时,重金属便被吸附。该方法可实现大流量水处理且无需停机,适用于家庭、工厂及市政处理厂。.
柱式工艺的优势:
您能获得稳定的金属去除效果。.
您可以检查随时间变化的吸附容量。.
您可以在需要时更换或清洁活性炭。.
柱状装置可帮助您了解生物质衍生活性炭何时需要更换。.
流化床
在流化床法中,水流向上穿过储罐内由生物质衍生的活性炭层。水流将碳颗粒托起使其悬浮并移动,从而促进水与碳的充分混合。由于更多碳表面接触水体,重金属的吸附过程得以加速。该方法适用于快速处理且具有高吸附容量。.
为何选择流化床?
您将获得更优的混合效果和更快的重金属吸附速度。.
您可以处理水流或金属含量的变化。.
可选用不同尺寸的生物质活性炭以获得更佳效果。.
注:当需要快速去除重金属且要求高吸附容量时,流化床法最为理想。.
每种方法都以独特的方式利用重金属的吸附特性。在选择方法前,请综合考虑您的用水需求、需要去除的金属种类以及生物质活性炭的吸附能力。.
方法比较
您或许会思考哪种金属去除方法最适合您的需求。每种方法——批处理法、塔式法和流化床法——都有其独特的优势与挑战。让我们对比分析它们的特点,助您做出明智的选择。.
批处理
当您需要一次性处理固定水量时,可采用批处理工艺。此方法能精确控制活性炭与水体的接触时长,便于测试不同条件下的最佳效果。批处理工艺通常需要更长时间让活性炭充分吸附金属物质,具体时长取决于水质及目标金属种类,通常需等待6分钟至3小时不等。.
列式反应
对于持续流动的水源,应采用柱式过滤工艺。该方法适用于家庭、工厂或市政水厂。水流经装满活性炭的过滤柱时,炭粒会吸附其中的金属杂质。此工艺能稳定处理大量水源,对铅、铬等金属的接触时间约为2至3小时,之后需更换或清洗活性炭。.
流化床
当需要快速处理时,可采用流化床法。水流自下而上穿过活性炭层,使颗粒悬浮并充分混合,从而增强水与活性炭的接触效果。该方法能快速处理水质,并适应流量或金属浓度的变化。虽然科学家们并未始终报告此法的精确接触时间,但其处理速度通常优于其他两种方法。.
下表显示了典型的接触时间 对于每个进程:
流程类型 | 接触时间(分钟) | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
批次 | 6, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180 | 时间取决于您的设置和目标 |
专栏 | 128 (铅), 177 (铬) | 其他金属的突破时间则介于其间 |
流化床 | 不适用 | 通常更快,但没有固定时间 |
小贴士 若需测试新型活性炭或处理小批量样品,可选用批处理工艺。对于稳定的持续处理需求,建议采用固定床工艺。若追求处理速度与操作灵活性,流化床工艺可能是最佳选择。.
摘要列表:
批处理:最适合小任务和测试。提供控制权,但耗时较长。.
专栏:适用于大流量、稳定的流量。适用于家庭和工厂。.
流化床:快速灵活,可应对水流或金属含量的变化。.
您应考虑自身用水需求、需处理的水量以及所需的处理速度。选择合适的方法有助于获得洁净水源并保障健康。.
金属去除活性炭的优势
效率
你想要一种见效快又能清除大量金属的东西。. 金属去除活性炭 它在这项工作中表现非常出色。它能从水中去除几乎所有的重金属,这使得您的用水更加安全。您可以饮用它,给植物浇水,或在工厂中使用。.
让我们看看它与其他方法相比的表现如何:
技术 | |
|---|---|
活性炭 | ~99% |
反渗透 | 98.75% |
离子交换 | ~90% |
活性炭的净化效果不逊于其他方法,甚至更胜一筹。它能去除几乎所有金属杂质,如铅、镉和铬。您无需担心水中残留金属。这种高效性意味着您处理水的时间更少。.
提示:高效能意味着您能节省时间,并减少对健康问题的担忧。.
费用
你可能会认为这 强溶液成本 很多。但金属去除活性炭通常比其他选择更便宜。你可以购买粉末状、颗粒状或颗粒状的活性炭。这让你能根据预算选择合适的产品。.
以下是您能省下钱的原因:
您可以在不需要复杂设备的简单系统中使用它。.
你可以为大型工程大量采购,也可以为家庭需求少量购买。.
你不必花太多钱在维护上,因为它经久耐用。.
许多人选择这种方法,因为它效果显著且成本不高。.
可重用性
你想要的是不会产生大量废弃物的解决方案。金属去除活性炭可以重复使用多次。每次使用后,只需清洗即可再次投入使用。.
下表展示了不同类型在多次使用后的效果:
活性炭类型 | 第二周期清除(%) | 第三周期清除(%) | 第四周期清除(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CMA | >90 | 逐渐下降 | 不适用 | 不适用 |
CMAT | ~90 | ~90 | ~90 | ~90 |
A | >90 | 不适用 | 不适用 | 72 |
某些型号可重复去除超过90%的金属,最多可循环使用四次。您无需每次都购买新活性炭,这既能节省开支,又能减少废弃物产生,为保护地球贡献力量。.
注意:每次使用后务必检查活性炭的过滤效果。这有助于您判断何时需要清洁或更换。.
多功能性
金属去除活性炭用途广泛,是处理水质的灵活工具。无论家庭、商业场所还是工厂,都能灵活运用。针对不同需求,总有一款解决方案。.
活性炭在几乎所有存在金属污染的问题场所都能发挥良好作用。它可用于家庭、学校、工厂或市政水厂,这充分证明了其实用性和适应性。.
应用领域 | 有效范围 | 影响效率的关键因素 |
|---|---|---|
工业废水处理 | 75% – 96% | 剂量、溶液pH值、表面性质、污染物浓度 |
重金属清除 | 高 | 改性活性炭展现出有前景的吸附动力学特性 |
研究与开发 | 持续进行中 | 需要经济高效的合成方法和现实世界疗效研究 |
在工厂中,它能够清除 75% 至 96% 金属。结果取决于所用活性炭的量和水的pH值。金属类型也至关重要。改良型活性炭能去除更多金属。科学家们正持续努力使其性能更优、成本更低。.
提示:您可以更换活性炭的类型或增加用量,这有助于获得最佳净水效果。.
使用活性炭无需复杂设备,既可装入简易过滤器,也可应用于大型水处理厂。许多家庭通过家用过滤器使用活性炭来去除铅等金属。工厂采用大型系统处理大量水源,市政水厂则借助活性炭满足安全规范要求。.
您还可以将活性炭与其他处理方式结合使用。例如,可将其与砂滤器或反渗透系统配合使用,从而使水质更加洁净。无论是针对单一金属还是多种金属,它都能有效处理。.
以下是金属去除活性炭的几种使用方法:
工厂排放至河流前的清水
让家中的饮用水安全无忧
帮助学校和医院提供安全饮用水
支持研究以寻找去除金属的新方法
注:无论你的用水问题规模大小,总能找到使用活性炭的方法。.
金属去除活性炭适用于多种需求。它能在多种场合处理多种金属,值得信赖。对于追求洁净水源的人而言,这是明智之选。.
新手入门指南
选择碳
您需要选择 最适合您饮用水的活性炭. 并非所有活性炭都具有相同功效。首先需确认目标金属类型:某些活性炭更适用于去除铅,另一些则对汞或镉效果最佳。颗粒较小的活性炭能吸附更多铅,含硫活性炭则有助于清除汞。处理砷时应选用改性活性炭并监测pH值。若需去除铬,需保持水体酸性环境。针对铜和锌,快速反应能显著提升处理效果。.
以下表格可供您参考选择:
重金属 | 最佳pH值范围 | 清除效率 | 关键考虑因素 |
|---|---|---|---|
铅 (Pb) | 5-7 | 90% | 更细的颗粒尺寸可提高效果 |
汞(Hg) | 不适用 | 95% | 硫浸渍碳的使用至关重要 |
镉(Cd) | 中性至微碱性 | 最高可达85% | 温度敏感性很重要 |
铬(Cr) | 对六价铬呈酸性 | 80-90% | 竞争离子影响效率 |
砷(As) | 不适用 | 不适用 | 改性碳和pH值监测至关重要 |
铜(Cu) | 宽pH范围 | 85-95% | 快速平衡是有益的 |
锌(Zn) | 中性 | 75-85% | 竞争金属可能影响去除 |
镍(Ni) | 不适用 | 70-80% | 温度控制至关重要 |
提示:请始终选用与金属相匹配的碳。为获得最佳效果,请检查pH值和温度。.
系统设置
您需要为活性炭系统做好充分准备。确保水质清洁后再接触活性炭。预处理水质以去除污垢和较大杂质,这能保持活性炭高效运作。根据用水量选用足量活性炭——用量充足效果更佳,但切勿浪费。.
遵循以下步骤打造强大系统:
为您的金属选择合适的孔径和表面处理。.
根据水流情况使用足够的碳。.
设置系统使水流能均匀地穿过活性炭。.
注意:良好的设置能延长碳刷的使用寿命,并使其发挥更佳性能。.
监测
你希望你的系统始终运行良好。. 经常检查以尽早发现问题. 注意监测水中的金属含量。若金属含量上升,可能是活性炭已饱和。需频繁检测pH值,因其对金属去除至关重要。确保进水水质符合系统要求。.
以下是检查系统的方法:
经常检测水中的金属含量。.
检测pH值,使其保持在最佳范围内。.
留意碳箱已满的迹象。.
当活性炭效果不佳时,请更换或清洗。.
监测水质在处理前后的变化。.
提示:定期检查系统可确保水质安全,并延长滤芯使用寿命。.
常见错误
当您开始使用活性炭去除金属时,可能会犯一些常见错误。了解这些错误有助于您获得更佳效果,并确保水质安全。.
旧滤芯的再利用
你可能以为活性炭滤芯可以清洗后重复使用。但这种做法效果不佳。清洗无法清除所有吸附的金属。旧滤芯会失去吸附能力,导致金属物质渗出。旧滤芯失效后,请务必更换全新滤芯。.尝试用阳光给过滤器充电
有人认为将滤芯置于阳光下能使其恢复功效。阳光并不能为活性炭充电。事实上,将滤芯暴晒在阳光下反而会滋生霉菌。霉菌会使水质变得不安全。请直接更换滤芯,而非试图为其充电。.折叠式或弯曲式过滤器
您可能需要将滤芯折叠以适应您的系统。折叠或弯曲会损坏滤芯。受损滤芯无法有效捕获金属。请始终保持滤芯平整,并小心操作。.未检测水质
您可能会忘记在使用活性炭前后检测水质。若不进行检测,便无法确认过滤器是否有效。请务必定期检测水中的金属含量,这有助于您判断何时需要更换滤芯。.使用错误类型的碳
并非所有活性炭都适用于每种金属。使用错误的类型意味着无法去除目标金属。请确认需要去除的金属种类,并选择合适的活性炭进行处理。.忽略pH值
水的pH值会影响活性炭的净化效果。若pH值过高或过低,滤芯可能无法有效吸附金属。请务必测试并调节pH值至目标金属的最佳处理范围。.系统过载
一次性通过过滤器的水量过多会降低其性能。活性炭需要时间来吸附金属。请根据您的系统使用正确的流量。.
小贴士 请轻柔地处理过滤器,并在需要时及时更换。经常检测水质,确保系统运行良好。.
避免这些错误有助于您从活性炭系统中获得最佳效果。您能让水源保持清洁安全,惠及所有人。.
应用
工业用途
工厂以多种方式使用生物质衍生的活性炭。在排放废水前,必须对水体进行净化处理。这种活性炭常见于化工厂和制药厂。. 食品饮料工厂 也使用它。处理放射性气体的场所同样采用它。每个场所都有其特定需求,用于捕获重金属及其他有害物质。.
工业部门 | |
|---|---|
化学加工 | 捕获危险化学品,防止其污染自然环境。. |
制药加工 | 清除毒素,保持产品纯净无瑕。. |
餐饮 | 去除化学物质、异味和细菌,确保食物安全。. |
放射性气体去除 | 捕获放射性碘,以保护工人和环境。. |
使用这种活性炭,您就是在助力遏制污染。它能有效吸附大量金属与毒素。众多工厂选择这种活性炭,因其卓越的净化性能。它不仅能去除重金属,更能保障工人健康与自然环境安全。.
家庭使用
您可以在家中使用这种活性炭来净化水质。许多家用过滤器内部都装有生物质衍生的活性炭。当水流经时,活性炭会吸附金属等有害物质。其巨大的表面积和微小孔隙有助于捕获更多杂质。.
在家里是这样运作的:
机制 | 说明 |
|---|---|
吸附 | 污染物附着在碳上,, 捕获重金属. |
离子交换 | 重金属与更安全的离子互换位置,从而降低污染。. |
表面积 | 大面积有助于捕获更多有害物质。. |
多孔结构 | 微小孔洞使水能接触更多碳,从而提升过滤效果。. |
化学活化 | 磷酸等化学物质能形成更多孔洞,从而帮助过滤器捕获更多金属。. |
吸附能力强的滤芯效果更佳。它能从水中去除铅、镉等金属,保障家人远离健康隐患。同时减少污水排放,为地球环境贡献力量。这种活性炭源自植物,使用它对自然有益。.
市政用途
城市在大型水处理厂中使用这种碳。这些工厂为许多人净化水源。碳有助于去除重金属,以满足安全标准。.
城市植物存在一些问题:
它并不总能捕获所有无机污染物
水中的其他物质可能阻碍碳的吸收
碳并非永恒存在
您可以通过以下方式解决这些问题:
将碳与其他清洁方法混合使用
利用污泥制成的碳来节省成本并去除铬和镉等金属
如果活性炭堵塞,就无法吸附足够的金属。需要更换或清洗活性炭以保持其效能。如今许多城市采用多种方法来提升水质净化效果。.
提示:在城市水厂使用这种活性炭有助于保障全民饮用水安全。.
案例研究
从真实案例中可以获得许多启示。这些实例展示了生物质衍生活性炭在不同场景中的应用效果,您能观察到每个项目中吸附能力的变化情况。通过分析这些案例,您将理解为何人们信赖生物质衍生活性炭用于重金属去除。.
某项目采用轮胎衍生生物质活性炭进行水净化处理。待处理水体含有铅、铜和锌。研究团队利用废旧轮胎制备热解炭,该炭对每种金属均具有高吸附能力。具体结果见下表:
你注意到基于轮胎的生物质衍生活性炭效果显著。这种炭能轻松吸附铅、铜和锌。使用改性炭时,还能去除砷。这表明生物质衍生活性炭具有很强的适应性。.
另一案例采用磁活化碳净化水质。该水源含有 六价铬. 该项目表明,磁性生物质衍生活性炭具有较高的吸附能力。具体数据可参见下表:
重金属 | 清除方法 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|
六价铬 | 磁活化碳 |
您会发现这种磁性生物质活性炭对铬污染效果显著。即使水中存在其他污染物,其吸附能力依然保持在较高水平。这使其成为工厂和城市水处理厂的理想选择。.
生物炭基生物质衍生活性炭在许多地方也发挥着作用。一项研究将其用于小镇的净水工程,发现其对重金属的吸附能力很强。研究团队证实,这种活性炭能有效去除饮用水中的铅、铜和锌。该方法适用于家庭或学校环境。.
使用生物质衍生活性炭时,您将获得对多种金属的强吸附能力。这有助于保障全民用水安全。.
以下是应用程序的汇总表:
生物质衍生活性炭在多处均能发挥作用。无论在工厂、家庭还是市政处理厂,其吸附能力始终保持高效。这种方法值得信赖,能确保水质安全。.
当你审视这些案例研究时,便会明白吸附能力为何如此重要。你还会发现,生物质衍生活性炭源自轮胎、植物等材料。每种类型都为净化水源提供了强有力的解决方案。你可以运用这些理念来解决自身的水资源问题。.
您现在知道,金属去除活性炭是净化水质、去除有害金属的便捷方法。最新研究表明, 使用孔径尺寸合适的碳 由植物废料等原料制成的产品效果更佳且成本更低。为获得最佳效果,您应:
在开始之前,请向专家寻求帮助。.
使用您现有的能源来驱动您的系统。.
洁净水源始于明智之选。立即了解金属去除活性炭解决方案,满足您的需求!
