
Pretende obter os melhores resultados com o carvão ativado. Primeiro, combine as suas caraterísticas com os seus objectivos de filtragem. Pense no que precisa. Pode querer remover pesticidas. Pode querer melhorar o sabor e o cheiro. Pode querer um passo final de limpeza da água. O aparelho certo carvão ativado granular ajuda-o a atingir os seus objectivos. Eis os objectivos mais comuns:
Descrição | |
|---|---|
Remoção de micropoluentes | Elimina os pesticidas e os produtos químicos. |
Remoção de sabores e odores | Torna a água mais saborosa e cheirosa. |
Etapa final de polimento | Dá-lhe água potável limpa. |
Barreira contra a contaminação | Protege contra a contaminação surpresa. |
Escolha o carvão ativado com base no seu objetivo. As suas necessidades decidem a sua escolha.
Principais conclusões
Decida o que quer que o seu filtro faça antes de escolher o carvão ativado. Alguns objectivos são livrar-se de pesticidas, tornar a água mais saborosa e ter água limpa para beber.
Saiba de que é feito o carvão ativado. Coisas como cascas de coco e madeira alteram o funcionamento do carvão.
Pensar sobre como é feito o carvão ativado. Os passos chamados carbonização e ativação fazem com que o carbono tenha uma grande área de superfície. Isto ajuda-o a reter mais coisas más.
Escolha o tamanho de partícula correto para o seu sistema de filtragem. As partículas pequenas retêm mais coisas, mas as partículas grandes permitem que a água se mova mais rapidamente.
Veja a área de superfície e a quantidade que o carbono pode adsorver. Números maiores significam que o carbono pode limpar mais poluição.
Cuide dos seus filtros de carvão ativado com frequência. Mude o carvão a cada 3 a 6 meses para que o seu filtro funcione da melhor forma.
Leia as fichas de produto e os testes de outras empresas. Isto ajuda-o a saber se o carvão ativado é adequado para si.
Peça ajuda a especialistas se as suas necessidades em termos de filtros forem difíceis de perceber. Eles podem dar bons conselhos e ajudá-lo a escolher o melhor carvão ativado.
O que é carvão ativado granular
Matérias-primas
O carvão ativado é fabricado a partir de materiais como a madeira, cascas de coco, carvão ou turfa. Cada material confere ao carvão ativado as suas próprias caraterísticas especiais. As cascas de coco produzem carvão ativado que é forte e tem muitos buracos minúsculos. A madeira e a turfa criam carvão ativado com diferentes tamanhos e minerais. O carvão castanho precisa de aglutinantes extra da madeira ou dos alimentos para manter a sua forma. Estes aglutinantes tornam o carvão ativado mais forte e mais reativo. Quando escolher carvão ativado, pense no material de que é feito. A matéria-prima altera a sua eficácia.
Processo de produção
O carvão ativado é produzido em duas etapas principais. Primeiro, a matéria-prima é aquecida sem oxigénio. Este passo remove o que não é necessário e deixa o carvão ativado. De seguida, o carvão é tratado com vapor ou produtos químicos a alta temperatura. Isto faz milhões de pequenos buracos no carvão. O produto acabado tem uma grande área de superfície. Pode reter mais material indesejado através da adsorção.
Etapa | Descrição | Influência na eficácia |
|---|---|---|
Carbonização | As matérias-primas são aquecidas a temperaturas muito elevadas sem oxigénio. | Isto faz com que um produto rico em carbono que pode adsorver bem. |
Ativação | O carbono é tratado com vapor ou produtos químicos a um calor ainda mais elevado. | Isto acrescenta mais orifícios minúsculos e aumenta a área de superfície. |
Como funciona
O carvão ativado actua como uma esponja para as coisas más. O seu segredo é a sua estrutura. O processo de ativação dá-lhe uma enorme área de superfície. Existem muitos buracos minúsculos no carvão ativado. Estes orifícios captam químicos, compostos orgânicos e alguns metais da água ou do ar. A isto chama-se adsorção. O carvão ativado retém as moléculas na sua superfície em vez de as absorver.
Muitas coisas alterar o funcionamento do carvão ativado:
As partículas mais pequenas ajudam-no a adsorver-se melhor.
O pH baixo torna-o mais eficaz.
As temperaturas mais frias ajudam o carvão ativado a fazer o seu trabalho.
A utilização de mais carvão ativado permite obter melhores resultados.
Mais contaminantes no início ajudam a adsorção.
Caudais mais lentos dão mais tempo para a adsorção.
O carvão ativado pode ser utilizado para limpar a água, eliminar odores ou limpar o ar. O carvão ativado é uma boa escolha para muitos trabalhos de filtragem. Se escolher o tipo correto, obterá água mais limpa e ar mais fresco.
Aplicações do carvão ativado
Tratamento da água
O carvão ativado é muito utilizado no tratamento da água. As pessoas utilizam-no para limpar a água das casas, cidades e fábricas. O carvão ativado agarra as coisas que fazem com que a água tenha mau gosto ou cheiro. Também remove os poluentes orgânicos. Se quer água segura, confie no carvão ativado. Encontra-o nas estações de tratamento de água e nos filtros domésticos. O carvão ativado ajuda a limpar também as águas residuais. Elimina os produtos químicos e torna a água segura para a natureza.
Eis como o carvão ativado ajuda a limpar a água:
Tipo de aplicação | Contaminantes visados |
|---|---|
Poluentes orgânicos, sabores, odores | |
Tratamento de águas industriais | Vários poluentes orgânicos |
O carvão ativado permite obter uma água mais limpa. Elimina os pesticidas e os herbicidas. Elimina outras substâncias indesejáveis. Nota-se que a água sabe e cheira melhor. O carvão ativado funciona bem na limpeza da água. As pessoas utilizam-no para as etapas finais de limpeza e para impedir a contaminação surpresa.
Filtragem de ar e gás
Quer ar puro em casa ou no trabalho. O carvão ativado ajuda a purificar o ar. Utiliza-se filtros com carvão ativado para apanhar as coisas más no ar. Estes filtros retêm os COV e os gases nocivos. Respira-se melhor porque o carvão ativado elimina os odores e os produtos químicos.
Os filtros de carvão ativado eliminam os COV do ar interior e do ar de trabalho.
A qualidade do ar melhora e protege os pulmões.
O carvão ativado granular agarra rapidamente os COV.
A sua área de superfície e o volume dos poros ajudam a reter mais contaminantes.
O carvão ativado é utilizado na limpeza de gases e no tratamento de COV.
O carvão ativado encontra-se nos purificadores de ar e nas máscaras de gás. Também se encontra em sistemas de ventilação no trabalho. Confia nele para manter o seu ar limpo e seguro.
Utilizações industriais
O carvão ativado é utilizado em muitas indústrias. Ajuda na filtragem, limpeza e purificação. O carvão ativado elimina a cor, o sabor e o odor da água potável. As pessoas utilizam-no nos sistemas de água para eliminar pesticidas e herbicidas. As empresas de energia utilizam o carvão ativado para limpeza. As centrais de resíduos utilizam-no para limpar os fluxos de resíduos. As fábricas utilizam o carvão ativado no fabrico de produtos. Pode ser visto na limpeza ambiental, na produção de alimentos e em utilizações médicas.
Indústria | Processos específicos |
|---|---|
Água municipal | |
Água Comercial e Residencial | Remoção de contaminantes como pesticidas e herbicidas |
Energia | Vários processos de purificação |
Resíduos | Tratamento e purificação de fluxos de resíduos |
Indústria e fabrico | Filtragem e purificação nos processos de produção |
Remediação | Limpeza ambiental e remoção de contaminantes |
Alimentação e bebidas | Purificação de ingredientes e produtos finais |
Produtos químicos finos e médicos | Purificação em síntese química e aplicações médicas |
Vê-se carvão ativado em todo o lado. É utilizado para limpar a água, o ar e os resíduos. O carvão ativado ajuda a resolver problemas em muitos locais. As pessoas dependem do carvão ativado para uma boa filtragem e purificação.
Necessidades de filtragem

Quando quiser escolher carvão ativado, pense primeiro no que precisa de remover. Cada trabalho de filtragem não é igual. Pode querer água limpa para beber. Pode querer ar fresco em sua casa. Pode querer manter a sua casa a salvo de químicos nocivos. O carvão ativado funciona melhor quando se adequa às suas necessidades.
Tipos de contaminantes
O carvão ativado pode remover muitos tipos de coisas más. As pessoas utilizam-no para limpar a água, limpar o ar e até mesmo em fábricas. Vejamos as principais coisas de que se pode querer livrar.
Poluentes orgânicos
Os poluentes orgânicos encontram-se na água e no ar. Estes incluem pesticidas, herbicidas e COVs. O carvão ativado agarra estas moléculas nos seus pequenos orifícios. Isto dá-lhe água mais limpa e ar mais fresco.
Pesticidas e herbicidas
COVs (Compostos Orgânicos Voláteis)
Hidrocarbonetos poliaromáticos
O carvão ativado é bom para remover estes poluentes. Vê-se em filtros de água e purificadores de ar. Se se preocupa com os PFAS ou outros químicos fortes, o carvão ativado é uma escolha inteligente.
Metais pesados
O carvão ativado pode ajudar a eliminar os metais pesados, mas funciona melhor com os materiais orgânicos. Alguns sistemas utilizam carvão ativado com outros materiais para remover mais metais pesados. Isto pode ser visto em fábricas ou em sistemas especiais de limpeza de água.
Metais pesados | Eficácia do carvão ativado |
|---|---|
Chumbo | Moderado (frequentemente misturado com outras coisas) |
Mercúrio | Moderado (funciona melhor com misturas especiais) |
Crómio | Limitada (necessita de métodos de tratamento adicionais) |
Se precisar de remover muitos metais pesados, utilize misturas de carvão ativado ou misture-as com outros filtros.
Sabor e odor
Quer que a água tenha um bom sabor e um cheiro agradável. O carvão ativado é ótimo para esta tarefa. Remove o cloro, a cloramina e outras coisas que fazem com que a água tenha um sabor ou cheiro desagradável. Nota-se logo a mudança.
Cloro
Cloramina
Compostos de sabor e odor
Sulfureto de hidrogénio
O carvão ativado é uma das melhores opções para a remoção de sabores e odores. Encontra-o em filtros de água domésticos e em grandes sistemas. Torna a água mais saborosa e com um cheiro mais fresco.
Dica: Se a sua água tiver um sabor ou cheiro estranho, o carvão ativado pode resolvê-lo rapidamente.
Objectivos de utilização
Antes de escolher o carvão ativado, defina objectivos claros para o seu filtro. Pergunte a si próprio o que pretende fazer. Quer um ar melhor em casa? Quer água potável muito limpa? Talvez precise de remover certos químicos dos resíduos da fábrica.
Eis alguns objectivos comuns para os sistemas de carvão ativado:
O ar interior é melhor, especialmente em locais movimentados.
Pretende-se uma potência elevada para captar gases, odores e produtos químicos.
São necessários filtros que funcionem para contaminantes especiais com métodos avançados.
O carvão ativado permite-lhe escolha diferentes tipos de acordo com as suas necessidades. Se quiser remover os COV, escolha carvão ativado com uma grande área de superfície. Se quiser corrigir o sabor e o cheiro, escolha carvão ativado feito para a limpeza da água.
Defina os seus objectivos antes de comprar. Isto ajuda-o a escolher o melhor carvão ativado e a obter excelentes resultados com o seu filtro.
Propriedades GAC
Tamanho das partículas
O tamanho das partículas é importante quando se escolhe o carvão ativado. As partículas mais pequenas têm mais área de superfície. Apanham mais contaminantes. As partículas maiores permitem que a água ou o ar se movam mais rapidamente. Mas podem não apanhar tanta coisa má. Tem de escolher o tamanho certo para o seu sistema.
Eis como funcionam os diferentes tamanhos de partículas:
Tamanho das partículas (Mesh) | Eficiência de filtragem | Comparação de caudais |
|---|---|---|
8 por 30 | 2-3 vezes melhor do que 12 por 40 | Metade do caudal de 20 por 50 |
12 por 40 | Eficiência padrão | Duas vezes o caudal de 8 por 30 |
20 por 50 | Melhor para o caudal | Pode funcionar com o dobro do caudal de 12 por 40 |
As malhas mais pequenas são as melhores para filtragem. As malhas maiores são melhores para um fluxo mais rápido. É necessário equilibrar estes dois factores. O tamanho correto das partículas ajuda o seu filtro a funcionar bem.
Área de superfície
A área de superfície é muito importante para o carvão ativado. Mais área de superfície significa mais lugares para os contaminantes se fixarem. A maioria dos carvões activados tem entre 600 e 1200 m² por grama. É muito espaço numa peça pequena!
Uma maior área de superfície proporciona mais pontos de adsorção.
Obtém-se uma melhor remoção dos compostos orgânicos.
A estrutura e o tamanho dos poros também contribuem para a adsorção.
Verifique a área de superfície quando escolher o carvão ativado. Se quiser uma forte adsorção, escolha um número mais elevado. Obterá melhores resultados para contaminantes difíceis.
Sugestão: Para produtos químicos difíceis de remover, escolha carvão ativado com mais área de superfície.
Capacidade de adsorção
A capacidade de adsorção mostra a quantidade de coisas más que o carvão ativado consegue reter. Isto indica-lhe quando é necessário mudar o filtro. A maior parte do carvão ativado consegue reter cerca de 10-20% do seu peso seco em contaminantes. Por exemplo, 100 libras de carvão ativado podem remover 10 a 20 libras de poluentes.
A capacidade de adsorção pode ser medida de várias formas:
Número de iodo: Mostra a quantidade de iodo que pode adsorver.
Índice de azul de metileno: Indica a capacidade de agarrar moléculas do tamanho do azul de metileno.
Calorimetria de imersão: Mede a quantidade de fenol que consegue adsorver de uma solução.
Se quiser que o seu filtro dure mais tempo, escolha carvão ativado com maior capacidade de adsorção. Isto significa menos mudanças de filtro e melhor desempenho.
Nota: Verifique sempre os dados do produto relativamente à capacidade de adsorção antes de o comprar. Isto ajuda-o a evitar problemas e mantém o seu sistema a funcionar bem.
Atividade biológica
Quando se utiliza carvão ativado num filtro, este faz mais do que reter químicos. Com o tempo, pequenos seres vivos chamados micróbios começam a viver no carvão. Estes micróbios ajudam o filtro a funcionar melhor. Fazem mais do que apenas a adsorção. Também ajudam a decompor os poluentes. A isto chama-se biodegradação.
Os micróbios crescem na superfície do carvão ativado. Comem alguns poluentes que se colam ao carvão. Isto ajuda a remover o carbono orgânico dissolvido e outras coisas más. A água fica mais limpa porque os micróbios decompõem os químicos apanhados pelo carvão.
Vejamos como a atividade biológica altera o seu filtro:
Ponto-chave | Descrição |
|---|---|
Biomassa microbiana | Os micróbios alimentam-se de carbono orgânico dissolvido e de outros poluentes. |
Fase de adaptação | Os micróbios precisam de tempo para se instalarem e crescerem. Isto ajuda a equilibrar a adsorção e a biodegradação. |
Bioregeneração | Os micróbios decompõem os produtos químicos presos ao carvão. Isto faz com que o carvão ativado dure mais tempo. |
Adsorção vs. Biodegradação | Níveis elevados de poluentes significam mais adsorção. Níveis mais baixos permitem que os micróbios façam mais bioregeneração. |
O carvão ativado funciona melhor quando ocorre tanto a adsorção como a biodegradação. No início, o carvão ativado agarra a maior parte dos poluentes. Mais tarde, os micróbios crescem e ajudam a limpar o que o carvão apanhou. A isto chama-se bioregeneração. Ajuda o filtro a durar mais tempo. Não é necessário mudar o carvão com tanta frequência.
Pode perguntar-se quanto tempo é que os micróbios demoram a crescer. Existe uma fase de adaptação. Durante este tempo, os micróbios instalam-se e começam a multiplicar-se. A adsorção e a biodegradação trabalham em conjunto. Se houver muitos poluentes, o carvão ativado faz a maior parte do trabalho. Quando há menos poluentes, os micróbios assumem o controlo e mantêm o filtro a funcionar.
O carvão ativado com forte atividade biológica é designado por carvão ativado biológico (BAC). Os filtros BAC funcionam melhor e duram mais tempo. Removem mais carbono orgânico dissolvido. Poupa dinheiro porque não precisa de mudar o filtro tantas vezes.
Sugestão: Se quiser que o seu filtro dure mais tempo, escolha carvão ativado que suporte a atividade biológica. Procure filtros BAC para obter os melhores resultados.
A atividade biológica é visível nos filtros de água e de ar. Os micróbios ajudam a decompor os químicos e a manter o sistema a funcionar bem. A água e o ar ficam mais limpos. O carvão ativado trabalha mais para si.
O carvão ativado é mais do que uma esponja química. É um sistema vivo que mantém a água e o ar limpos. Quando conhece a atividade biológica, pode fazer melhores escolhas para as suas necessidades de filtragem.
Dados de desempenho
Especificações do fabricante
Quando escolher carvão ativado, verifique primeiro as especificações. Estas especificações mostram como funciona no seu filtro. Verá números relativos à área de superfície e ao volume dos poros. O tamanho das partículas também é indicado nas especificações. Estes pormenores ajudam-no a saber até que ponto o carvão ativado retém as coisas más.
Procure estes elementos nas especificações:
A área de superfície específica significa mais espaço para adsorção.
O volume dos poros indica o número de locais onde os contaminantes se podem fixar.
O tamanho das partículas é importante para a sua capacidade de adsorção.
O carvão ativado forte dura mais tempo no seu filtro.
Menos cinzas significa carvão ativado mais limpo.
O teor de água deve ser o correto.
A densidade de carga indica a quantidade que cabe no seu filtro.
Verificar também os indicadores da capacidade de adsorção. Procure o índice de iodo e o azul de metileno. A capacidade de adsorção de tetracloreto de carbono é importante. Estes números mostram a capacidade de adsorção de diferentes contaminantes.
Dica: Compare sempre as especificações antes de comprar. O carvão ativado adequado ajuda o seu filtro a funcionar melhor e a durar mais tempo.
Testes de terceiros
Não tem de confiar apenas no fabricante. Pode procurar testes efectuados por terceiros. Estes testes mostram como o carvão ativado funciona na vida real. Os laboratórios testam as taxas de adsorção e remoção. Utilizam métricas de adsorção estática como o iodo e o azul de metileno. As métricas de adsorção dinâmica incluem a eficiência de remoção de DOC e UV254.
Os testes efectuados por terceiros também verificam a resistência à abrasão. Isto mostra o grau de resistência do carvão ativado. O carvão ativado deve ser capaz de suportar o fluxo e a pressão. Estes testes ajudam-no a escolher o melhor para as suas necessidades.
Eis o que os testes de terceiros verificam:
A adsorção estática significa a quantidade de iodo ou azul de metileno que pode conter.
A adsorção dinâmica mostra a eficácia da remoção de DOC e UV254.
A resistência à abrasão indica o grau de resistência durante a utilização.
Nota: Os testes efectuados por terceiros dão-lhe mais confiança. Sabe que o carvão ativado vai cumprir a sua função.
Remoção de contaminantes
Quer saber até que ponto o carvão ativado remove os contaminantes. As taxas de remoção variam consoante o tipo e a idade do filtro. Nas estações de tratamento de água, os filtros de carvão ativado removem cerca de 60% de contaminantes. A infiltração artificial pode atingir 65% de remoção. O tratamento convencional só consegue cerca de 38%.
O novo carvão ativado proporciona melhores resultados. Um filtro com 12 meses de idade com carvão ativado novo pode remover até 92% de contaminantes. Após 25 meses, a remoção cai para 76%. Aos 71 meses, desce para 34%. É necessário mudar o carvão ativado para manter o bom funcionamento do filtro.
Segue-se um quadro que mostra as taxas de remoção ao longo do tempo:
Idade do filtro (meses) | Taxa de remoção (%) |
|---|---|
12 | 92 |
25 | 76 |
71 | 34 |
Carvão ativado A adsorção retém os poluentes orgânicos, os compostos de sabor e odor e alguns metais pesados. A adsorção agarra estes contaminantes e mantém-nos na superfície. Obtém-se água e ar mais limpos quando se utiliza o carvão ativado adequado.
Advertência: Mude frequentemente o carvão ativado para obter as melhores taxas de remoção. O carvão ativado fresco proporciona uma adsorção mais forte e melhores resultados.
Pode confiar no carvão ativado para melhorar a água e o ar. Quando verifica as especificações, analisa os testes de terceiros e observa as taxas de remoção, faz escolhas inteligentes para o seu sistema de filtragem.
Factores práticos
Custo
Quer saber quanto custa o carvão ativado. Os preços variam muito consoante as suas necessidades. Um pequeno filtro doméstico pode custar menos de $100. Um grande sistema de fábrica pode custar milhares de dólares. O tamanho e o caudal do seu sistema são mais importantes.
Eis uma tabela que mostra alguns preços habituais dos sistemas de filtragem de carvão ativado:
Descrição do produto | Caudal (GPM) | Preço ($) |
|---|---|---|
Sistema de filtro de carvão ativado granular | 10,020.00 | |
Sistema de filtro de carvão ativado granular | 62-188 | 16,795.00 |
Sistema de filtro de carvão ativado granular | 7-21 | 1,486.00 |
Sistema de filtro de carvão ativado granular | 24-74 | 7,520.00 |
Filtro de carvão ativado granular | 2-6 | 1,050.00 |
Filtro para toda a casa - carvão ativado granular | N/A | 49.99 |
Carvão ativado granular a granel de substituição para purificadores de ar | N/A | 299.99 |
Pode ver que o carvão ativado está disponível em várias gamas de preços. Os filtros para toda a casa custam menos. Os grandes sistemas para muita água custam mais. O tipo de carvão ativado também altera o preço. Alguns tipos duram mais tempo ou funcionam melhor para determinados trabalhos.
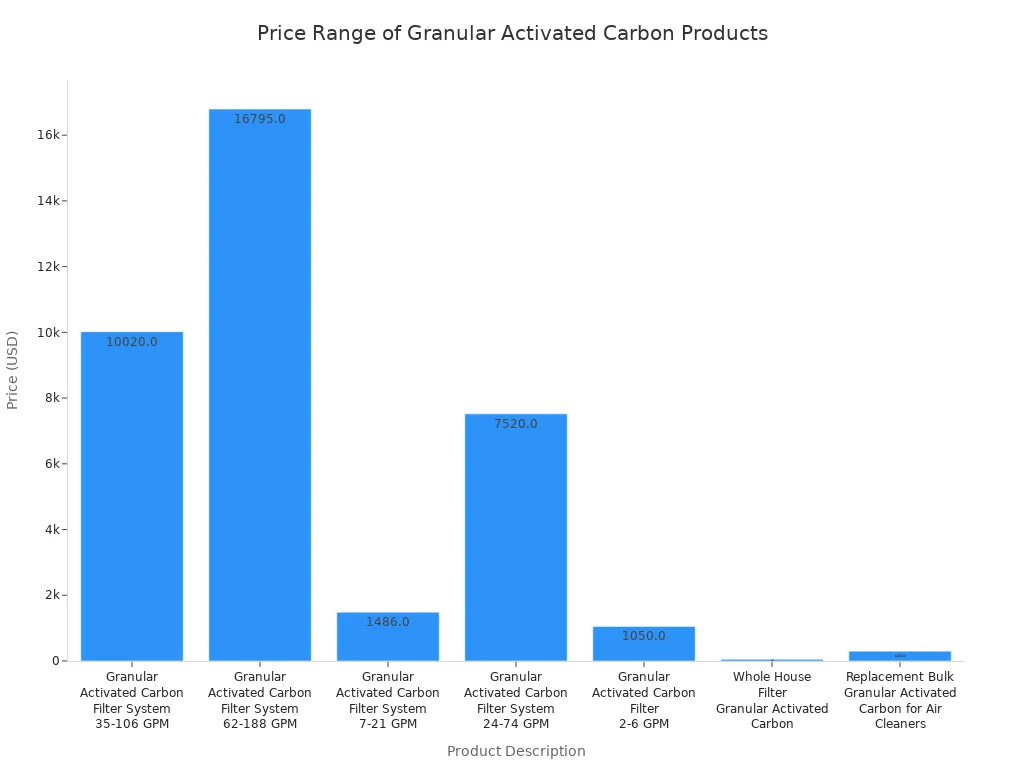
Se quiser poupar dinheiro, escolha carvão ativado que possa ser reutilizado. Alguns sistemas permitem-lhe renovar o carvão ativado em vez de comprar um novo de cada vez. Isto reduz os seus custos a longo prazo.
Dica: Verifique sempre o preço por libra ou por filtro. Isto ajuda-o a comparar produtos e a encontrar o melhor negócio para as suas necessidades.
Disponibilidade
O carvão ativado é fácil de comprar na maioria dos locais. Pode adquiri-lo para utilização na água, no ar ou nos alimentos. Muitos fornecedores vendem carvão ativado feito de diferentes materiais. A casca de coco, a madeira, o carvão e a turfa são fontes comuns.
Eis um breve resumo de alguns tipos e fornecedores populares:
Tipo de carvão ativado | Fornecedor | Aplicações | Segmento de preços |
|---|---|---|---|
Carvão ativado granular e em pó à base de carvão | Tratamento de águas residuais | Acessível | |
Carvão ativado granular à base de madeira | Suneeta Carbons | Filtros de ar | Competitivo |
Carvão ativado granular à base de casca de coco | Suneeta Carbons | Diversos | Alta qualidade |
Pode comprar carvão ativado à Suneeta Carbons, à Donau Carbon e à Calgon Carbon. Cada empresa oferece diferentes tipos para diferentes trabalhos. Algumas concentram-se em opções mais baratas para grandes projectos. Outras vendem carvão ativado de alta qualidade para utilizações especiais.
Suneeta Carbons: Oferece muitos tipos nos EUA.
Donau Carbon: Tem produtos feitos de diferentes materiais.
Calgon Carbon: Conhecido pelo carvão ativado granular personalizado.
A Calgon Carbon fabricou o primeiro carvão ativado granular a partir do carvão betuminoso na década de 1940 e tem liderado o sector desde então.
Pode escolher carvão ativado fabricado a partir de cascas de coco, madeira, turfa, lenhite, carvão vegetal ou carvão betuminoso. Cada tipo funciona melhor para determinados contaminantes. Se precisar de carvão ativado para um trabalho especial, pergunte ao seu fornecedor o que está disponível perto de si.
Compatibilidade do sistema
O carvão ativado deve ser adequado ao seu sistema de filtragem. Nem todos os tipos funcionam para todas as configurações. É necessário verificar alguns aspectos antes de comprar.
Compatibilidade química: Certifique-se de que o carvão ativado pode remover os contaminantes que tem.
Regeneração e reutilização: Alguns carvões activados podem ser reutilizados. Isto poupa dinheiro e ajuda o ambiente.
Qualidade e certificação: Procure carvão ativado com certificações de confiança. Isto significa que é seguro e funciona bem.
Embalagem e formato: O carvão ativado apresenta-se sob a forma de grânulos, pellets ou pós. Escolha a forma que corresponde ao seu filtro.
Se utilizar carvão ativado num filtro de água, verifique o tamanho e a forma. Alguns sistemas precisam de grânulos grandes. Outros funcionam melhor com pó fino. Para a limpeza do ar, escolha carvão ativado feito para filtros de ar. Verifique sempre o rótulo e pergunte ao seu fornecedor se não tiver a certeza.
Nota: Escolher o carvão ativado certo para o seu sistema ajuda-o a obter os melhores resultados. Evita problemas e mantém o filtro a funcionar durante mais tempo.
Pretende um carvão ativado que corresponda ao seu sistema e aos seus objectivos. Quando se verifica o custo, a disponibilidade e a compatibilidade, faz-se uma escolha inteligente para água e ar limpos.
Manutenção
É importante cuidar do seu filtro de carvão ativado. Ele ajuda a manter a água e o ar limpos. O objetivo é que o filtro funcione bem todos os dias. Se se esquecer de fazer a manutenção, o filtro deixa de funcionar também. As coisas más podem passar se não fizer a limpeza. Vejamos como pode manter o seu filtro a funcionar bem.
Deve limpar e mudar frequentemente o carvão ativado. A maioria das pessoas mudá-lo de três em três ou de seis em seis meses. Se utilizar muito o seu filtro, substitua-o mais cedo. Leia sempre as instruções da empresa. Eles sabem o que é melhor para o seu carvão ativado.
Aqui está um guia fácil para cuidar do seu filtro:
Desligue o filtro e deixe sair a pressão.
Desmontar o filtro com as ferramentas adequadas.
Utilize uma escova macia ou um aspirador para limpar o pó e a sujidade.
Enxaguar o carvão ativado com água limpa para eliminar os resíduos retidos.
Se necessário, mergulhe o carvão ativado numa solução de limpeza.
Enxaguar novamente para garantir que todo o produto de limpeza e sujidade desapareceram.
Deixe o carvão ativado secar ao ar até não estar molhado. O carvão húmido não funciona tão bem.
Volte a montar o filtro e siga as instruções para o instalar.
Também deve verificar frequentemente os pré-filtros. Limpe-os e mude-os quando necessário. Os pré-filtros apanham os pedaços grandes antes de chegarem ao carvão ativado. Isto ajuda o carvão ativado a durar mais tempo e a funcionar melhor.
Eis algumas dicas adicionais para manter o seu filtro em bom estado:
Procurar obstruções no filtro. Substitua o cartucho se a água se mover lentamente ou parecer suja.
Limpe o filtro da forma indicada pela empresa. Isto impede o crescimento de bactérias.
Certifique-se de que a água que vai para o filtro está limpa. Uma água mais limpa ajuda o carvão ativado a funcionar melhor.
Cuidado com a parte do filtro. Substitua-o de seis em seis meses, mesmo que pareça estar bem.
Tarefa de manutenção | Com que frequência | Porque é que é importante |
|---|---|---|
Substituir o carvão ativado | A cada 3-6 meses | Mantém a adsorção forte |
Limpar os pré-filtros | Mensal | Evita o entupimento de partículas grandes |
Verificar a existência de obstruções | Cada utilização | Evita o fluxo lento e os maus resultados |
Higienizar o filtro | Conforme necessário | Impede o crescimento de bactérias |
Monitorizar a qualidade da água | Sempre | Ajuda o carvão ativado a durar mais tempo |
O carvão ativado funciona melhor quando se cuida dele. Se se esquecer de o limpar ou de o mudar, o filtro não funciona bem. Poderá notar maus cheiros, um sabor estranho ou água turva. O carvão ativado não aguenta muito antes de ser necessário renová-lo.
Não são necessárias ferramentas sofisticadas para efetuar a manutenção. Uma escova macia, água limpa e um pouco de tempo são suficientes. Se seguir estes passos, o seu filtro manterá a água e o ar frescos. Pode sentir-se bem sabendo que o seu carvão ativado está a funcionar.
Dica: Defina um lembrete no seu telemóvel ou calendário para verificar o seu filtro. A manutenção regular poupa dinheiro e mantém o seu sistema a funcionar bem.
O carvão ativado ajuda-o a obter água e ar limpos. Cuide dele e ele também o ajudará.
Escolher o carvão ativado granular certo
A escolha do carvão ativado certo pode parecer complicada, mas pode ser dividida em passos simples. Deve fazer corresponder as caraterísticas do carvão às suas necessidades. Pense no que pretende remover, como funciona o seu sistema e quanto tempo pretende que o filtro dure. Vamos percorrer o processo juntos.
Comparação de opções
Ao fazer compras, encontrará muitos tipos de carvão ativado. Cada um deles funciona melhor para determinadas tarefas. Alguns são óptimos para eliminar o cloro e os maus cheiros. Outros são melhores para trabalhos difíceis, como a remoção de pfas ou sulfureto de hidrogénio. É necessário comparar as opções lado a lado.
Eis uma tabela para o ajudar a ver as diferenças:
Critérios | Carvão ativado granular (GAC) | Carbono catalítico |
|---|---|---|
Capacidade de adsorção | Remove contaminantes orgânicos, cloro e alguns COVs. | Elimina bem as cloraminas e o sulfureto de hidrogénio. |
Remoção de sabores e odores | Melhora o sabor e o odor da água. | Não principalmente pelo sabor e odor. |
Manutenção e longevidade | Necessita de substituição regular quando os poros estão cheios. | Dura mais tempo para certos contaminantes. |
Custo-eficácia | Custo inicial mais baixo, pode necessitar de mudanças mais frequentes. | Custo mais elevado, mas melhor valor para utilizações especiais. |
É necessário ter em conta os seguintes pontos:
O que é que precisa de remover (cloro, COV, PFA ou maus cheiros)?
Com que frequência pretende mudar o filtro?
Pretende o preço mais baixo agora ou um melhor valor ao longo do tempo?
Se quiser melhorar o sabor e o odor, o carvão ativado granular é uma boa escolha. Se precisar de lidar com contaminantes especiais, o carvão catalítico pode funcionar melhor. Combine sempre o carvão com o seu objetivo principal.
Fichas de dados do produto
As fichas de dados do produto fornecem-lhe os factos de que necessita. Pode encontrar pormenores sobre a área de superfície do carvão, o tamanho dos poros e a sua eficácia para diferentes trabalhos. Estas fichas ajudam-no a escolher o melhor carvão para o seu sistema.
Quando ler uma ficha de dados, procure estes aspectos:
Área de superfície (medida em m²/g): Números mais elevados significam mais locais para os contaminantes se fixarem.
Estrutura de poros: Um maior número de microporos e mesoporos ajuda a lidar com produtos químicos orgânicos.
Tamanho do grânulo: O tamanho consistente impede o entupimento.
Teor de cinzas: Um teor mais baixo de cinzas (inferior a 5%) significa uma melhor adsorção.
Valor de iodo: Para o tratamento de água potável, procurar 1000 mg/g ou mais.
Densidade aparente: Para o carvão de casca de coco, o ideal é 0,45-0,55 g/cc.
Certificações: Verificar se existem normas AWWA ou ISO.
Dica: Verifique sempre a folha de dados do produto antes de o comprar. Quer ter a certeza de que o carvão ativado corresponde às suas necessidades de filtragem e purificação.
O processo de ativação aumenta o volume dos poros e a área de superfície do carbono. Isto torna-o poderoso para o tratamento da água e do ar. Pode confiar nos números da folha de dados para orientar a sua escolha.
Conselhos de especialistas
Por vezes, é necessária uma ajuda suplementar. Os especialistas sabem qual o carvão ativado mais adequado para a sua situação. Podem ajudá-lo a conceber o seu sistema, a escolher o carbono certo e até a testar amostras no laboratório.
Eis como os especialistas o podem ajudar:
Aconselham sobre o melhor tipo de carvão ativado para o seu trabalho.
Ajudam-no a configurar o seu sistema para obter o melhor desempenho.
Orientam-no através de testes laboratoriais para garantir que o carbono funciona como prometido.
Ajudam-no com a amostragem, para que obtenha resultados reais do seu filtro.
Nota: Se tiver um trabalho difícil, como a remoção de pfas ou a instalação de um sistema de grandes dimensões, fale com um especialista. Eles podem poupar-lhe tempo e dinheiro.
Também pode pedir análises laboratoriais de rotina e avançadas. Estes testes mostram até que ponto o carbono actua na sua água ou ar. Uma boa amostragem garante que se obtém a informação correta. Os especialistas podem ajudá-lo a manter o seu sistema a funcionar sem problemas durante muito tempo.
Lista de controlo passo a passo
Pode utilizar esta lista de verificação para fazer a sua escolha final:
Decida o que pretende remover (orgânicos, metais, sabor, odor ou pfas).
Escolha o tipo de carvão ativado (carvão ativado granular para utilização contínua, carvão ativado para trabalhos especiais).
Verificar a folha de dados do produto quanto à área de superfície, tamanho dos poros e certificações.
Certifique-se de que o tamanho do grânulo é adequado ao seu sistema.
Procurem um baixo teor de cinzas e um elevado valor de iodo.
Pense no custo e na frequência com que pretende mudar o filtro.
Pergunte a um especialista se tiver um trabalho complexo ou precisar de testes laboratoriais.
Aviso: Não é preciso adivinhar. Utilize folhas de dados, compare opções e fale com especialistas. Encontrará o melhor carvão ativado para o seu sistema de filtragem ou de purificação.
Pode sentir-se confiante se seguir estes passos. O carvão ativado certo ajudá-lo-á a obter água limpa, ar fresco e paz de espírito.
Quer que o seu filtro funcione bem. Primeiro, combine as caraterísticas do carvão ativado com as suas necessidades. Veja na tabela o que é importante:
Fator | Descrição |
|---|---|
Camas mais profundas permitem que o carvão ativado retenha mais e vaze menos. | |
Velocidade de troca | O fluxo correto ajuda o carvão ativado a durar mais tempo. |
Matriz Orgânica | O material orgânico presente na água pode impedir que o carvão ativado apanhe os poluentes. |
O carvão ativado tem muitas funções. É necessário verificar a sua eficácia adsorveO produto é um material de alta qualidade, com um grau de resistência e densidade. Leia os dados do produto, compare as opções e pergunte a especialistas se tiver dúvidas. Escolher o carvão ativado granular certo proporciona-lhe água e ar mais limpos. Pode sentir-se seguro e fazer sempre boas escolhas.
