
You make physically activated carbon by heating things like wood or coconut shells with hot gases. This way does not use any chemicals. The finished carbon has many tiny holes. These holes help catch things you do not want. People use this carbon in lots of ways. The table below shows some common uses:
アプリケーションエリア | 説明 |
|---|---|
Takes out bad things like VOCs and ozone from the air. | |
浄水 | Grabs bad stuff in water, so it is safe to drink or use in factories. |
Medical Applications | Helps with drug overdoses and stomach problems by catching harmful toxins in the body. |
要点
Physically activated carbon is made by heating things like wood or coconut shells with hot gases. No chemicals are used in this process.
The small pores in activated carbon help it trap things we do not want. This makes it good for cleaning air and water.
People use it for air filters, water cleaning, and medical help for poison or overdose.
Activated carbon can come from many plant materials, like farm waste and rice husks. This makes it better for the environment.
Using physically activated carbon is safer for nature than using chemically activated carbon. It does not make harmful waste.
Activated carbon works well because it has a big surface area and tiny holes. These let it catch many kinds of pollution.
Changing activated carbon filters often in home systems helps them work their best. This gives us cleaner water and air.
Pressurized physically activated carbon can trap even more things. This makes it useful for special jobs like storing ethanol and cooling systems.
Physically Activated Carbon Overview
What Is Physically Activated Carbon
Physically activated carbon is a type of carbon with lots of tiny holes. These holes help it trap things you do not want. People also call it activated charcoal or granular activated carbon. To make it, you heat natural things like wood or shells with steam or hot air. No chemicals are used in this process. The heating makes many small spaces inside the carbon. These spaces can hold odors, chemicals, or toxins. You can find physically activated carbon in water filters and air purifiers. It is also used in some medicines.
Biomass Sources
Granular activated carbon comes from many natural materials. These are called biomass sources. Some common ones are date seeds, corn cobs, grape seeds, birch, and pine. Producers also use things like agricultural waste, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse. Each source has special features. The table below lists some popular biomass sources and what makes them useful:
Biomass Source | 特徴 |
|---|---|
Agricultural Waste | High cellulose and lignin content, excellent thermal stability |
Rice Husks | Significant carbon content, low ash, substantial surface area |
Sugarcane Bagasse | Large surface area, effective dye adsorption capabilities |
These materials have a lot of carbon and are very stable. This helps make activated carbon that can adsorb things well.
Comparison to Chemical Activation
You might want to know how physical activation is different from chemical activation. Physical activation uses steam or hot gases, not chemicals. This makes it safer for people and better for nature. Here are some main points to compare both ways:
Physical steam activation is better for the environment. It uses water vapor and does not make harmful chemical waste.
Chemical activation, like using phosphoric acid, can save energy and works well for liquids. But it can be hard to handle chemicals and get rid of waste.
Some new chemical methods try to recycle chemicals or use new biomass sources to be safer.
People often pick physically activated carbon when they want a safer and greener choice. Granular activated carbon made this way is good for many kinds of filters. You can use it for cleaning water and air without worrying about leftover chemicals.
Physical Activation Process
To make physically activated carbon, you follow a few steps. Each step helps build a material that can trap things you do not want. Let’s look at how this process works.
Carbonization
Carbonization is the first thing you do. You start with materials that have a lot of carbon.
原材料
を使うことができる。 wood, coconut shells, or farm waste. These materials have lots of carbon and are easy to get. People pick them because they are stable and good for making 活性炭.
Heating Process
You heat these materials where there is no oxygen. This is called pyrolysis. The heat goes up to about 500 °C. Heating takes out water and gases that are not carbon. What is left is called char, which has lots of carbon. You keep oxygen out so the material does not burn. The goal is to make a solid base for the next step.
ヒント Using an inert gas keeps the material from burning. This helps save more carbon for the final product.
Activation with Hot Gases
After carbonization, you do the activation step. This step gives the carbon its special trapping power.
Air Introduction
You heat the char again and add gases like steam or carbon dioxide. The heat is much higher, from 800 to 1000 °C. The gas you use and the time you heat it both matter. Air and other gases help open up the carbon’s structure.
Porous Structure Formation
Hot gases react with the char during this step. This makes lots of tiny holes called pores inside the carbon. Pores are important because they make more surface area. More surface area means better adsorption. Now the carbon can trap odors, chemicals, and toxins. The temperature, gas type, and time all change how many pores you get and how big they are.
ステップ | Temperature Range | 目的 |
|---|---|---|
Carbonization | ~500 °C | Remove non-carbon parts, make char |
アクティベーション | 800–1000 °C | Create pores for adsorption |
注: More pores mean the carbon works better for adsorption and for use in adsorption heat pumps.
No Chemical Additives
You do not need to add chemicals in this process. Only heat and gases are used. This makes physically activated carbon safer for you and the environment. You do not have chemical waste or extra steps. The finished carbon is clean and ready for water filters, air purifiers, and adsorption heat pumps.
Not using chemicals means the product is pure and safe for many uses.
When you finish all the steps, you get physically activated carbon with lots of pores. This helps with adsorption. The carbon is good for cleaning water, filtering air, and even for advanced systems like adsorption heat pumps.
活性炭の特性
細孔構造
Activated carbon has lots of tiny holes called pores. These pores help the carbon trap things. There are two main kinds of pores. Micropores are very small, less than 2 nanometers wide. Mesopores are bigger, between 2 and 50 nanometers wide. The way you make activated carbon changes the pore sizes. If you use CO₂ activation, you get mostly micropores. This method gives a BET surface area of 717 m²/g and an average pore size of 2.56 nm. If you use KOH activation, you get more mesopores. The surface area is 613 m²/g and the average pore size is 2.72 nm.
Activation Method | BET Surface Area (m²/g) | Pore Volume (cm³/g) | Pore Size Distribution Type |
|---|---|---|---|
CO₂ Activation | 717 | 0.2135 | Microporous (Type I) |
KOH Activation | 613 | 0.7426 | Mesoporous (Type IV) |
Physically activated carbon has 92% microporosity. This means most pores are very small. These tiny spaces help trap molecules. That makes the carbon work well as an adsorbent.
吸着容量
Activated carbon works well because it has a huge surface area. The pores give more places for molecules to stick. This is called adsorption. More pores mean higher adsorption capacity. If you want to trap small molecules, you need lots of micropores. Mesopores help catch bigger molecules. You measure adsorption capacity by how much material the carbon can hold. In water filters, activated carbon grabs chlorine, odors, and chemicals. In air purifiers, it traps gases and smells. The capacity depends on pore structure and surface area. More surface area means better adsorption.
Tip: Pick activated carbon with the right pore size for your job. Microporous carbon is best for tiny pollutants. Mesoporous carbon helps with bigger contaminants.
Van der Waals Forces
Activated carbon uses van der Waals forces to help with adsorption. These forces are weak attractions between molecules. They do not change the chemicals that stick to the carbon. They just hold the molecules on the surface. Physical adsorption grabs toxins, odors, or gases without changing them. The large surface area and mix of micropores and mesopores make these forces stronger. When molecules touch the carbon, van der Waals forces pull them in and keep them there. No chemical reaction is needed for this to happen. This makes activated carbon safe and useful for many things.
Note: Van der Waals forces let you use activated carbon again. You can clean it and reuse it because the molecules do not bond forever.
Efficiency and Microporosity
When you look at activated carbon, you see more than black powder. Its real strength comes from microporosity. Microporosity means there are many tiny holes. Each hole is smaller than two nanometers. These small spaces give it a huge surface area. Imagine a sponge with millions of tiny pockets. These pockets help trap and hold many molecules.
Activated carbon works well because it can catch unwanted things. People use it to clean water, air, and even the body. The secret is how the micropores work. They let activated carbon grab very small particles. These include micropollutants. Micropollutants are tiny chemicals that are hard to remove with other things.
You might wonder if activated carbon works better than other adsorbents. Studies say it does, especially in powdered or granular form. Here are some important facts about its efficiency:
Powdered activated carbon removes many medicines from water. You get high removal rates, so water is cleaner.
Granular activated carbon treats wastewater with micropollutants very well. Sometimes, it removes more than 90% of certain chemicals.
In tests, granular activated carbon removed 50% to over 90% of different micropollutants.
This high efficiency comes from its special structure. The micropores make a large area for adsorption. Activated carbon traps odors, chemicals, and toxins in these pores. The process does not change the chemicals. It just holds them inside.
You can use activated carbon in many places. Water plants use it to make water safe. Air filters use it to catch gases and smells. Hospitals use it to treat poisonings. Microporosity makes all these uses possible. It works fast and holds a lot of unwanted things.
Tip: For the best results, pick activated carbon with lots of microporosity. This kind works best for small and hard-to-remove pollutants.
Activated carbon is special because of its structure. It is a strong tool for cleaning and protecting your environment. More micropores mean better adsorption. That is why many people and companies use activated carbon every day.
Water Purification Uses

臭いの除去
Sometimes tap water smells strange. These smells come from things like algae or chemicals. Activated carbon helps get rid of these odors. It has lots of tiny pores. The pores trap the molecules that make water smell bad. When you use activated carbon, your water tastes and smells better. Many people use it at home. You can find it in pitcher filters and faucet attachments. Big water systems use it too. Activated carbon works well because it holds onto the things that cause bad smells. After using it, you do not have to worry about weird tastes or odors.
Chlorine Reduction
City water often has chlorine in it. Cities add chlorine to kill germs. But chlorine can make water taste and smell strong. It can also mix with other things and make unwanted byproducts. Activated carbon lowers chlorine in water fast. This is called dechlorination. Activated carbon has a big surface area. As water moves through it, chlorine sticks to the carbon and gets taken out. After a while, the carbon fills up and stops working as well. You need to change the activated carbon often to keep water clean. Many water filters use activated carbon for this reason. You get water that tastes better and has fewer bad chemicals.
Tip: Change your activated carbon filter when needed. This helps your water filter work its best.
Clarity Enhancement
Clear water looks nice and feels good. Sometimes water has tiny bits that make it cloudy. These bits can be dirt, rust, or other stuff. Activated carbon helps make water clearer. Its pores catch small particles and pollutants. When you use activated carbon, your water looks much better. It can also take away some color from water. This color comes from natural things. You get water that tastes good and looks clean.
Activated carbon is important for cleaning water. It removes smells, lowers chlorine, and makes water clear. You can use it at home or in big factories. Activated carbon gives you safe, clean, and tasty water every day.
Household and Industrial Systems
You find activated carbon in many water cleaning systems. People use it at home and in factories. It helps make water safe to drink every day. You might have a pitcher filter in your kitchen. Big water plants use large tanks with activated carbon. Both types trap things you do not want in your water.
Household Systems
Many home water filters use activated carbon. These filters go on faucets, in pitchers, or under sinks. When water goes through the filter, the carbon grabs chlorine and bad smells. It also catches tiny chemicals. Your water tastes better and looks clear. You do not need special tools to use these filters. Most let you change the carbon when it is full.
Here are some household systems that use activated carbon:
Pitcher Filters: You pour tap water into the pitcher. The water moves through activated carbon and comes out cleaner.
Faucet Attachments: You put these filters on your kitchen faucet. The carbon takes away bad tastes and smells as you use the tap.
Under-Sink Units: These filters go under your sink. They use activated carbon to clean water before you drink it.
Tip: Read your filter’s guide. Change the activated carbon often to keep water fresh.
Industrial Systems
Factories and water plants use much more activated carbon. These places clean water for many people or for making things. They use big tanks filled with granular activated carbon. Water flows through these tanks. The carbon traps unwanted stuff.
Factories use activated carbon for different reasons:
Removing Organic Pollutants: Factories sometimes put chemicals in water. Activated carbon helps catch these before they get to rivers or lakes.
Treating Wastewater: Plants use activated carbon to clean water after making products. This keeps bad things out of nature.
Protecting Equipment: Clean water helps machines last longer. Activated carbon removes bits that can hurt pumps and pipes.
System Type | Main Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Household Pitcher | Improve taste and odor | Drinking water at home |
Faucet Filter | Remove chlorine and chemicals | Kitchen tap water |
Industrial Tank | Treat large volumes | Municipal water treatment plant |
Wastewater Plant | Remove toxins | Factory water discharge |
You get help from activated carbon at home or from city water. Factories and water plants also use it to keep people and nature safe. Activated carbon makes water better for drinking, cooking, and making things.
Note: Activated carbon works best when the system fits your needs. Big tanks are good for factories. Small filters are best for homes.
You can count on activated carbon to keep water clean. This simple material is important in homes and factories. You get safer water every time you use it.
Air Filtration Applications
Indoor Air Purifiers
活性炭を使用 in many indoor air purifiers. These machines help make the air cleaner at home or in offices. Air goes through a filter with activated carbon inside. The carbon has lots of tiny holes. These holes trap gases and bad smells. VOCs from things like cleaners, paint, or furniture get caught in the filter.
Most air purifiers use activated carbon to catch VOCs. It works by adsorption. The carbon holds gas molecules on its surface. But sometimes, it does not catch all the VOCs. The filter can fill up and stop working well. When this happens, some VOCs might go back into the air. You need to change the filter often to keep it working. Some air purifiers can also make byproducts, so check what kind you have.
Tip: Change your activated carbon filter when the maker says to. This keeps your air clean and healthy.
産業排出物
Factories and power plants use activated carbon to clean the air. You find it in systems that catch gases before they leave smokestacks. Activated carbon is good at trapping CO2 and other bad gases. It works better than some chemical ways. It does not need strong chemicals or lots of energy.
使用 activated carbon helps lower pollution. The carbon’s surface can be changed to catch more CO2. This makes it work even better. Many factories pick activated carbon because it is safe and easy to use. You do not have to worry about dangerous chemicals or waste. Activated carbon helps keep the air cleaner for everyone.
臭気対策
Activated carbon is great for stopping bad smells in many places. You can use it at home, in schools, or at work. The carbon traps smells from cooking, pets, smoke, and chemicals. Hospitals use it to control odors from cleaning and medical work. Hotels use it to keep rooms smelling nice for guests. Restaurants and kitchens use it for strong food smells and grease.
Here are some places where activated carbon helps with odors:
Homes and apartments: Removes cooking, pet, and smoke smells.
Hospitals and clinics: Controls cleaning and medical odors.
Hotels: Keeps rooms and kitchens fresh.
Restaurants and kitchens: Handles food and grease smells.
Schools: Reduces odors in lunchrooms and labs.
Offices: Traps smells from new furniture and cleaners.
Labs: Catches chemical vapors.
Factories: Protects workers from gases and odors.
Car air filters: Blocks outside smells and pollution.
You see activated carbon in many air filters. It keeps your air clean and free from bad smells. The tiny holes in the carbon make it good at trapping many kinds of gases and odors.
Note: Activated carbon works best when you pick the right filter size and type for your needs.
Pressurized Physically Activated Carbon
Adsorbent Systems
Pressurized physically 活性炭 is used in many adsorbent systems. It has lots of pores and a strong build. This makes it better than regular activated carbon. Pressurizing it adds even more pores. That means it can hold more molecules inside.
You find pressurized physically activated carbon in air cleaners, water plants, and cooling systems. It works well for trapping gases and liquids. Because it has higher bulk density and porosity, you need less of it to do the same job.
Let’s see how pressurized physically activated carbon compares to other adsorbents. The table below shows some key numbers:
Metric Type | PAC | PPAC | CAC |
|---|---|---|---|
730 | 1730 | 1630 | |
Effective adsorption amount (weight basis) (mg g−1) | 70 | 570 | 580 |
Effective adsorption amount (volume basis) (mg cm−3) | 40 | 220 | 120 |
Pressurized physically activated carbon (PPAC) holds more than regular physically activated carbon (PAC). It also does as well or better than chemically activated carbon (CAC). Its bulk density is about twice as high as CAC. This means you get more adsorbent power in the same space.
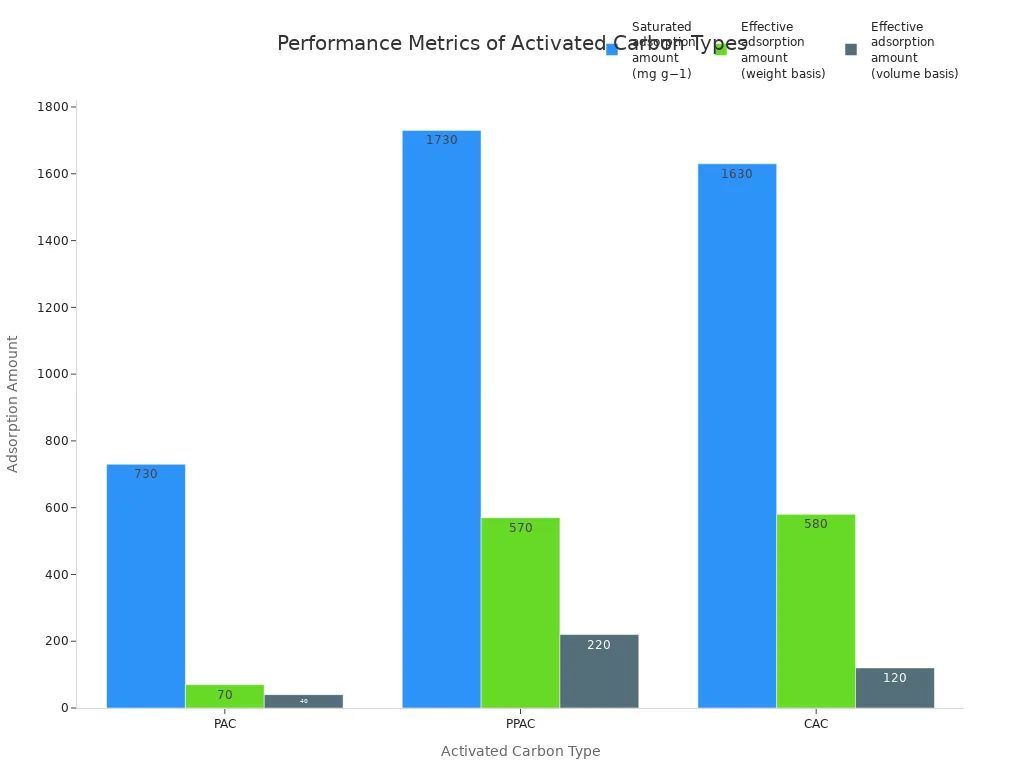
Pressurized physically activated carbon has the highest porosity at 0.69 cm³/cm³. This lets it trap more molecules. That makes it a great choice for many systems. You can count on it for strong and efficient adsorption.
Activated Carbon-Ethanol Applications
Pressurized physically activated carbon is important for storing and cleaning ethanol. You use it in systems that need to hold or release ethanol. Its high porosity and bulk density let you store more ethanol in less space. This makes it good for ethanol cooling and refrigeration systems.
Many studies show how well it works with ethanol. For example, researchers tested it in new adsorption refrigerators. These use ethanol vapor and pressurized physically activated carbon to move heat. The adsorbent holds more ethanol, so you get better cooling.
Here are some results from recent studies:
Study | 調査結果 |
|---|---|
A. Frazzica et al. | Tested how well activated carbon/ethanol vapor works in a new adsorption refrigerator. |
I.I. El-Sharkawy et al. | Maxsorb III holds 1.2 kg of ethanol vapor per kg of adsorbent, with a cooling power of 420 kJ/kg. |
Study on Maxsorb III and modified carbons | Looked at how ethanol sticks to three types of activated carbon, showing physisorption and interactions. |
Adsorption of ethanol on activated carbon | Described how ethanol is held by van der Waals and hydrogen bonds. |
You can also use pressurized physically activated carbon to clean ethanol. The adsorbent traps ethanol molecules with van der Waals and hydrogen bonds. This is called physisorption. No chemical changes happen, so the ethanol stays pure.
Pressurized physically activated carbon helps you study how much ethanol it can hold at different pressures and temperatures. These curves help you design better ethanol tanks and cooling systems.
When you pick pressurized physically activated carbon for ethanol jobs, you get:
High ethanol storage in less space
Fast adsorption and release of ethanol
Good performance over many uses
Safe and clean operation
You can trust pressurized physically activated carbon to make your ethanol systems better. It gives you strong results, high capacity, and works well every time.
Medical and Other Uses
Poison Treatment
Activated carbon helps treat poison fast. Hospitals use it when someone swallows something harmful. The carbon traps toxins in its pores. This stops poison from getting into your blood.
Doctors use activated carbon for many poisoning cases. You see it in emergency rooms and ambulances. Studies show it is a common treatment:
In the USA, doctors used activated carbon for about 50,000 patients in 2013.
In Germany, doctors gave activated carbon in 4.37% of 268,787 poisoning cases in 2016.
The World Health Organization says activated carbon is an important medicine. Emergency teams in Bavaria also use it.
Activated carbon works quickly. You take it as a powder or drink mixed with water. The carbon adsorbs the poison. This makes the treatment safe and helps you get better. It works best if you use it soon after swallowing poison.
Tip: Always go to a doctor for poison treatment. Activated carbon works best when a doctor gives the right amount.
医薬品
Activated carbon is found in many medicines. Drug makers use it to clean ingredients and remove chemicals. It helps make solutions pure during production. Its strong adsorption traps unwanted things.
Pharmacies sell activated carbon tablets and capsules. You use these for stomach problems or mild poisoning. The carbon adsorbs toxins and gases in your stomach. This helps you feel better and keeps you safe.
Activated carbon also helps make medicines cleaner. Factories use it to filter water and liquids. This keeps drugs pure and free from bad stuff.
Note: Activated carbon does not change the chemicals it adsorbs. You can trust it for safe medicine use.
Food and Beverage Processing
Activated carbon is used in food and drink factories every day. It removes bad tastes and smells from products. This keeps your food fresh and clean. Activated carbon also helps keep food healthy while making it taste and smell better.
Activated carbon is important for making juices clear and oils pure. Its tiny pores trap color and impurities. You get clear juice and pure oil because the carbon catches unwanted things.
Here is how activated carbon helps in food and drink processing:
Takes away bad tastes and smells from foods.
Keeps food healthy while making it taste and smell better.
Factories must follow strict rules when using activated carbon in food. They follow FDA and EFSA guidelines. Heavy metals must be less than 0.1 parts per million. Labs test the carbon to make sure your food is safe.
Regulatory Standard | Requirement |
|---|---|
食品医薬品局 | Heavy metals < 0.1 ppm |
EFSA | Independent adsorption verification |
Always pick food and drinks made with safe activated carbon. This helps you get good products without harmful things.
利点と限界
Environmental Benefits
Choosing activated carbon made by physical activation helps the environment. This process uses only heat and gases, not strong chemicals. You do not have to worry about chemical waste or dangerous leftovers. Many people like that activated carbon comes from things like coconut shells, wood, or farm waste. These materials are natural and can be used again. They often come from stuff that would be thrown away. Using activated carbon helps with recycling and keeps more trash out of landfills.
Activated carbon also helps clean water and air. It takes away bad chemicals, smells, and toxins from homes and factories. This makes places safer for people and animals. You can even use activated carbon again after cleaning it. This means you make less waste over time.
🌱 ヒント Using activated carbon from things that grow back can help lower your carbon footprint and keep the planet cleaner.
コスト要因
You might want to know how much activated carbon costs. The price depends on what you use to make it, how you make it, and how much you need. Here are some common things that change the cost:
Making activated carbon can cost between $1.08 and $2.49 for each kilogram, depending on what you start with.
Some studies say making it from rice straw can give a high return, up to 44.06%.
Factories look at the cost to make, use, and clean activated carbon. They also check if they can use it again.
It is usually cheaper if you use waste like coconut shells or rice husks.
You save money if you do not need to buy expensive chemicals.
Activated carbon is often a good deal, especially if you use local or recycled stuff.
💡 注: Always check where your activated carbon comes from and how it is made to get the best deal.
Performance Comparison
You may want to know how physically activated carbon compares to chemically activated carbon. Both types work well, but they are different in some ways. The table below shows how they are not the same in important areas:
アスペクト | 物理的活性炭 | 化学活性炭 |
|---|---|---|
Preparation Method | Uses water vapor or carbon dioxide | Uses chemicals like KOH or HCl |
表面積 | Lower surface area | Higher surface area |
多孔性 | Less control over pore size | More control over pore size |
コスト | Cheaper and simpler to produce | More expensive due to chemicals |
活性化温度 | Lower, less control | Higher, more controlled reactions |
Physically activated carbon is safer and better for the environment. Chemically activated carbon has more surface area and better control of pore size. This can make it better for some special jobs. But most of the time, physically activated carbon works well for cleaning water and air. It also costs less and does not have chemical dangers.
📝 ヒント Pick the type of activated carbon that matches your needs and budget. For most homes and factories, physically activated carbon gives you good results and is safe to use.
You can use physically activated carbon to clean water and air. It also helps doctors treat some medical problems. This carbon is made from natural things like wood or shells. People use heat and gases to make it, not chemicals. It can trap many things in water because it has high adsorption capacity. Studies show it works well for cleaning water and helps the environment. There are some limits, like cost and needing more research. If you want safer water at home or in factories, this carbon is a good choice.
